Abstract
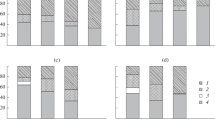
We studied the distribution and seasonal abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates from July 1975 through September 1976 in a hypereutrophic lake in subtropical Florida. The benthic community was comprised principally of oligochaetes (56.1%), chironomids (37.1%), and chaoborids (5.7%). Numbers of taxa and mean densities correlated negatively with depth and positively with mean grain size of the substratum and dissolved oxygen concentration at the mud-water interface. Seasonal abundances and life history information obtained for the predominant species of Chironomidae (Polypedilum halterale, Glyptotendipes paripes, Chironomus crassicaudatus, Cryptochironomus fulvus, C. blarina, Cladotanytarsus sp., Procladius culiciformis, and Coelotanypus concinnus) indicated that all of these species are multivoltine with rapid generation times. Larval lengths of life at summer temperatures, 27–31 °C, ranged from 14–22 days indicating that sampling in subtropical lakes should be at short intervals (approximately 3 days) if the life cycles, ecology, and function of the components of the benthic community is to be understood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. O. 1959. A modified floatation technique for sorting bottom fauna samples. Limnol. Oceanogr. 4: 223–225.
Barnes, H. 1959. Apparatus and methods of oceanography. Geo. Allen and Unwin Ltd., London. 341 p.
Beck, W. M. Jr. 1975. Chironomidae. p. 159–180. In: F. K. Parrish (ed.). Keys to water quality indicative organisms of the southeastern United States. U. S. Environm. Protect. Agency. Cincinnati.
Beck, W. M. Jr. 1976. Biology of the larval chironomids. Fla. Dept. Environm. Reg. Tech. Ser. Vol. 2, No. I. 57 p.
Beck, W. M. Jr. 1977. Environmental requirements and pollution tolerance of common freshwater Chironomidae. EPA 600/477–024. U. S. Environm. Protect. Agency. Cincinnati. 261 p.
Bloom, S. A., Santos, S. L. & Field, J. G. 1977. A package of computer programs for benthic community analyses. Bull. Mar. Sci. 27: 577–580.
Brinkhurst, R. O. 1966. Detection and assessment of water pollution using oligochaete worms. Water Sewage Works 113: 398–401 (Pt. 1), 438–441 (Pt. 2).
Brinkhurst, R. O. 1970a. The fauna of pollution. p. 94–112. In: D. V. Anderson (ed.). The great lakes as an environment. Univ. Toronto Greak Lakes Inst. Rep. P.R. 39.
Brinkhurst, R. O. 1970b. Distribution and abundance of tubificid (Oligochaeta) species in Toronto Harbour, Lake Ontario. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 27: 1961–1969.
Cannings, R. A. & Scudder, G. G. E. 1978. The littoral Chironomidae (Diptera) of saline lakes in central British Columbia. Can. J. Zool. 56: 1144–1155.
Cowell, B. C., Dye, C. W. & Adams, R. C. 1975. A synoptic study of the limnology of Lake Thonotosassa, Florida. Part I. Effects of primary treated sewage and citrus wastes. Hydrobiologia 46: 301–345.
Curry, L. L. 1965. A survey of environmental requirements for the midge. p. 127–141. In: Biological problems in water pollution. U. S. Publ. Health Serv. Publ. 999-WP-25. Cincinnati.
Danks, H. V. 1971. Overwintering of some north temperate and arctic Chironomidae. II. Chironomid biology. Can. Entomol. 103: 1875–1910.
Danks, H. V. & Oliver, D. R. 1972. Seasonal emergence of some high arctic Chironomidae (Diptera). Can. Entomol. 104: 661–686.
Field, J. G. & MacFarlane, G. 1968. Numerical methods in marine ecology. I. A quantitative ‘similarity’ analysis of rocky shore samples in False Bay, South Africa. Zoologica Africana 3: 119–137.
Ford, J. B. 1962. The vertical distribution of larval Chironomidae (Diptera) in the mud of a stream. Hydrobiologia 19: 262–272.
Fremling, C. R. & Evans, J. J. 1963. A method of determining the dissolved oxygen concentration near the mud-water interface. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8: 363–364.
Heuschele, A. S. 1969. Invertebrate life cycle patterns in the benthos of a floodplain lake in Minnesota. Ecology 50: 998–1011.
Humphries, C. F. 1936. An investigation of the profundal and sublittoral fauna of Windermere. J. Anim. EcOl. 5: 29–52.
Hunt, B. P. 1953. The life history and economic importance of a burrowing mayfly, Hexagenia limbata, in southern Michigan lakes. Mich. Cons. Dept. Bull. Inst. Fish. Res. No. 4. 151 p.
Iovino, A. J. & Miner, F. D. 1970. Seasonal abundance and emergence of Chironomidae of Beaver Reservoir Arkansas. J. Kan. Ent. Soc. 43: 197–216.
Jónasson, P. M. & Kristiansen, J. 1967. Primary and secondary production in Lake Esrom. Growth of Chironomus anthracinus in relation to seasonal cycles of phytoplankton and dissolved oxygen. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 52: 163–217.
Jónasson, P. M. & Thorhauge, F. 1976. Population dynamics of Potamothrix hammoniensis in the profundal of Lake Esrom with special reference to environmental and competitive factors. Oikos 27: 193–203.
Mason, W. T., Jr. & Yevich, P. P. 1967. The use of phloxine B and rose bengal stains to facilitate sorting benthic samples. Trans. Amer. Microscop. Soc. 86: 221–223.
Moore, J. W. 1978. Some factors influencing the diversity and species composition of benthic invertebrate communities in twenty arctic and subarctic lakes. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 63: 757–771.
Mundie, J. H. 1957. The ecology of Chironomidae in storage reservoirs. Trans. Roy. Ent. Soc. London 109: 149–232.
Oliver, D. R. 1971. Life history of the Chironomidae. Ann. Rev. Ent. 16: 211–230.
Ramcharan, V. & Paterson, C. G. 1978. A partial analysis of ecological segregation in the chironomid community of a bog lake. Hydrobiologia 58: 129–135.
Saether, O. A. 1975. Nearctic chironomids as indicators of lake typology. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 19: 3127–3133.
Vodopich, D. S. 1980. The influence of sediment type and food availability on the distribution of Procladius culiciformis (Linnaeus) (Diptera: Chironomidae) in a subtropical Florida lake. Ph. D. thesis. University of South Florida, Tampa.
Ward, G. M. & Cummins, K. W. 1978. Life history and growth pattern of Paratendipes albimanus in a Michigan headwater stream. Ann. Ent. Soc. Amer. 71: 272–284.
Welch, H. E. 1976. Ecology of Chironomidae (Diptera) in a polar lake. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 33: 227–247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cowell, B.C., Vodopich, D.S. Distribution and seasonal abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates in a subtropical Florida lake. Hydrobiologia 78, 97–105 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007582
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007582