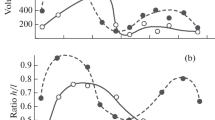
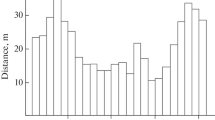
Synopsis
Quantification of fish school structure is difficult because of: (1) the large amount of positional data that must be recorded, (2) the fact that schools are moving, and (3) the fact that schools are threedimensional. Computer tools for addressing these problems include x,y digitizing devices interfaced to computers and interactive computer graphics systems. General computer algorithms now exist for 3-D reconstruction of schools given any two 2-D views such as photographs.
Our computerized film analyzer, the Galatea system, is described in detail. This system allows for rapid, accurate input of multiple points which can be followed through each frame in a film sequence. Its software packages perform 3-D reconstructions, analyze undulatory motion, and do extensive statistical tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Box, G.E.P. & G.M. Jenkins. 1970. Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Holden-Day, San Francisco, 575 pp.
Breder, C.M., Jr. 1954. Equations descriptive of fish schools and other animal aggregations. Ecology 35: 361–370.
Burgess, J.W. 1979. Measurement of spatial behavior: methodology applied to rhesus monkeys, neon tetras, communal and solitary spiders, cockroaches and gnats in open fields. Behav. & Neural Biol. 26: 132–160.
Burgess, J.W. & E. Shaw. 1979. Development and ecology of fish schooling. Oceanus 22: 11–17.
Clark, P.J. & F.C. Evans. 1979. Generalization of a nearest neighbor measure of dispersion for use in K dimensions. Ecology 60: 316–317.
Cullen, J.M., E. Shaw & H.A. Baldwin. 1965. Methods for measuring the three-dimensional structure of fish schools. Anim. Behav. 13: 534–543.
Dambach, M. 1963. Vergleichende Untersuchungen über das Schwarmverhalten von Tilapia — Jungfischen (Cichlidae. Teleostei). 2. Tierpsychol. 20: 267–296.
Dill, L.M. & R.L. Dunbrack & P.F. Major. 1981. A new stereophotographic technique for analyzing the three-dimensional structure of fish schools. Env. Biol. Fish. 6: 7–13.
Duda, R.O. & P.E. Hart. 1973. Pattern classification and scene analysis. Wiley, N.Y. 482 pp.
Hunter, J.R. 1965. Procedure for analysis of schooling behavior. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 23: 547–562.
Hurley, A.C. 1978. School structure of the squidLoligo opalescens. U.S. Fish. Bull. 76: 433–442.
Katz, L.C., M.J. Potel & R.J. Wassersug. 1981. Structure and mechanisms of schooling in tadpoles of the clawed frog,Xenopus laevis. Anim. Behav. 29: 20–33.
Major, P.F. & L.M. Dill. 1978. The three-dimensional structure of airborne bird flocks. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 4 111–122.
Muybridge, E. 1887. Animal locomotion. University of Pennsylvania. Philadelphia. (Selected reprints In: Animals in Motion, Dover, New York (1957)).
Newman, W.M. & R.F. Sproull. 1979. Principles of interactive computer graphics, 2nd Ed. McGraw-Hill, N.Y. 541 pp.
Otnes, R.K. & L. Enochson. 1978. Applied time series analysis. Vol I: Basic techniques. Wiley, N.Y. 449 pp.
Partridge, B.L. 1980. The effect of school size on the structure and dynamics of minnow schools. Anim. Behav. 28: 68–77.
Partridge, B.L. & J.M. Cullen. 1977. A low cost interactive coordinate plotter. Behav. Res. Meth. & Instr. 9: 473–479.
Partridge, B.L. & T.J. Pitcher. 1980. The sensory basis of fish schools: relative roles of lateral line and vision. J. Comp. Physiol. 135: 315–325.
Partridge, B.L., T. Pitcher, J.M. Cullen & J. Wilson. 1980. The three-dimensional structure of fish schools. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 6: 277–288.
Pitcher, T.J. 1973. The 3-dimensional structure of schools in the minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus). Anim. Behav. 21: 673–686.
Pitcher, T.J. 1975. A periscopic method for determining the three-dimensional positions of fish in schools. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 32: 1533–1538.
Pitcher, T. 1979. Sensory information and the organization of behavior in a shoaling cyprinid fish. Anim. Behav. 27: 126–149.
Pitcher, T.J. & B.L. Partridge. 1979. Fish school density and volume. Mar. Biol. 54: 383–394.
Potel, M.J. & S.A. MacKay. 1979. Preaggregative cell motion inDictyostelium, J. Cell. Sci. 36: 281–309.
Potel, M.J., R.F. Sayre & S.A. MacKay. 1980. Graphics input tools for interactive motion analysis. Comput. Graphics & Image Processing 14: 1–23.
Potel, M.J., R.E. Sayre & A. Robertson. 1979. A system for interactive film analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 9: 237–256.
Radakov, D.V. 1973. Schooling in the ecology of fish. John Wiley & Sons, New York, New York. 173 pp.
Rogers, D.J. & J.A. Adams. 1976. Mathematical elements for computer graphics. McGraw-Hill, N.Y. 239 pp.
Rubin, J.M., N.J. Patronas, E.E. Duda, R.E. Sayre & M.J. Potel. 1980. Clinical applications of combined cerebral angiograms and brain CT scans. Amer. J. Neuroradiology 1: 83–87.
Rubin, J.M. & R.E. Sayre. 1978. A computer-aided technique for overlaying cerebral angiograms onto computed tomograms. Investigative Radiology 13: 362–367.
Rubin, J. 1978a. A comparative study of tadpole locomotion. Amer. Zool. 17: 973.
Rubin, J. 1978b. Computer-aided film analysis of tadpole swimming. M. Sc. Thesis. Dept. of Anatomy. Univ. of Chicago. 39 pp.
Sakamoto, W., T. Inagaki & T. Kuroki. 1976. Studies on the schooling behavior of fish — IV some discussions concerning continuity of swimming speed and response time of individuals. Bull. Jap. Soc Sci. Fisheries 42: 1083–1091.
Sayre, R.E., J.M. Rubin, E.E. Duda & N.J. Patronas. 1979. Quantitative three-dimensional angiograms: applications, including augmentation of computed tomograms. pp. 95–102. Proc. IEEE 6th Conf. on Comput. Applic. in Radiology, Newport Beach, CA.
Shaw, E. 1978. Schooling fishes. Amer. Sci. 66: 66–125.
Southwood, T.R.E. 1978. Ecological methods. Chapman and Hall, London, England. 524 pp.
Stauffer, H.B. 1979. A generalization of Pielou's index of nonrandomness. J. Theor. Biol. 77: 19–25.
Sutherland, I.E. 1974. Three-dimensional data input by tablet. Proc. IEEE 62: 453–461.
Symons, P.E.K. 1971. Spacing and density in schooling threespine sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus) and mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 28: 999–1004.
Thompson, M.M. (ed.) 1966. Manual of photogrammetry, 3rd. Ed. American Society of Photogrammetry, Washington, D.C. 1199 pp.
Underwood, E.E. 1970. Quantitative Stereology. Addison-Wesley, Reading, M.A. 274 pp.
Wassersug, R., A. Lum & M. Potel. 1981. An analysis of school structure for tadpoles (Anura: Amphibia). Behav. Fcol. Sociobiol. (submitted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potel, M.J., Wassersug, R.J. Computer tools for the analysis of schooling. Environ Biol Fish 6, 15–19 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00001794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00001794