Abstract
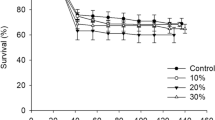
Augmentative biological control by the parasitoid Habrobracon hebetor (Say) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) is the most promising strategy to control millet head miner, Heliocheilus albipunctella (De Joannis) a major insect pest of pearl millet in the Sahel. As H. hebetor survival is somehow challenging during the nine month long off-season when the host, H. albipunctella is in diapause, there needs to be a sufficient supply of parasitoids for fresh release each year. Therefore, the aim of this study was to establish a small-scale parasitoid rearing process adjusted to the Sahel conditions that can be scaled-up as necessary. We conducted experiments to fine-tune and standardize the rearing technique of H. hebetor for cottage industrial use. The results showed that parasitoids fed with 30% honey solution and supplied daily with one late-larval-stage Corcyra cephalonica Stainton (Lepidotera, Pyralidae) produced highest number of progeny. The optimal times for mating and egg fertilization, was achieved when a male and female pair was confined for 24 h in a 30-cc vial. Our findings indicated that, compared with the conventional rearing method -2 females supplied once with 25 C. cephalonica larvae-, this new method resulted in 14-times greater parasitoid production. Furthermore parasitoid female can be stored for up to three weeks at fluctuating 23–32°C temperature and 25%–80% relative humidity for numbers accumulations prior to on-farm augmentative releases without altering its fitness.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir-maafi M, Chi H (2006) Demography of Habrobracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on two pyralid hosts (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:84–90
Antolin MF, Strand MR (1992) Mating system of Bracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Ecol Entomol 17:1–7
Antolin MF, Ode PJ, Strand MR (1995) Variable sex ratios and ovicide in an outbreeding parasitic wasp. Anim Behav 49:589–600
Ba NM, Baoua IB, N’Diaye M, Dabire-Binso C, Sanon A, Tamò M (2013) Biological control of the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (de Joannis) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Sahelian region by augmentative releases of the parasitoid wasp Habrobracon hebetor (say)(Hymenoptera: Braconidae): effectiveness and farmers’ perceptions. Phytoparasitica 41:569–576
Ba NM, Baoua IB, Kabore A, Amadou L, Oumarou N, Dabire-Binso C, Sanon A (2014) Augmentative on-farm delivery methods for the parasitoid Habrobracon hebetor say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) to control the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (de Joannis) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Burkina Faso and Niger. BioControl 59:689–696
Bal AB, Kogo S, Dankoulou A, Gagaré S (2002) Guide d'élevage et de lâchers de Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera, Braconidae) parasitoïde de la chenille mineuse de l'épi de mil et de son hôte de substitution Corcyra cephalonica (Stainton) Lepidoptera, Pyralidae. Technical document, AGRHYMET Centre, Niamey
Baoua IB, Amadou L, Oumarou N, Payne W, Roberts JD, Stefanova K, Nansen C (2014) Estimating effect of augmentative biological control on grain yields from individual pearl millet heads. J Appl Entomol 138:281–288
Baoua IB, Ba MN, Amadou L, Kabore A, Dabire-Binso CL (2018) Field dispersal of the parasitoid wasp Habrobracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) following augmentative release against the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Sahel. Biocontrol Sci Tech 28:404–415
Benson JF (1973) Intraspecific competition in the population dynamics of Bracon hebetor say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Anim Ecol 42:105–124
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 17:15–26
Bloem S, Carpenter JE, Bloem KA, Tomlin L, Taggart S (2004) Effect of rearing strategy and gamma radiation on field competitiveness of mass-reared codling moths (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). J Econ Entomol 97:1891–1898
Boivin G, Colinet H (2011) Insect parasitoids cold storage: a comprehensive review of factors of variability and consequences. Biol Control 58:83–95
Burger JMS, Reijnen TM, van Lenteren JC, Vet LEM (2004) Host feeding in insect parasitoids: why destructively feed upon a host that excretes an alternative? Entomol Exp Appl 112:207–215
Chen H, Opit GP, Sheng P, Zhang H (2011) Maternal and progeny quality of Habrobracon hebetor say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) after cold storage. Biol Control 58:255–261
Collier T, Steenwyk RV (2004) A critical evaluation of augmentative biological control. Biol Control 31:245–256
Dai P, Ruan C, Zang L, Wan F, Liu L (2014) Effects of rearing host species on the host-feeding capacity and parasitism of the whitefly parasitoid Encarsia formosa. J Insect Sci 14:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.014.118
Damiens D, Bressac C, Chevrier C (2003) The effect of age on sperm stock and egg laying in the parasitoid wasp, Dinarmus basalis. J Insect Sci 3:22–25
Eisa M. A., Elamin E. M., Elbadawi A., El Hassan A. E. B., Rudwan M. K., Ratschker U. M. and Roth M. (2007) Ecological characteristics of the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), a pest on pearl millet in Sudan. In: Tropentag 2007 Conference on International Agricultural Research for Development (pp. 1–7), University of Kassel-Witzenhausen and University of Gottingen, Germany
Eliopoulos PA, Stathas GJ (2008) Life tables of Habrobracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) parasitizing Anagasta kuehniella and Plodia interpunctuella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): effect of host density. J Econ Entomol 101:982–988
Gahukar RT, Guèvremont TH, Bhatnagar VS, Doumbia YO, Ndoye M, Pierrard G (1986) A review of the pest status of the millet spike worm, Rhaguva albipunctella de Joannis (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) and its management in the Sahel. Insect Sci Appl 7:457–463
Gandolfi M, Mattiacci L, Dorn S (2003) Mechanisms of behavioral alterations of parasitoids reared in artificial systems. J Chem Ecol 29:1871–1887
Ghimire NM (2008) Reproductive performance of the parasitoid Bracon hebetor say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on various host species of Lepidoptera. PhD thesis. Oklahoma State University, USA, p 116
Godfray HCJ (1994) Parasitoids behavioral and evolutionary ecology. Princeton University press, New Jersey
Hagstrum DW, Smittle BJ (1977) Host-finding ability of Bracon hebetor and its influence upon adult parasite survival and fecundity. Environ Entomol 6:437–439
Harvey JA, Gols GJZ (1998) The influence of host quality on progeny and sex allocation in the pupal ecto parasitoid, Muscidifurax raptellus (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Bull Entomol Res 88:299–304
Heimpel GE, Collier TR (1996) The evolution of host-feeding behaviour in insect parasitoids. Biol Rev 71:373–400
Henry LM, May N, Acheampong S, Gillespie DR, Roitberg BD (2010) Host-adapted parasitoids in biological control: does source matter? Ecol Appl 20:242–250
Holloway KA, Heimpel GE, Strand MR, Antolin MF (1999) Survival of diploid males in Bracon sp. near hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 92:110–116
Hossain MA, Haque MA (2015) Influence of food supplements on the reproductive potential of the parasitoid, Dinarmus basalis (Rondani) (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) on Callosobruchus chinensis(L.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Afr Entomol 23:88–93
Jarosik V, Holy I, Lapchin L, Havelka J (2003) Sex ratio in the aphid parasitoid Aphidius colemani (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in relation to host size. Bull Entomol Res 93:255–258
Jervis MA, Kidd NAC (1986) Host-feeding strategies in hymenopteran parasitoids. Biol Rev 61:395–434
Jervis MA, Kidd NAC, Heimpel GE (1996) Parasitoid adult feeding behaviour and biocontrol – a review. Biocontrol News Inform 17:11N–26N
Joyce AL, Aluja M, Sivinski J, Vinson SB, Ramirez-Romero R, Bernal JS, Guillen L (2010) Effect of continuous rearing on courtship acoustics of five braconid parasitoids, candidates for augmentative biological control of Anastrepha species. Biocontrol 55:573–582
Kabore A, Ba NM, Dabire-Binso CL, Sanon A (2017) Field persistence of Habrobracon hebetor (say) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) following augmentative releases against the millet head miner, Heliocheilus albipunctella (de Joannis) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), in the Sahel. Biol Control 108:64–69
King BH (1987) Offspring sex ratios in parasitoid wasps. Q Rev Biol 62:367–396
Krall S, Youm O, Kogo SA (1995) Panicle insect pest damage and yield loss in pearl millet. In: Nwanze KF, Youm O (eds) Proceeding of an international consultative workshop on panicle insect pest of sorghum and millet. ICRISAT Sahelian Centre, Niamey, pp 135–145
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Ndoye M (1991) Biologie et dynamique des populations de Heliocheilus albipunctella (De Joannis) ravageur de la chandelle de mil dans le Sahel. Sahel PV Info 39:11–20
Nikam PK, Pawar CV (1993) Life tables and intrinsic rate of natural increase of Bracon hehetor say (Hym., Braconidae) population on Corcyra cephalonica Staint. (Lep., Pyralidae), a key parasitoid of Helicoverpa armigera Hbn. (Lep., Noctuidae). J Appl Entomol 115:210–213
Nwanze KF, Harris KM (1992) Insect pests of pearl millet in West Africa. Rev Agric Entomol 80:1133–1155
Nwanze KF, Sivakumar MVK (1990) Insect pests of pearl millet in Sahelian West Africa-II. Raghuva albipunctella De Joannis (Noctuidae, Lepidoptera): distribution, population dynamics and assessment of crop damage. Int J Pest Manage 36:59–65
Ode PJ, Antolin MF, Strand MR (1995) Brood-mate avoidance in the parasitic wasp Bracon hebetor say. Anim Behav 49:1239–1248
Ode PJ, Antolin MF, Strand MR (1996) Sex allocation and sexual asymmetries in intra-brood competition in the parasitic wasp Bracon hebetor. J Anim Ecol 65:690–700
Ode PJ, Antolin MF, Strand MR (1997) Constrained oviposition and female-biased sex allocation in a parasitic wasp. Oecologia 109:547–555
Payne W, Tapsoba H, Baoua IB, Ba NM, N’Diaye M, Dabire-Binso C (2011) On-farm biological control of the pearl millet head miner: realization of 35 years of unsteady progress in Mali, Burkina Faso and Niger. Int J Agric Sustain 9:186–193
Radhika P, Chitra KC (1998) Correlation between life expectancy and adult emergence in Bracon hebetor (say) as influenced by host level nutrition. Indian J Plant Prot 26:68–71
Rahat S, Geoff MG, Wratten SD, Jianhua m, Robyn N (2005) Effect of plant nectars on adult longevity of the stinkbug parasitoid, Trissolcus basalis. Int J Pest Manage 51:321–324
Saadat D, Seraj A, Goldansaz S, Williams L (2016) Factors affecting reproductive success and life history parameters of Bracon hebetor say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) from three host-associated populations. Biol Control 96:86–92
SAS (2003) SAS version 9.1 for windows. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina
Sepúlveda DA, Zepeda-Paulo F, Ramírez CC, Lavandero B, Figueroa CC (2017) Loss of host fidelity in highly inbred populations of the parasitoid wasp Aphidius ervi (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Pest Sci 90:649–658
Temerak SA (1983) Longevity of Bracon brevicornis [Hym: Braconidae] adults as influenced by nourishment on artificial and natural foods. Entomophaga 28:145–150
Tena A, Pekas A, Cano D, Wackers FL, Urbaneja A (2015) Sugar provisioning maximizes the biocontrol service of parasitoids. J Appl Ecol 52:795–804
Tian JC, Wang GW, Romeis J, Zheng XS, Xu HX, Zang LS, Lu ZX (2016) Different performance of two Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) species feeding on sugars. Environ Entomol 45:1316–1321
Tooker JF, Hanks LM (2000) Flowering plant hosts of adult hymenopteran parasitoids of Central Illinois. Ann Entomol Soc Am 93:580–588
van Lenteren JC (2012) The state of commercial augmentative biological control: plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. Biol Control 57:1–20
Youm O, Owusu EO (1998) Assessment of yield loss due to the millet head miner, Heliocheilus albipunctella (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) using a damage rating scale and regression analysis in Niger. Int J Pest Manage 44:119–121
Yu S-H, Ryoo MI, Na JH (1999) Life history of Bracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on a dried vegetable commodity. J Asia Pac Entomol 2:149–152
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Collaborative Crop Research Program (CCRP) of the McKnight Foundation, Minneapolis, MN [grant numbers 09-038; 2009-2012]. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the McKnight Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabore, A., Ba, N.M., Dabire-Binso, C. et al. Towards development of a parasitoid cottage industry of the parasitoid wasp Habrobracon hebetor (say): optimum rearing and releases conditions for successful biological control of the millet head miner Heliocheilus albipunctella (De Joannis) in the Sahel. Int J Trop Insect Sci 39, 25–33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-019-00005-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-019-00005-w