Summary
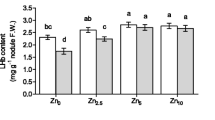
The effect of various doses of copper and zinc on their uptake and on the yield of rice were studied. Copper applications increased copper contents in the plants without effecting the zinc contents. However, zinc applications though increased zinc contents but markedly decreased the copper contents in the plants. This antagonistic effect of zinc on copper suggests that zinc applications can reduce rice yield if available copper is marginal in the soils. re]19720628
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
2 Beckwith, R. S., Availability of micronutrient metals to plants with special reference to Zn, Cu and Mn. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. of Western Australia (1972).
Bowen J. E., Absorption of copper, zinc and manganese by sugarcane leaf tissues. Plant Physiol. Lancaster 44, 255–261 (1969).
Chaudhry F. M. and Loneragan J. F., Effects of nitrogen, copper, and zinc fertilizers on the copper and zinc nutrition of wheat plants. Australian J. Agr. Research 21, 865–879 (1970).
Chaudhry F. M. and Loneragan J. F., Zinc absorption by wheat seedling: II. Effects of hydrogen ions and micronutrient cations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 36, 327–331 (1972).
Dunne T. C., A zinc-copper antagonism affecting cereals. Proc. Australian Conf. Plant Nutr. Melbourne, Vol. 1, pp. 278–283 (CSIRO Aust.: Melbourne) (1956).
Hawf L. R. and Schmid W. E., Uptake and translocation of zinc by intact plant. Plant and Soil 27, 249–260 (1967).
Hodgson J. F., Cobalt reactions with montmorillonite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 24, 165–168 (1960).
Riceman D. S. and Anderson A. J., The symptoms and effects of copper deficiency in cereal and pasture plants in South Australia. J. Dep. Agr. South Australia 47, 64–72 (1943).
Schmid W. E., Haag H. P. and Epstein E., Absorption of zinc by excised roots. Physiol. Plantarum 18, 860–869 (1965).
Shafi, M. and Majid, A., Evaluation of different zinc materials for remedy of zinc deficiency. Abstr. 24th All Pakistan Sci. Conf., Section Agr. & Forestry, A-70–71 (1971).
Shafi, M. and Majid, A., Effect of zinc application on growth and yield of rice at Rice Research Station, Kala Shah Kaku, Pakistan. Abstr. 24th All Pakistan Sci. Conf. Section Agr. & Forestry, A-71 (1971).
Smith P. F. and Specht A. W., Heavy metal nutrition and iron chlorosis of citrus seedlings. Plant Physiol. Lancaster 28, 371–382 (1953).
Tanaka A. and Yoshida S., Nutritional disorders of the rice plants in Asia. Intern. Rice Research Inst. Tech. Bull. 10 (1970).
Tiller K. G. and Hodgson J. F., The specific sorption of cobalt and zinc by layer silicates. Clays Clay Miner. 9, 393–403 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhry, F.M., Sharif, M., Latif, A. et al. Zinc-copper antagonism in the nutrition of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 38, 573–580 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010697
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010697