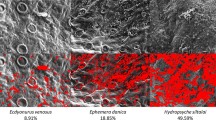
Abstract
Salmonids (Salmo salar, Salmo trutta) and mayflies (Baetis rhodani, Ecdyonurus venosus) which had been exposed to simulated episodes of low pH, and low pH with elevated aluminium, were examined histochemically for the presence of aluminium and mucus. The control fish and mayflies and those exposed to low pH did not stain for aluminium, although increased mucus production was demonstrated in fish gills. Trout and salmon exposed to aluminium at low pH exhibited extensive aluminium and mucus coating of the secondary gill lamellae. No mucus was produced by mayflies but aluminium was apparent on all parts of the body. Mean aluminium concentrations of digested fish gills were 2950 and 3050 μg g−1 dry wt. for trout and salmon respectively, whilst for whole specimens of B. rhodani and E. venosus values were 1 200 and 3 175 μg g−1 dry wt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almer, B., W. Dickson, C. Ekstrom, E. Hornstrom & V. Miller, 1974. Effects of acidification on Swedish Lakes. Ambio. 3: 30–36.
Ashley, L. M., 1970. Action of iron salts in solution on goldfish, Prog. Fish. Cult. 32: 109.
Baker, J. P. & C. L. Schofield, 1980. Aluminium toxicity to fish as related to acid precipitation and Adirondack surface water quality. In D. Drablos & A. Tollan (eds), Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F., Oslo: 292–293.
Baker, J. P. & C. L. Schofield, 1982. Aluminium toxicity to fish in acidic waters. Wat. Air Soil Pollut.18: 289–309.
Baker, J. T. P., 1969. Histological and electron microscopical observations on copper poisoning in the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). J. Fish Res. Bd Can. 26: 2785–2793.
Beamish, R. J. & H. H. Harvey, 1972. Acidification of the La Cloche Mountain Lakes, Ontario and resulting fish mortalities. J. Fish Res. Bd Can. 29: 1131–1143.
Daye, P. G. & E. T. Garside, 1976. Histopathologic changes in superficial tissues of brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchell) exposed to acute and chronic levels of pH. Can. J. Zool. 54: 2140–2155.
Denton, J., A. J. Freemont & J. Ball, 1984. Detection and distribution of aluminium in bone. J. Clin. Pathol. 37: 136–142.
Dickson, W., 1975. The acidification of Swedish Lakes. Rep. Inst. E. W. Res. Drottningholm 54: 8–21.
Driscoll, C. T., J. P. Baker, J. J. Bisogni & C. L. Schofield, 1980. Effect of aluminium speciation on fish in dilute acidified water. Nature 284: 161–164.
Engbolm, E. & P.-E. Lingdell, 1984. The mapping of short-term acidification with the help of biological pH indicators. Rep. Inst. F. W. Res. Drottningholm 61: 60–68.
Eisler, R. & G. R. Gardner, 1973. Acute toxicology to an estuarine teleost of mixtures of cadmium, copper and zinc. J. Fish Biol. 5: 131–142.
Eisler, R., 1974. Radiocadmium exchange with seawater by Fundulus heteroclitus (L.) (Pisces: Cyprinodontidae) J. Fish Biol. 6: 601–612.
Fivelstad, S. & H. Leivestad, 1984. Aluminium toxicity to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and brown trout (Salmo trutta L.): Mortality and Physiological response. Rep. Inst. F. W. Res. Drottningholm 61: 69–77.
Friberg, F., C. Otto & B. S. Svensson, 1980. Effects of acidification on the dynamics of allochthonous leaf material and benthic invertebrate communities of running waters. In D. Drablos & A. Tollan (eds), Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F., Oslo: 304–305.
Gardner, G. R. & P. P. Yevich, 1970. Histological and hematological responses of an estuarine teleost to cadmium. J. Fish Res. Bd. Can. 27: 2185–2196.
Haines, T. A., 1981. Acidic precipitation and its consequences for aquatic ecosystems: a review. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 110: 669–707.
Hall, R. J., J. M. Pratt & G. E. Likens, 1982. Effects of experimental acidification on macroinvertebrate drift diversity in a mountain stream. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 18: 273–288.
Hem, J. D., 1968. Graphical methods for studies of aqueous aluminium hydroxide, fluoride and sulphate complexes. U.S. Geol. Surv. Wat. Supply Paper 1827-B.
Hendrey, G. & R. Wright, 1976. Acid precipitation in Norway: effects on aquatic fauna. J. Great Lakes Res. 2: (Suppl. 1) 192–207.
Herrmann, J. & K. G. Andersson, 1986. Aluminium impact on respiration of lotic mayflies at low pH. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 30: 703–709.
Hughes, G. M., 1985. Comparative studies of respiration as a guide to the selection of bio-indicators. Symp. Biomonitoring State Environ. 126–141.
Jagoe, C. H. & T. A. Haines, 1983. Alterations in gill epithelial morphology of yearling Sunapee trout exposed to acute acid stress. Trans. am. Fish Soc. 112: 689–695.
Janssen, R. G. & D. J. Randall, 1975. The effect of changes in pH and pCO2 in blood and water on breathing in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri. Resp. Physiol. 25: 235–245.
Jones, J. R. E., 1939. The relation between the electrolytic solution pressures of the metals and their toxicity to the stickle-back (Gasterosteus aculeatus). J. Exp. Biol. 16: 425–439.
Kimmel, W. G., D. J. Murphey, W. E. Sharpe & D. R. De Walle, 1985. Macroinvertebrate community structure and detritus processing rates in two southwestern Pennsylvania streams acidified by atmospheric deposition. Hydrobiologia 124: 97–102.
Leivestad, H. & I. P. Muniz, 1976. Fish kill at low pH in a Norwegian river. Nature 259: 391–392.
Leivestad, H., 1982. Physiological effects of acid stress on fish. In T. A. Haines & R. E. Johnson (eds), Acid Rain/Fisheries. Proc. Int. Symp. on Acidic rain and and fishery impacts on northeastern North America. American Fisheries Soc: Maryland: 157–164.
Lind, C. J. & J. D. Hem, 1975. Effects of organic solutes on chemical reactions of aluminium. U.S. Geol. Surv. Wat. Supply Pap. 1827-G.
Lloyd, R., 1960. The toxicity of zinc sulphate to rainbow trout. Ann. appl. Biol. 48: 84–94.
Lloyd, R. & D. H. M. Jordan, 1964. Some factors affecting the resistance of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson) to acid waters. Int. J. Air. Wat. Pollut. 8: 393–403.
Muniz, I. P. & H. Leivestad, 1980. Toxic effects of aluminium on the brown trout Salmo trutta L. In D. Drablos & A. Tollan (eds), Ecological impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F., Oslo: 320–321.
Neville, C. M., 1985. Physiological response of juvenile rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri), to acid and aluminium - prediction of field responses from laboratory data. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 42: 2004–2019.
Norton, R. L. & J. R. Orpwood, 1980. Multi-element analysis using an inductively coupled plasma spectrophotometer. Part I. Commissioning and preliminary evaluation of performance. Water Research Centre, Technical Report 141.
Ormerod, S. J., P. Boole, C. P. McCahon, N. S. Weatherley, D. Pascoe & R. W. Edwards, 1987. Short-term experimental acidification of a Welsh Stream: comparing the biological effects on hydrogen ions and aluminium. Freshwat. Biol. 17: 341–356.
Orpwood, B., 1979. Concentration techniques for trace elements: a review. Water Research Centre, Technical Report 102.
Pascoe, D. & N. A. M. Shazili, 1986. Episodic Pollution — A comparison of brief and continuous exposure of rainbow trout to cadmium. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety 12: 189–192.
Plonka, A. C. & W. H. Neff, 1969. Mucopolysaccharide histochemistry of gill epithelial secretions in brook trout exposed to acid pH. Proc. PA. Acad. Sci. 43: 53–55.
Rosseland, B. O., 1980. Physiological responses to acid water in fish. 2. Effect of acid water on metabolism and gill ventilation in brown trout Salmo trutta L. and brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis Mitchell. In. D. Drablos & A Tollan (eds), Ecological Impact of Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F., Oslo: 348–349.
Schofield, C. L., 1976. Acid precipitation: effects on fish. Ambio 5: 228–230.
Schofield, C. L. & J. R. Trojnar, 1980. Aluminium toxicity to brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) in acidified waters. In T. Y. Toribara, M. W. Miller & P. E. Morrow (eds), Polluted Rain. Plenum Press, New York: 341–363.
Skidmore, J. F. & P. W. A. Tovell, 1972. Toxic effects of zinc sulphate on the gills of rainbow trout. Wat. Res. 6: 217–230.
Stoner, J. H., A. S. Gee & K. R. Wade, 1984. The effects of acidification on the ecology of streams in the Upper Tywi Catchment in west Wales. Envir. Pollut. (Ser. A.) 35: 125–157.
Townsend, C. R., A. G. Hildrew & J. Francis, 1983. Community structure in some southern English streams: the influence of physicochemical factors. Freshwat. Biol. 13: 521–544.
Ultsch, G. R. & G. Gros, 1979. Mucus as a diffusion barrier to oxygen: possible role in O2 uptake at low pH in carp (Cyprinus carpio) gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62A: 685–689.
West, R. H. & R. W. Williams, 1985. An automated method for the determination of sulphate by inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy. The Specialist. December 1985: 1–13.
Wingfield, C. A., 1939. The function of the gills of mayfly nymphs from different habitats. J. Exp. Biol. 16: 363–373.
Wright, R. F. & E. Gjessing, 1976. Acid precipitation: changes in the chemical composition of lakes. Ambio 5: 219–223.
Wright, R. F. & E. Snekvik, 1978. Acid precipitation: chemistry and fish populations in 700 lakes in southernmost Norway. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 765–775.
Wright, R. F., R. Harriman, A. Henriksen, B. Morrison & L. A. Caines, 1980. Acid lakes and streams in the Galloway area, southwestern Scotland. In D. Drablos & A. Tollan (eds), Ecological Impact of Acid Acid Precipitation. S.N.S.F., Oslo: 248–250.
Zischke, J. A., J. W. Arthur, K. J. Nordlie, R. O. Hermanutz, D. A. Standen & T. P. Henry, 1983. Acidification effects on macroinvertebrates and fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) in outdoor experimental channels. Wat. Res. 17: 47–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mc Cahon, C.P., Pascoe, D. & Mc Kavanagh, C. Histochemical observations on the salmonids Salmo salar L. and Salmo trutta L. and the ephemeropterans Baetis rhodani (Pict.) and Ecdyonurus venosus (Fabr.) following a simulated episode of acidity in an upland stream. Hydrobiologia 153, 3–12 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005500
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005500