Abstract
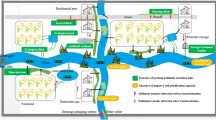
A study was carried out in the small watershed of Chaohu Lake, where a scattered multi-pond system, as a part of the land-inland water ecotone, was found to be a good protective zone in the management of the lake. This multi-pond system can effectively reduce the non-point source load of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen from runoff water, and filter out sediments before they reach the lake. There are 150 artificial ponds in this small watershed, covering a surface area of 35.54 ha, which represents just under 5% of the whole catchment area. The nutrient retention in the first 9 months of the dry year 1988 was more than 90%. This multi-pond system needs low capital cost and energy consumption for maintenance, and is suitable for irrigation and drainage, while it recycles water and nutrients within the terrestrial agroecosystem. As a result of this case study, a multipond system is being proposed as part of a long term management strategy for the watershed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhardt, H. & J. Clasen, 1985. Recent developments and perspective of restoration for artificial basins used for water supply. Lake Pollution and Recovery International Congress: European Water Pollution Control Association, Proceedings, Rome. 15–18.
Castri di, F., A. J. Hansen & M. M. Holland, 1988. Preface. Biology International, Special Issue 17: 1–8.
Ebina, J., T. Tsutsui & T. Shirai, 1983. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Wat. Res. 17: 1721–1726.
Hansen, A. J., F. di Castri & R. J. Naiman, 1988a. Ecotones: What and why. Biology International, Special Issue 17: 9–46.
Hansen, A. J., F. di Castri & P. G. Risser, 1988b. A New Scope Project. Ecotones in a changing Environment: The Theory and management of landscape boundaries. Biology International, Special Issue 17: 137–161.
Holland, M. M., 1988. SCOPE/MAB technical consultations on landscape boundaries. Report of a SCOPE/MAB workshop on ecotones. Biology International, Special Issue 17: 47–106.
Jin, X., H. Liu, Q. Tu, Z. Zhang & X. Zhu, 1990. Lake eutrophication in China. Environmental Sciences Press of China (in Chinese). 1–5, 103–115.
Naiman, R. J., M. M. Holland, H. Decamps & P. G. Risser, 1988. A new Unesco Programme: Research and management of land/inland water ecotones. Biology International, Special Issue 17: 107–136.
Needham, J., 1984. Science and civilization in China: Agriculture. Cambridge: The University Press. 1–9, 495–510.
Novotny, V. & G. Chesters, 1981. Handbook of nonpoint pollution: source and management. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. 555 pp.
Ryding, S.-O. & W. Rast, 1989. The control of eutrophication of lakes and reservoirs. Man and The Biosphere Series. UNESCO, Paris & The Parthenon Publishing Group. 314 pp.
Sas, H., 1989. Lake restoration by reduction of nutrient loading. Academia-Verl. Richarz. 497 pp.
Solbe, J. F. de., 1986. Effects of land use on fresh waters: agriculture, forestry, mineral exploitation, urbanization. Ellis Horwood Limited Publishers, Chichester. 568 pp.
Tu, Q., D. Gu, C. Yin, Z. Xu & J. Han, 1990. Chaohu Lake eutrophication study. University Press of Science and Technology of China (in Chinese). 226 pp.
Yin, C., W. Jin, Z. Lan & M. Zhao, 1991. Chaohu Lake eutrophication and nutrient load reduction. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 1086–1087.
Yin, C. & H. Bernhardt. 1992. A case study of shallow and eutrophic lakes in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China) 4 (2): 5–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, C., Zhao, M., Jin, W. et al. A multi-pond system as a protective zone for the management of lakes in China. Hydrobiologia 251, 321–329 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007191
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007191