Abstract
Purpose
This paper describes the origins and application of a theory, the social development model (SDM), that seeks to explain causal processes that lead to the development of prosocial and problem behaviors. The SDM was used to guide the development of a multicomponent intervention in middle childhood called Raising Healthy Children (RHC) that seeks to promote prosocial development and prevent problem behaviors. This paper reviews and integrates the tests of the SDM and the impact of RHC. While the original results of both model and intervention tests have been published elsewhere, this paper provides a comprehensive review of these tests. As such, this integrative paper provides one of the few examples of the power of theory-driven developmental preventive intervention to understand impact across generations and the power of embedding controlled tests of preventive intervention within longitudinal studies to understand causal mechanisms.
Methods
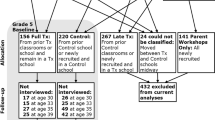
Application of the SDM in the RHC intervention was tested in a quasi-experimental trial nested in the Seattle Social Development Project (SSDP). SSDP is a longitudinal study of 808 students who attended 18 public schools in Seattle, WA, and whose parents consented for their participation in longitudinal research when they were in grade 5 (77% of the eligible population in participating schools). Students assented at each survey administration and consented to longitudinal follow-up when they turned 18. Panel subjects were followed and surveyed 15 times from grade 5 through age 39, with most completion rates above 90%.
Results
We describe effects of the full multicomponent RHC intervention delivered in grades 1 through 6 by comparing outcomes of those children assigned to the full RHC intervention condition to controls from middle childhood through age 39. We also report the effects of the full RHC intervention on the firstborn children of participants compared with the firstborn children of controls.
Conclusions
We discuss the use of the theory to guide the development and testing of preventive interventions and the utility of nesting intervention tests within longitudinal studies for testing both theory and interventions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, R. D., O’Donnell, J., Hawkins, J. D., Hill, K. G., Kosterman, R., & Catalano, R. F. (1998). Changing teaching practices to promote achievement and bonding to school. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 68(4), 542–552.
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Ayers, C. D., Williams, J. H., Hawkins, J. D., Peterson, P. L., Catalano, R. F., & Abbott, R. D. (1999). Assessing correlates of onset, escalation, deescalation, and desistance of delinquent behavior. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 15(3), 277–306.
Bailey, J. A., Epstein, M., Steeger, C. M., & Hill, K. G. (2018a). Concurrent and prospective associations between substance-specific parenting practices and child cigarette, alcohol, and marijuana use. Journal of Adolescent Health, 62(6), 681–687.
Bailey, J. A., Hill, K. G., Epstein, M., Steeger, C. M., & Hawkins, J. D. (2018b). Seattle Social Development Project – The Intergenerational Project (SSDP-TIP). In V. I. Eichelsheim & S. G. A. van de Weijer (Eds.), Intergenerational continuity of criminal and antisocial behavior. An international overview of current studies (pp. 186–206). New York: Routledge.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215.
Bandura, A., & Walters, R. H. (1977). Social learning theory (Vol. 1). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate - a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
Brown, E. C., Catalano, R. F., Fleming, C. B., Haggerty, K. P., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Adolescent substance use outcomes in the Raising Healthy Children project: A two-part latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(4), 699–710.
Bursik Jr., R. J., & Grasmick, H. G. (1996). The use of contextual analysis in models of criminal behavior. In J. D. Hawkins (Ed.), Delinquency and crime: Current theories (pp. 236–267). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Cambron, C., Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. D. (2019). The social development model. In D. P. Farrington, L. Kazemian, & A. R. Piquero (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of developmental and life-course criminology (pp. 224–247). New York: Oxford University Press.
Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. D. (1996). The social development model: A theory of antisocial behavior. In J. D. Hawkins (Ed.), Delinquency and crime: Current theories, Cambridge criminology series (pp. 149–197). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Newcomb, M. D., & Abbott, R. D. (1996). Modeling the etiology of adolescent substance use: A test of the social development model. Journal of Drug Issues, 26(2), 429–455.
Catalano, R. F., Oxford, M. L., Harachi, T. W., Abbott, R. D., & Haggerty, K. P. (1999). A test of the social development model to predict problem behaviour during the elementary school period. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 9(1), 39–56.
Catalano, R. F., Berglund, M. L., Ryan, J. A. M., Lonczak, H. S., & Hawkins, J. D. (2002). Positive youth development in the United States: Research findings on evaluations of positive youth development programs. Prevention and Treatment, 5(1), Article 15 (target article) June 24, 2002.
Catalano, R. F., Park, J., Harachi, T. W., Haggerty, K. P., Abbott, R. D., & Hawkins, J. D. (2005). Mediating the effects of poverty, gender, individual characteristics, and external constraints on antisocial behavior: A test of the social development model and implications for developmental life-course theory. In D. P. Farrington (Ed.), Advances in criminological theory: Vol. 14 . Integrated developmental and life-course theories of offending (pp. 93–123). New Brunswick: Transaction.
Choi, Y., Harachi, T. W., Gillmore, M. R., & Catalano, R. F. (2005). Applicability of the social development model to urban ethnic minority youth: Examining the relationship between external constraints, family socialization, and problem behaviors. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 15(4), 505–534.
Comprehensive Health Educational Foundation. (1999). Here’s Looking at You 2000. Seattle, WA: Author.
Cummings, C. (1983). Managing to teach. Edmonds, WA: Teaching, Inc..
Cummings, C., Barber, C., & Cuervo, A. G. (1982). School enhancement research and demonstration project. Methods of instruction. Teacher’s manual (secondary). Washington, DC: Prepared for Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, U.S. Department of Justice.
da Silva, L., Sanson, A., Smart, D., & Toumbourou, J. (2004). Civic responsibility among Australian adolescents: Testing two competing models. Journal of Community Psychology, 32(3), 229–255.
Deng, S., & Roosa, M. W. (2007). Family influences on adolescent delinquent behaviors: Applying the social development model to a Chinese sample. American Journal of Community Psychology, 40(3–4), 333–344.
Dishion, T. J., Patterson, G. R., Stoolmiller, M., & Skinner, M. L. (1991). Family, school, and behavioral antecedents to early adolescent involvement with antisocial peers. Developmental Psychology, 27(1), 172–180.
Durkheim, E. (1951). Suicide: A study in sociology [1897]. Translated by J. A. Spaulding and G. Simpson. Glencoe: Free Press.
Farrington, D. P. (1989). Early predictors of adolescent aggression and adult violence. Violence and Victims, 4(2), 79–100.
Farrington, D. P. (1992). The need for longitudinal-experimental research on offending and antisocial behavior. In J. McCord & R. E. Tremblay (Eds.), Preventing antisocial behavior (pp. 353–376). New York: Guilford.
Farrington, D. P. (2006). Key longitudinal-experimental studies in criminology. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 2(2), 121–141.
Farrington, D. P. (Ed.). (2017). Advances in crminological theory: Vol. 14. Integrated developmental and life-course theories of offending. London: Routledge.
Farrington, D. P., & Hawkins, J. D. (1991). Predicting participation, early onset and later persistence in officially recorded offending. Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 1(1), 1–33.
Farrington, D. P., & Loeber, R. (1999). Transatlantic replicability of risk factors in the development of delinquency. In P. Cohen, C. Slomkowski, & L. N. Robbins (Eds.), Historical and geographical influences on psychopathology (pp. 299–329). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Farrington, D. P., Loeber, R., & Welsh, B. C. (2010). Longitudinal-experimental studies. In A. R. Piquero & D. Weisburd (Eds.), Handbook of quantitative criminology (pp. 503–518). New York: Springer.
Farrington, D. P., Ttofi, M. M., & Piquero, A. R. (2016). Risk, promotive, and protective factors in youth offending: Results from the Cambridge Study in Delinquent Development. Journal of Criminal Justice, 45, 63–70.
Farrington, D. P., Gaffney, H., & Ttofi, M. M. (2017). Systematic reviews of explanatory risk factors for violence, offending, and delinquency. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 33, 24–36.
Fell, J. C., Fisher, D. A., Voas, R. B., Blackman, K., & Tippetts, A. S. (2009). The impact of underage drinking laws on alcohol-related fatal crashes of young drivers. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 33(7), 1208–1219.
Fleming, C. B., Catalano, R. F., Oxford, M. L., & Harachi, T. W. (2002). A test of generalizability of the social development model across gender and income groups with longitudinal data from the elementary school developmental period. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 18(4), 423–439.
Fleming, C. M., Eisenberg, N., Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Cambron, C., Hawkins, J. D., et al. (2019). Optimizing assessment of risk and protection for diverse adolescent outcomes: Do risk and protective factors for delinquency and substance use also predict risky sexual behavior? Prevention Science, 20(5), 788–799.
Gloppen, K. M., David-Ferdon, C., & Bates, J. (2010). Confidence as a predictor of sexual and reproductive health outcomes for youth. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(3 Suppl), 42–58.
Gottfredson, M. R., & Hirschi, T. (1990). A general theory of crime. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Guo, J., Hawkins, J. D., Hill, K. G., & Abbott, R. D. (2001). Childhood and adolescent predictors of alcohol abuse and dependence in young adulthood. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 62(6), 754–762.
Guttmannova, K., Jones, A. A., Johnson, J. K., Oesterle, S., Johnson, R. M., & Martins, S. S. (2019). Using existing data to advance knowledge about adolescent and emerging adult marijuana use in the context of changes in marijuana policies. Prevention Science, 20(2), 291–299.
Hawkins, J. D., & Catalano, R. F. (2003a). Guiding Good Choices. South Deerfield, MA: Channing Bete Company.
Hawkins, J. D., & Catalano, R. F. (2003b). Preparing for School Success. South Deerfield, MA: Channing Bete Company.
Hawkins, J. D., & Weis, J. G. (1985). The social development model: An integrated approach to delinquency prevention. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 6(2), 73–97.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Jones, G., & Fine, D. N. (1987). Delinquency prevention through parent training: Results and issues from work in progress. In J. Q. Wilson & G. C. Loury (Eds.), From children to citizens : Vol. III. Families, schools, and delinquency prevention (pp. 186–204). New York: Springer-Verlag.
Hawkins, J. D., Doueck, H. J., & Lishner, D. M. (1988). Changing teaching practices in mainstream classrooms to improve bonding and behavior of low achievers. American Educational Research Journal, 25(1), 31–50.
Hawkins, J. D., Von Cleve, E., & Catalano Jr., R. F. (1991). Reducing early childhood aggression: Results of a primary prevention program. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30(2), 208–217.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Miller, J. Y. (1992a). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 64–105.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Morrison, D. M., O’Donnell, J., Abbott, R. D., & Day, L. E. (1992b). The Seattle Social Development Project: Effects of the first four years on protective factors and problem behaviors. In J. McCord & R. E. Tremblay (Eds.), Preventing antisocial behavior: Interventions from birth through adolescence (pp. 139–161). New York: Guilford Press.
Hawkins, J. D., Graham, J. W., Maguin, E., Abbott, R. D., Hill, K. G., & Catalano, R. F. (1997). Exploring the effects of age of alcohol use initiation and psychosocial risk factors on subsequent alcohol misuse. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 58(3), 280–290.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Abbott, R., & Hill, K. G. (1999). Preventing adolescent health-risk behaviors by strengthening protection during childhood. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 153(3), 226–234.
Hawkins, J. D., Kosterman, R., Catalano, R. F., Hill, K. G., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Promoting positive adult functioning through social development intervention in childhood: Long-term effects from the Seattle Social Development Project. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 159(1), 25–31.
Hawkins, J. D., Kosterman, R., Catalano, R. F., Hill, K. G., & Abbott, R. D. (2008). Effects of social development intervention in childhood 15 years later. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 162(12), 1133–1141.
Herrenkohl, T. I., Hawkins, J. D., Chung, I.-J., Hill, K. G., & Battin-Pearson, S. (2001a). School and community risk factors and interventions. In R. Loeber & D. P. Farrington (Eds.), Child delinquents: Development, intervention, and service needs (pp. 211–246). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Herrenkohl, T. I., Huang, B., Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Smith, B. H. (2001b). A comparison of the social development processes leading to violent behavior in late adolescence for childhood initiators and adolescent initiators of violence. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 38(1), 45–63.
Hill, K. G., Bailey, J. A., Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Oesterle, S., et al. (2014). The onset of STI diagnosis through age 30: Results from the Seattle Social Development Project intervention. Prevention Science, 15(Suppl. 1), S19–S32.
Hill, K. G., Bailey, J. A., Steeger, C. M., Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., Kosterman, R., Epstein, M., & Abbott, R. D. (2020). Effects of childhood preventive intervention across two generations: A nonrandomized controlled trial. JAMA Pediatrics, 174, 764–771.
Hirschi, T. (1969). Causes of delinquency. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
House, L. D., Bates, J., Markham, C. M., & Lesesne, C. (2010a). Competence as a predictor of sexual and reproductive health outcomes for youth: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(Suppl. 3), S7–S22.
House, L. D., Mueller, T., Reininger, B., Brown, K., & Markham, C. M. (2010b). Character as a predictor of reproductive health outcomes for youth: A systematic review. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(Suppl. 3), S59–S74.
Huang, B., Kosterman, R., Catalano, R. F., Hawkins, J. D., & Abbott, R. D. (2001). Modeling mediation in the etiology of violent behavior in adolescence: A test of the social development model. Criminology, 39(1), 75–107.
Jacob, M. (2008). The significance of gender in choosing an etiological model of delinquency (doctoral dissertation). Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences, 68, 3591.
Kim, S. (2000). The effects of parent bonding, school bonding, belief on the structure of problem behaviors in elementary school-age children. Doctoral dissertation, University of Washington, Seattle.
Kim, M. J. (2009). Youth violence prevention: Social development model approaches to predicting and preventing the progression of childhood aggression into youth violence. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences, 69, 3320.
Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Haggerty, K. P., Spoth, R., & Redmond, C. (2001). Preparing for the Drug Free Years: Session-specific effects of a universal parent-training intervention with rural families. Journal of Drug Education, 31(1), 47–68.
Kosterman, R., Haggerty, K. P., Spoth, R., & Redmond, C. (2004). Unique influence of mothers and fathers on their children’s antisocial behavior. Journal of Marriage and Family, 66(3), 762–778.
Kosterman, R., Hill, K. G., Lee, J. O., Meacham, M. C., Abbott, R. D., Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. D. (2014). Young adult social development as a mediator of alcohol use disorder symptoms from age 21 to 30. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 28(2), 348–358.
Kosterman, R., Hawkins, J. D., Hill, K. G., Bailey, J. A., Catalano, R. F., & Abbott, R. D. (2019). Effects of social development intervention in childhood on adult life at ages 30 to 39. Prevention Science, 20(7), 986–995.
Laundra, K. H., Kiger, G., & Bahr, S. J. (2002). A social development model of serious delinquency: Examining gender differences. Journal of Primary Prevention, 22(4), 389–407.
Lengua, L. J., Sadowski, C. A., Friedrich, W. N., & Fisher, J. (2001). Rationally and empirically derived dimensions of children’s symptomatology: Expert ratings and confirmatory factor analyses of the CBCL. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 69(4), 683–698.
Locke, T. F., & Newcomb, M. D. (2004). Adolescent predictors of young adult and adult alcohol involvement and dysphoria in a prospective community sample of women. Prevention Science, 5(3), 151–168.
Loeber, R., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1998). Development of juvenile aggression and violence: Some common misconceptions and controversies. American Psychologist, 53(2), 242–259.
Lonczak, H. S., Huang, B., Catalano, R. F., Hawkins, J. D., Hill, K. G., Abbott, R. D., Ryan, J. A. M., & Kosterman, R. (2001). The social predictors of adolescent alcohol misuse: A test of the social development model. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 62(2), 179–189.
Lonczak, H. S., Abbott, R. D., Hawkins, J. D., Kosterman, R., & Catalano, R. F. (2002). Effects of the Seattle Social Development Project on sexual behavior, pregnancy, birth, and sexually transmitted disease outcomes by age 21 years. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 156(5), 438–447.
Markham, C. M., Lormand, D., Gloppen, K. M., Peskin, M. F., Flores, B., Low, B., & House, L. D. (2010). Connectedness as a predictor of sexual and reproductive health outcomes for youth. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(3 Suppl), S23–S41.
Matsueda, R. L. (1988). The current state of differential association theory. Crime and Delinquency, 34(3), 277–306.
McMahon, R. J., Forehand, R., & Griest, D. L. (1981). Effects of knowledge of social learning principles on enhancing treatment outcome and generalization in a parent training program. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 49(4), 526–532.
Moffitt, T. E., Arseneault, L., Belsky, D., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., Harrington, H., Houts, R., Poulton, R., Roberts, B. W., Ross, S., Sears, M. R., Thomson, W. M., & Caspi, A. (2011). A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108(7), 2693–2698.
National Academies of Sciences Engineering and Medicine (2019). Fostering healthy mental, emotional, and behavioral development in children and youth: A national agenda. https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24625/the-health-effects-of-cannabis-and-cannabinoids-the-current-state.
O’Donnell, J., Hawkins, J. D., & Abbott, R. D. (1995). Predicting serious delinquency and substance use among aggressive boys. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 63(4), 529–537.
Patterson, G. R. (1975). Families: Applications of social learning to family life. Champagne, IL: Research Press.
Piquero, A. R., Farrington, D. P., Welsh, B. C., Tremblay, R., & Jennings, W. G. (2009). Effects of early family/parent training programs on antisocial behavior and delinquency. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 5(2), 83–120.
Piquero, A. R., Jennings, W. G., Diamond, B., Farrington, D. P., Tremblay, R. E., Welsh, B. C., & Gonzalez, J. M. R. (2016). A meta-analysis update on the effects of early family/parent training programs on antisocial behavior and delinquency. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 12(2), 229–248.
Ramchandani, P., Stein, A., Evans, J., & O’Connor, T. G. (2005). Paternal depression in the postnatal period and child development: A prospective population study. Lancet, 365(9478), 2201–2205.
Reiss, F. (2013). Socioeconomic inequalities and mental health problems in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Social Science & Medicine, 90, 24–31.
Roosa, M. W., Zeiders, K. H., Knight, G. P., Gonzales, N. A., Tein, J.-Y., Saenz, D., O’Donnell, M., & Berkel, C. (2011). A test of the social development model during the transition to junior high with Mexican American adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 47(2), 527–537.
Rose, G. (1981). Strategy of prevention: Lessons from cardiovascular disease. British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Editions), 282(6279), 1847–1851.
Scales, P. C., Benson, P. L., Oesterle, S., Hill, K. G., Hawkins, J. D., & Pashak, T. J. (2016). The dimensions of successful young adult development: A conceptual and measurement framework. Applied Developmental Science, 20(3), 150–174.
Seligman, M. E. P., Steen, T. A., Park, N., & Peterson, C. (2005). Positive psychology progress: Empirical validation of interventions. American Psychologist, 60(5), 410–421.
Shek, D. T. L., Siu, A. M. H., & Lee, T. Y. (2007). The Chinese Positive Youth Development Scale: A validation study. Research on Social Work Practice, 17(3), 380–391.
Shure, M. B., & Spivack, G. (1980). Interpersonal problem solving as a mediator of behavioral adjustment in preschool and kindergarten children. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 1(1), 29–44.
Shure, M. B., & Spivack, G. (1988). Interpersonal cognitive problem solving. In R. H. Price, E. L. Cowan, R. P. Lorion, & J. Ramos-McKay (Eds.), Fourteen ounces of prevention: A casebook for practitioners (pp. 69–82). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Singh, A., Squires, J., Yeh, C. J., Heo, K. H., & Bian, H. (2016). Validity and reliability of the developmental assessment screening scale. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 5(1), 124–128.
Slavin, R. E. (1991). Synthesis of research of cooperative learning. Educational Leadership, 48(5), 71–82.
Squires, J., Potter, L., & Bricker, D. (1999). The ASQ user’s guide for the Ages & Stages Questionnaires: A parent-completed, child-monitoring system (2nd ed.). Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes.
Stone, A. L., Becker, L. G., Huber, A. M., & Catalano, R. F. (2012). Review of risk and protective factors of substance use and problem use in emerging adulthood. Addictive Behaviors, 37(7), 747–775.
Sullivan, C. J., & Hirschfield, P. (2011). Problem behavior in the middle school years: An assessment of the social development model. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 48(4), 566–593.
Sutherland, E. H. (1973). Development of the theory [Private paper published posthumously]. In K. Schuessler (Ed.), Edwin Sutherland on analyzing crime (pp. 13–29). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
The Commission on Positive Youth Development. Seligman, M. E. P., Berkowitz, M. W., Catalano, R. F., Damon, W., Eccles, J. S., et al. (2005). The positive perspective on youth development. In D. L. Evans, E. B. Foa, R. E. Gur, H. Hendin, C. P. O’Brien, M. E. P. Seligman, et al. (Eds.), Treating and preventing adolescent mental health disorders: What we know and what we don’t know (pp. 496–527, 760–769). New York: Oxford University Press. The Annenberg Foundation Trust at Sunnylands, and The Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania.
Vogel, M., & Jaecques, B. (2016). Contextual analysis of crime. https://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780195396607/obo-9780195396607-0200.xml.
Walker, H. M., & McConnell, S. R. (1988). The Walker-McConnell Scale of Social Competence and School Adjustment. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Wasserman, G. A., Keenan, K., Tremblay, R. E., Coie, J. D., Herrenkohl, T. I., Loeber, R., et al. (2003). Risk and protective factors of child delinquency. OJJDP Juvenile Justice Bulletin, Child Delinquency Bulletin Series, April.
Funding
Work on this paper was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse grant numbers R01DA021426, R01DA003721, R01DA009679, R01DA033956, and R01DA023089. The content of this paper is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the University of Washington Institutional Review Board and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catalano, R.F., Hawkins, J.D., Kosterman, R. et al. Applying the Social Development Model in Middle Childhood to Promote Healthy Development: Effects from Primary School Through the 30s and Across Generations. J Dev Life Course Criminology 7, 66–86 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-020-00152-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-020-00152-6