Abstract
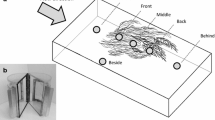
The aquatic macrophytes Ranunculus aquatilis and Rorippa nasturtium-aquaticum were transplanted into substrate trays and placed in a stream alongside unvegetated substrate. Macrophytes were observed to have significant effects on 1) invertebrate community structure, 2) guild structure, and 3) microdistribution. 1) Significantly higher taxa richness and community abundances were associated with macrophytes. 2) Significantly higher abundances of shredder, scraper, and predator guilds were associated with macrophytes in fall, and all guilds had higher abundances in macrophytes in spring. However, guild frequency distributions did not differ among habitats except in spring. 3) Enallagma, Gammarus, Gyraulus, Physa, and Pisidium exhibited a strong association with macrophytes, while Hydropsyche, Simulium, Baetis tricaudatus, Glossosoma velona, and Helicopsyche borealis appeared to avoid them. A strong correlation appeared to exist between current velocity preferences of these taxa and their selection or avoidance of vegetated habitat. Thus, the effect of macrophytes in reducing current velocities appeared to be the most important influence on invertebrate microdistribution. However, macrophytes also increase physical heterogeneity and their large surface areas benefit invertebrate community abundances by creating additional living spaces in the water column where none exist above unvegetated substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, W. E. & N. R. Kevern, 1973. Ecological factors influencing macroinvertebrate standing crop distribution. Hydrobiologia 43: 53–73.
Berg, C. O., 1949. Limnological relations of insects to plants of the genus Potamogeton. Trans. am. microsc. Soc. 68: 279–291.
Butcher, R. W., 1927. A preliminary account of the vegetation of the River Itchen. J. Ecol. 15: 55–65.
Coen, L. D., K. L. Heck & L. G. Abele, 1981. Experiments on competition and predation among shrimps of seagrass meadows. Ecology 62: 1484–1493.
Crowder, L. B. & W. E. Cooper, 1982. Habitat structural complexity and the interaction between bluegills and their prey. Ecology 63: 1802–1813.
Cummins, K. W. & G. H. Lauff, 1969. The influence of substrate particle size on the microdistribution of stream macrobenthos. Hydrobiologia 34: 145–181.
Frohne, W. C., 1938. Contribution to the knowledge of the limnological role of the higher aquatic plants. Trans. am. microsc. Soc. 57: 256–268.
Friberg, F., L. M. Nilsson, C. Otto, P. Sjostrum, B. W. Svensson, B. Svensson & S. Ulfstrand, 1977. Diversity and environments of benthic invertebrate communities in south Swedish streams. Arch. Hydrobiol. 81: 129–154.
Gilinksy, E., 1984. The role of fish predation and spatial heterogeneity in determining benthic community structure. Ecology 65: 455–468.
Godfrey, P. J., 1978. Diversity as a measure of benthic macroinvertebrate community response to water pollution. Hydrobiologia 57: 111–122.
Gregg, W. W. & F. L. Rose, 1982. The effects of aquatic macrophytes on the stream micro-environment. Aquat. Bot. 14: 309–324.
Harrod, J. J., 1964. The distribution of invertebrates on submerged aquatic plants in a chalk stream. J. anim. Ecol. 33: 335–341.
Hawkins, C. P., M. L. Murphy & N. H. Anderson, 1982. Effects of canopy, substrate composition, and gradient on the structure of macroinvertebrate communities in Cascade Range streams of Oregon. Ecology 63: 1840–1856.
Heck, K. L. & G. S. Wetstone, 1977. Habitat complexity and invertebrate species richness and abundance in tropical seagrass meadows. J. Biogeogr. 4: 135–142.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1960. The biology of polluted waters. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Canada, Buffalo, N.Y., 202 pp.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970a. The ecology of running waters. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Canada, 555 pp.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970b. The ecology of stream insects. Ann. Rev. Ent. 15: 25–42.
Jaag, O. & H. Ambuhl, 1964. The effect of current on the biocoenosis in flowing water streams. In Int. Conf. Wat. Pollut. Res., Lond. Pergamon Press, Oxford: 31–49.
Kondratieff, P. F. & G. M. Simmons, 1982. Nutrient retention and macroinvertebrate community structure in a small stream receiving sewage effluent. Arch. Hydrobiol. 94: 83–98.
Krecker, F. H., 1939. A comparative study of the animal population of certain submerged aquatic plants. Ecology 20: 553–562.
Krull, J. H., 1970. Aquatic plant-macroinvertebrate associations and waterfowl. J. Wildl. Mgmt. 34: 707–718.
Ladle, M. & H. Casey, 1971. Growth and nutrient relationships of Ranunculus penicillatus var. calcareous in a small chalk stream. In Proc. eur. Weed Res. Conn., 3rd int. Symp. aquat. Weeds: 53–63.
Macan, T. T., 1949. Survey of a moorland fishpond. J. anim. Ecol. 18: 160–186.
Margalef, R., 1960. Ideas for a synthetic approach to the ecology of running waters. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 45: 133–153.
McGaha, Y. J., 1952. The limnological relations of insects to certain aquatic flowering plants. Trans. am. microsc. Soc. 71: 335–381.
McLachlan, A. J., 1969. The effect of aquatic macrophytes on the variety and abundance of benthic fauna in a newly created lake in the tropics (Lake Kariba). Arch. Hydrobiol. 66: 212–231.
Merritt, R. W. & K. W. Cummins, 1978. An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. Kendall-Hunt Publishing Co., Dubuque, Iowa, 441 pp.
Minckley, W. L., 1963. The ecology of a spring stream, Doe Run, Meade County, Kentucky Wildl. Monogr. 11: 1–124.
Minshall, G. W. & D. A. Andrews, 1973. An ecological investigation of the Portneuf River, Idaho: a semiarid land-stream subjected to pollution. Freshwat. Biol. 3: 1–30.
Minshall, G. W. & J. N. Minshall, 1977. Microdistribution of benthic invertebrates in a Rocky Mountain (U.S.A.) stream. Hydrobiologia 55: 231–249.
Odum, H. T., 1957. Trophic structure and productivity of Silver Springs, Florida. Ecol. Monogr. 27: 55–112.
Percival, E. & H. Whitehead, 1929. A quantitative study of the fauna of some types of stream bed. J. Ecol. 17: 282–314.
Petr, T., 1968. Population changes in aquatic invertebrates living on two water plants in a tropical man-made lake. Hydrobiologia 32: 449–485.
Pip, E., 1978. A survey of the ecology and composition of submerged aquatic snail-plant communities. Can. J. Zool. 56: 2263–2279.
Pip, E. & J. M. Stewart, 1976. The dynamics of two aquatic plant-snail associations. Can. J. Zool. 54: 1192–1205.
Rabeni, C. F. & G. W. Minshall, 1977. Factors affecting microdistribution of stream benthic invertebrates. Oikos 29: 33–43.
Reice, S. R., 1977. The role of animal associations and current velocity in sediment-specific leaf litter decomposition. Oikos 29: 357–365.
Reice, S. R., 1980. The role of substratum in benthic macroinvertebrate microdistribution and litter decomposition in a woodland stream. Ecology 61: 580–590.
Rosine, W. N., 1955. The distribution of invertebrates on submerged aquatic plant surfaces in Muskee Lake, Colorado. Ecology 36: 308–314.
Shannon, C. E. & W. Weaver, 1964. The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, Ill., 125 pp.
Shaw, S. W. & G. W. Minshall, 1980. Colonization of an introduced substrate by stream macroinvertebrates. Oikos 34: 259–271.
Shelly, T. E., 1979. The effect of rock size upon the distribution of Orthocladiinae (Chironomidae: Diptera) and Baetis intercalaris McDunnough (Baetidae: Ephemeroptera). Ecol. Ent. 4: 95–100.
Soszka, G. J., 1975a. Ecological relations between invertebrates and submerged macrophytes in the lake littoral. Ekol. pol. 23: 393–415.
Soszka, G. J., 1975b. The invertebrates on submerged macrophytes in three Masurian lakes. Ekol. pol. 23: 371–391.
Thorp, J. H. & E. A. Bergey, 1981. Field experiments on responses of a freshwater, benthic macroinvertebrate community to vertebrate predators. Ecology 62: 365–375.
Urban, E., 1975. The mining fauna in four macrophyte species in Mikolajskie Lake. Ekol. pol. 23: 417–435.
Westlake, D. F., 1965. Some basic data for investigations of the productivity of aquatic macrophytes. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol., Suppl. 19: 229–248.
Westlake, D. F., 1973. Aquatic macrophytes in rivers. A review. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 20: 31–40.
Westlake, D. F., 1975. Macrophytes. In B. A. Whitton (ed.), River Ecology. University of California Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles: 106–128.
Whitehead, H., 1935. An ecological study of the invertebrate fauna of a chalk stream near Great Driffield, Yorkshire. J. anim. Ecol. 4: 58–78.
Wright, J. F., P. D. Hiley, A. C. Cameron, M. E. Wigham & A. D. Berrie, 1983. A quantitative study of the macroinvertebrate fauna of five biotopes in the River Lamourn, Berkshire, England. Arch. Hydrobiol. 96: 271–292.
Zar, J. H., 1974. Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 620 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregg, W.W., Rose, F.L. Influences of aquatic macrophytes on invertebrate community structure, guild structure, and microdistribution in streams. Hydrobiologia 128, 45–56 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00008939
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00008939