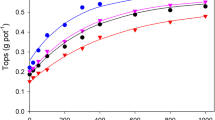
Abstract
The objective of this research was to show how a mechanistic uptake model that accurately predicts phosphorus (P) uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) in a pot experiment may be used to evaluate the reasons for the differences in P availability observed when soil pH is varied. The model predicts P uptake by integrating soil P supply by mass flow and diffusion; size, shape and growth rate of roots; and P uptake kinetics of the root. The P supply parameters of the model that may be affected by soil pH are Pli, initial P concentration in the soil solution; b, the buffer power of P in the soil, Psi, for Pli, and De, effective diffusion coefficient. The effect of these changes on P uptake was predicted with the model by using measured values of the three soil supply parameters and of size, shape, and growth rate of roots and keeping the other parameters at values characteristic of maize. Values for three soil supply parameters can be calculated from measurements of Pli, Psi, and θ, volumetric water content. The predictions of the model closely agreed with observed uptake when form of P present at the higher pH's was accounted for. There was a significant positive correlation (r=0.94) between Pli and observed P uptake and a significant negative correlation (-0.93) between Psi and observed P uptake. The use of the model demonstrated the significance of P form and the importance of Pli in P uptake. It also showed importance of root growth rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber S A and Cushman J H 1981 Nitrogen uptake model for agronomic crops. In Modeling Wastewater Renovationland Treatment. Ed. I K Iskander. pp 382–409. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Barber S A 1984 Soil Nutrient Bioavailability: A Mechanistic Approach. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 398 p.
Hendrix J E 1967 The effect of pH on the uptake and accumulation of phosphate and sulfate ions by bean plants. Am. J. Bot. 54, 560–564.
Murphy J and Riley J D 1962 A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chem. Acta 27, 31–36.
Schenk M K and Barber S A 1979 Phosphate uptake by corn as affected by soil characteristics and root morphology. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 43, 880–883.
Silberbush M and Barber S A 1983 Sensitivity of simulated phosphorus uptake by parameters used by a mechanistic-mathematical model. Plant and Soil 74, 93–100.
Tennant D 1975 A test of a modified line intersect method of estimating root length. J. Ecol. 63, 995–1001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barber, S.A., Chen, JH. Using a mechanistic model to evaluate the effect of soil pH on phosphorus uptake. Plant Soil 124, 183–186 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009257
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009257