Abstract
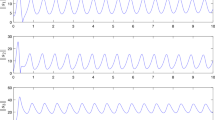
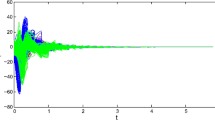
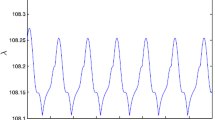
This paper is concerned with the adaptive synchronization of multi-agent systems via variable impulsive control method. Based on the theory of impulsive differential equations, adaptive control technique, Lyapunov stability theory and comparison system method, some novel adaptive synchronization conditions with impulsive time window are given to realize the synchronization of multi-agent nonlinear systems with uncertain parameters. Different from the existing investigations of impulsive synchronization of multi-agent systems, the proposed impulsive control protocol with impulsive time window is more effective in practical systems. Finally, two simulation results demonstrate the validity of the theoretical results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang YW, Liu XK, Xiao JW, Shen YJ (2018) Output formation-containment of interacted heterogeneous linear systems by distributed hybrid active control. Automatica 93:26–32
Ma TD (2015) Synchronization of multi-agent stochastic impulsive perturbed chaotic delayed neural networks with switching topology. Neurocomputing 151:1392–1406
Ma TD, Lewis FL, Song YD (2016) Exponential synchronization of nonlinear multi-agent systems with time delays and impulsive disturbances. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 26:1615–1631
Wang YW, Wei YW, Liu XK, Zhou N, Cassandras CG (2018) Optimal persistent monitoring using second-order agents with physical constraints. IEEE Trans Autom Control. https://doi.org/10.1109/tac.2018.2879946
Yang DS, Pang YH, Zhou BW, Li K (2019) Fault diagnosis for energy internet using correlation processing-based convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 49:1739–1748. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2019.2919940
Lewis FL, Cui B, Ma TD, Song YD, Zhao CH (2016) Heterogeneous multi-agent systems: reduced-order synchronization and geometry. IEEE Trans Autom Control 61(5):1391–1396
Liu ZW, Saberi A, Stoorvogel AA, Zhang MR (2018) Passivity-based state synchronization of homogeneous multi-agent systems via static protocol in the presence of input saturation. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 28(7):2720–2741
Cui B, Zhao CH, Ma TD, Feng C (2017) Leaderless and leader-following consensus of multi-agent chaotic systems with unknown time delays and switching topologies. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 24:115–131
Liu ZW, Stoorvogel AA, Saberi A, Nojavanzadeh D (2019) Squared-down passivity based state synchronization of homogeneous continuous-time multi-agent systems via static protocol in presence of time-varying topology. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 29:3821–3840. https://doi.org/10.1002/rnc.4585
Ma TD, Li T, Cui B (2018) Coordination of fractional-order nonlinear multi-agent systems via distributed impulsive control. Int J Syst Sci 49(1):1–14
Wang FY, Liu ZX, Cheng ZQ (2018) A novel leader-following consensus of multi-agent systems with smart leader. Int J Control Autom Syst 16(4):1483–1492
Ma TD, Cui B, Wang YJ, Liu K (2019) Stochastic synchronization of delayed multi-agent networks with intermittent communications: an impulsive framework. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 29(13):4537–4561
Wang YW, Lei Y, Bian T, Guan ZH (2019) Distributed control of nonlinear multi-agent systems with unknown and nonidentical control directions via event-triggered communication. IEEE Trans Cybern 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2019.2908874
Shen Y, Li F, Zhang D, Wang YW, Liu Y (2019) Event-triggered output feedback H∞ control for networked control systems. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 29(1):166–179
Liu ZW, Zhang MR, Saberi A, Stoorvogel AA (2018) State synchronization of multi-agent systems via static or adaptive nonlinear dynamic protocols. Automatica 95:316–327
Fu J, Bai JF, Lai JJ, Li PD, Yu M, Lam HK (2019) Adaptive fuzzy control of a magnetorheological elastomer vibration isolation system with time-varying sinusoidal excitations. J Sound Vib 456:386–406
Morstyn T, Savkin AV, Hredzak B, Agelidis VG (2018) Multi-agent sliding mode control for state of charge balancing between battery energy storage systems distributed in a DC microgrid. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 9(5):4735–4743
Zhao L, Yu JP, Lin C, Yu HS (2017) Distributed adaptive fixed-time consensus tracking for second-order multi-agent systems using modified terminal sliding mode. Appl Math Comput 312:23–35
Wang Y, Ma ZJ, Zheng S, Chen GR (2017) Pinning control of lag-consensus for second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(8):2203–2211
Lu JQ, Ding CD, Lou JG, Cao JD (2015) Outer synchronization of partially coupled dynamical networks via pinning impulsive controllers. J Franklin Inst 352(11):5024–5041
Huang WC, Huang YW, Chen SB (2018) Robust consensus control for a class of second-order multi-agent systems with uncertain topology and disturbances. Neurocomputing 313:426–435
Yang DS, Li T, Zhang HG, Xie XP (2019) Event-trigger-based robust control for nonlinear constrained-input systems using reinforcement learning method. Neurocomputing 349:158–170
Ao WG, Ma TD, Sanchez RV, Gan HT (2019) Finite-time and fixed-time impulsive synchronization of chaotic systems. J Franklin Inst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.07.023
Ma TD, Zhang ZL, Cui B (2018) Adaptive consensus of multi-agent systems via odd impulsive control. Neurocomputing 321:139–145
Ma TD, Fu J (2011) On the exponential synchronization of stochastic impulsive chaotic delayed neural networks. Neurocomputing 74(5):857–862
Li XD, Wu JH (2018) Sufficient stability conditions of nonlinear differential systems under impulsive control with state-dependent delay. IEEE Trans Autom Control 63(1):306–311
Ma TD, Zhang ZL, Cui B (2019) Variable impulsive consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 31:1–18
Wang X, Wang H, Li CD, Huang TW (2017) Stability analysis of hybrid neural networks with impulsive time window. Int J Biomath 10(1):1750011
Zou LM, Peng Y, Feng YM, Tu ZW (2018) Impulsive control of nonlinear systems with impulse time window and bounded gain error. Nonlinear Anal Model Control 23(1):40–49
Feng YM, Yu JZ, Li CD, Huang TW, Che HJ (2017) Linear impulsive control system with impulse time windows. J Vib Control 23(1):111–118
Zhou YH, Li CD, Huang TW, Wang X (2017) Impulsive stabilization and synchronization of Hopfield-type neural networks with impulse time window. Neural Comput Appl 28(4):775–782
Feng YM, Li CD, Huang TW (2016) Periodically multiple state-jumps impulsive control systems with impulse time windows. Neurocomputing 193:7–13
Wang X, Wang H, Li CD, Huang TW (2016) Synchronization of coupled delayed switched neural networks with impulsive time window. Nonlinear Dyn 84(3):1747–1757
Sun JT, Zhang YP, Wu QD (2003) Less conservative conditions for asymptotic stability of impulsive control systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 48(5):829–831
Tan J, Li CD, Huang TW (2018) Comparison system method for a class of stochastic systems with variable-time impulses. Int J Control Autom Syst 16(2):702–708
Feng YM, Li CD (2017) Comparison system of impulsive control system with impulse time windows. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(6):4197–4204
Tan J, Li CD, Huang TW (2015) Stability of impulsive systems with time window via comparison method. Int J Control Autom Syst 13(6):1346–1350
Ma TD, Li T, Cui B (2018) Adaptive impulsive consensus of multi-agent systems. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 28(6):2031–2046
Ai XL, Yu JQ, Jia ZY, Shen YC, Ma PB, Yang D (2017) Adaptive robust consensus tracking for nonlinear second-order multi-agent systems with heterogeneous uncertainties. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 27(18):5082–5096
Ma TD, Yu TT, Cui B (2018) Adaptive synchronization of multi-agent systems via variable impulsive control. J Franklin Inst 355(15):7490–7508
Wang R, Dong XW, Li QD, Ren Z (2017) Distributed adaptive control for time-varying formation of general linear multi-agent systems. Int J Syst Sci 48(16):3491–3503
Shilnik LP (1994) Chua’s circuit: rigorous result and future problems. Int J Bifurc Chaos 3:489–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, L., Xiao, J., Guo, X. et al. Adaptive Variable Impulsive Synchronization of Multi-agent Systems. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 15, 259–268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00315-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-019-00315-6