Synopsis
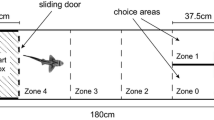
We investigated the ability of two congeneric species of sunfish to learn to forage on a novel prey item in feeding arenas containing structured habitats. Eight bluegill sunfish and eight pumpkinseed sunfish were given the opportunity to forage on whiteworms daily for 10 days. Each day, several behavioural measures were recorded for each fish. Both species of sunfish learned to feed over the 10-day period but the bluegill sunfish learned to feed more quickly than the pumpkinseed sunfish. Pumpkinseeds, however, attained a higher level of foraging efficiency. The differences in learning and foraging efficiency were related to body morphology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Brown, J.A. 1985. The adaptive significance of behavioural ontogeny in some centrarchid fish. Env. Biol. Fish. 13: 25–34.
Colgan, P.W. V. Gotceitas & J. Frame. 1991. Individual variation, acquisition, and re-acquisition in a foraging task by juvenile bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). J. Comp. Psych. 105: 78–84.
Ehlinger, T.J. 1990. Learning and individual variation in bluegill foraging: habitat-specific techniques. Anim. Behav. 38: 643–658.
Ehlinger, T.J. & D.S. Wilson. 1988. A complex foraging polymorphism in bluegill sunfish. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85: 1878–1882.
Emery, A.R. 1973. Preliminary comparisons of day and night habits in freshwater fish in Ontario lakes. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 30: 761–774.
Gotceitas, V. & P. Colgan. 1988. Individual variation in learning by foraging juvenile bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). J. Comp. Psych. 102: 294–299.
Hughes, R.N. 1979. Optimal diets under the energy maximization premise: the effects of recognition time and learning. Amer. Nat. 113: 209–211.
Keast, A. 1978. Feeding interactions between age groups of pumpkinseed sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus and comparisons with the bluegill sunfish (L. macrochirus). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 35: 12–27.
Kieffer, J. D. & P.W. Colgan. 1991. Individual variation in learning by foraging pumpkinseed sunfish, Lepomis gibbosus: the influence of habitat. Anim. Behav. (in press).
Krebs, J.R., D.W. Stephens & W.J. Sutherland. 1983. Perspectives in optimal foraging. pp. 165–216. In: A.H. Brush & C.A. Clark Jr. (ed.) Perspectives in Ormithology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Magurran, A.E. 1986. Individual differences in fish behaviour. pp. 338–365. In: T.J. Pitcher(ed.) The Behaviour of Teleost Fishes, Croom Helm, London.
Mittelbach, G.G. 1981. Foraging efficiency and body size: a study of optimal diet and habitat use by bluegills. Ecology 62: 1370–1386.
Mittelbach G.G. 1984. Predation and resource partitioning in two sunfishes (Centrarchidae). Ecology 65: 499–513.
Mittelbach, G.G. 1986. Predator-mediated habitat use: some consequences for species interactions. Env. Biol. Fish. 16: 159–169.
Osenberg, C.W., E.E. Werner, G.G. Mittelbach & D.J. Hall. 1988. Growth patterns in bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) and pumpkinseed (L. gibbosus) sunfish: environmental variation and the importance of ontogenetic niche shifts. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 45: 17–26.
Ringler, N.H. 1983. Variation in foraging tactics of fishes. pp. 159–171. In: D.L.G. Noakes, D.G. Linquist, G.S. Hellman & J.A. Ward(ed.) Predators and Prey in Fishes, Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague.
Ross, S.T. 1986. Resources partitioning in fish assemblages: a review of field studies. Copeia 1986: 352–388.
SAS Institute 1985. Users guide: Statistics. Version 5 Edition. SAS Institute, Cary. 956 pp.
Scott, W.B. & E.J. Crossman. 1973. Freshwater fishes of Canada. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa. 966 pp.
Sheldon, R.B. & C.W. Boylen. 1977. Maximum depth inhabited by aquatic vascular plants. Amer. Midl. Nat. 97: 248–254.
Ware, D.M. 1973. Risk of epibenthic prey predation by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 30: 787–797.
Webb, P.W. 1984. Body form, locomotion, and foraging in aquatic vertebrates. Amer. Zool. 24: 107–120.
Werner, E.E. 1986. Species interactions in freshwater fish communities. pp. 344–357. In: J. Diamond & T.J. Case(ed.) Community Ecology, Harper and Row, New York.
Werner, E.E., D.J. Hall. D.R. Laughlin, D.J. Wagner, L.A. Wilsmann & F.C. Funk. 1977. Habitat partitioning in a freshwater fish community. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 34: 360–370.
Werner, E.E., G.G. Mittelbach & D.J. Hall. 1981. The role of profitability and experience in habitat use by the bluegill sunfish. Ecology 62: 116–125.
Williamson, T.M. 1987. Comparative retinal organization and visual acuity in four members of the Centrarchidae (Perciformes). M. Sc. Thesis, Queen's University, Kingston. 58 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kieffer, J.D., Colgan, P.W. Differences in learning by foraging juvenile pumpkinseed and bluegill sunfish in a structured habitat. Environ Biol Fish 33, 359–366 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010948
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010948