Abstract
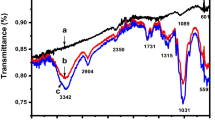
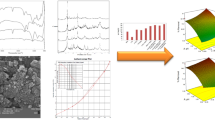
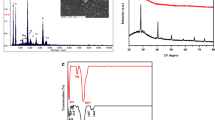
Currently, the pollution of water by heavy metals is a common environmental problem because heavy metals are non-biodegradable and dangerous to human health at very low concentrations. Lead is one of the most prevalent heavy metals utilized in various industrial processes. In this study, an adsorbent made from nano Prosopis cineraria leaf ash (NPCLA) was successfully synthesized and characterized for the first time using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and energy-dispersive analysis of X-rays (EDAX). The findings from the XRD analysis showed that the structure of the NPCLA predominantly included CaCO3 and SiO2 crystal phases. Batch adsorption experiments were performed as a function of reaction time, pH (2–10), initial concentration of lead (30–120 mg/L), and NPCLA dosage (1–3 g/L). According to the results, the lead ions were completely removed from an aqueous solution at a temperature of 25 °C with an NPCLA dosage of 2.5 g/L, an initial lead concentration of 30 mg/L, pH of 6, and after 100 min of reaction time. The NPCLA adsorbent demonstrated high stability and recyclability after six runs of the lead removal experiments. The equilibrium adsorption data were fitted to a pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi M, Hazrati Niari M, Kakavandi B (2017) Development of maghemite nanoparticles supported on cross-linked chitosan (γ-Fe2O3@CS) as a recoverable mesoporous magnetic composite for effective heavy metals removal. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.10.014
Al-Zboon K, Al-Harahsheh MS, Hani FB (2011) Fly ash-based geopolymer for Pb removal from aqueous solution. J Hazardous Mater 188(1–3):414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.133
Bachari Z, Isari AA, Mahmoudi H, Moradi S, Mahvelati EH (2019) Application of natural surfactants for enhanced oil recovery–critical review. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, Vol 221, issue 1. IOP Publishing, p 012039
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2010) Utilization of agro-industrial and municipal waste materials as potential adsorbents for water treatment: a review. Chem Eng J 157(2–3):277–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.007
Bhattacharyya KG, Sharma A (2004) Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by Azadirachta indica (neem) leaf powder. J Hazard Mater 113(1–3):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.05.034
Bux SK et al (2010) Rapid solid-state synthesis of nanostructured silicon. Chem Mater 22(8):2534–2540. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm903410s
Chakravarty S et al (2010) Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by adsorption using bael leaves (Aegle marmelos). J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):502–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.113
Dippong T et al (2017) Size and shape-controlled synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles embedded in a PVA-SiO2 hybrid matrix. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 128(August):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.10.018
Dizadji N, Abootalebi Anaraki N (2011) Adsorption of chromium and copper in aqueous solutions using tea residue. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(3):631–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326248
Dubey A, Shiwani S (2012) Adsorption of lead using a new green material obtained from Portulaca plant. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9(1):15–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-011-0012-8
El-Ashtoukhy ESZ, Amin NK, Abdelwahab O (2008) Removal of lead (II) and copper (II) from aqueous solution using pomegranate peel as a new adsorbent. Desalination 223(1–3):162–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.206
Eshraghi F et al (2016) Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Prosopis Cineraria leaf ash abstract. Am J Oil Chem Technol 4(1):4–11
Garg A, Mittal SK (2013) Review on Prosopis cineraria: a potential herb of Thar desert. Drug Invent Today 5(1):60–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dit.2013.03.002
Garg U et al (2008) Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. J Hazard Mater 154(1–3):1149–1157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.040
Gholipour Z et al (2012) Sturctural flexibility under oxidative coupling of methane; main chemical role of alkali ion in [Mn + (Li, Na, K or Cs) + W]/SiO2 catalysts. Iran J Sci Technol Trans A Sci 36(2):189–211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1130992
Granbohm H et al (2017) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of quaternary GO/TiO2/Ag/AgCl nanocomposites. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3313-9
Gueu S et al (2007) Kinetics and thermodynamics study of lead adsorption on to activated carbons from coconut and seed hull of the palm tree. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325956
Günay A, Arslankaya E, Tosun I (2007) Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.034
Gupta VK et al (2003) Removal of cadmium and nickel from wastewater using bagasse fly ash: a sugar industry waste. Water Res 37(16):4038–4044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00292-6
Hafshejani LD et al (2015) Removal of zinc and lead from aqueous solution by nanostructured cedar leaf ash as biosorbent. J Mol Liq 211(December):448–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.07.044
Hayati F et al (2018) Photocatalytic decontamination of phenol and petrochemical wastewater through ZnO/TiO2 decorated on reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite: influential operating factors, mechanism, and electrical energy consumption. RSC Adv 8(70):40035–40053. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA07936F
Hayati F, Isari AA, Anvaripour B, Fattahi M, Kakavandi B (2019) Ultrasound-assisted photocatalytic degradation of sulfadiazine using MgO@ CNT heterojunction composite: effective factors, pathway and biodegradability studies. Chem Eng J 381:122636
Isari AA et al (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B and real textile wastewater using Fe-doped TiO2 anchored on reduced graphene oxide (Fe-TiO2/rGO): characterization and feasibility, mechanism and pathway studies. Appl Surf Sci 462:549–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.133
Jafari AJ et al (2016) Application of mesoporous magnetic carbon composite for reactive dyes removal: process optimization using response surface methodology. Korean J Chem Eng 33(10):2878–2890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0155-x
Jorfi S et al (2017) Adsorption of Cr(VI) by natural clinoptilolite zeolite from aqueous solutions: isotherms and kinetics. Pol J Chem Technol 19(3):106–114. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjct-2017-0056
Karimi Pasandideh E et al (2016) Silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles core-shell spheres (Fe3O4@SiO2) for natural organic matter removal. J Environ Health Sci Eng 14(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-016-0262-y
Kaushik N, Kumar V (2003) Khejri (Prosopis cineraria)-based agroforestry system for arid Haryana, India. J Arid Environ 55(3):433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-1963(02)00289-6
King P et al (2007) Removal of lead from aqueous solution using Syzygium cumini L.: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.027
Kumar A et al (2018) Development of g-C3N4/TiO2/Fe3O4@SiO2 heterojunction via sol-gel route: a magnetically recyclable direct contact Z-scheme nanophotocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic removal of ibuprofen from real sewage effluent under visible light. Chem Eng J 353:645–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.153
Li YH et al (2002) Lead adsorption on carbon nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 357(May):263–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(02)00502-X
Liu P, Zhang L (2007) Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions or suspensions with clay nano-adsorbents. Sep Purif Technol 58(1):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.07.007
Malakootian M et al (2017) Phenol removal from aqueous solution by adsorption process: study of the nanoparticles performance prepared from aloe vera and mesquite (Prosopis) leaves. Sci Iran 24(6):3041–3053. https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2017.4524
Manikandar RVM et al (2009) Analgesic and anti-pyretic activity of stem bark of Prosopis cineraria (Linn) Druce. J Pharm Res 2(4):60–62
Mondal MK (2009) Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution using activated tea waste: adsorption on a fixed-bed column. J Environ Manag 90(11):3266–3271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.05.025
Moradi S, Isari AA, Bachari Z, Mahmoodi H (2019) Combination of a new natural surfactant and smart water injection for enhanced oil recovery in carbonate rock: Synergic impacts of active ions and natural surfactant concentration. J Pet Sci Eng 176:1–10
Nadeem M et al (2006) Sorption of lead from aqueous solution by chemically modified carbon adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 138(3):604–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.098
Naiya TK et al (2009) The sorption of lead(II) ions on rice husk ash. J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):1254–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.119
Oh SY, Imagawa H, Itahara H (2014) Si-based nanocomposites derived from layered CaSi2: influence of synthesis conditions on the composition and anode performance in Li ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 2(31):12501–12506. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta01318b
Okoye AI, Ejikeme PM, Onukwuli OD (2010) Lead removal from wastewater using fluted pumpkin seed shell activated carbon: adsorption modeling and kinetics. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(4):793–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326188
Onundi YB et al (2010) Adsorption of copper, nickel and lead ions from synthetic semiconductor industrial wastewater by palm shell activated carbon. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7(4):751–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326184
Ozdes D et al (2009) Removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solution by a waste mud from copper mine industry: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):1480–1487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.073
Payan A, Isari AA, Gholizade N (2019) Catalytic decomposition of sulfamethazine antibiotic and pharmaceutical wastewater using Cu-TiO2@ functionalized SWCNT ternary porous nanocomposite: influential factors, mechanism, and pathway studies. Chem Eng J 361:1121–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.118
Ponce-Lira B et al (2017) Lead removal from aqueous solution by basaltic scoria: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(6):1181–1196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1234-6
Pouretedal HR, Sadegh N (2014) Effective removal of amoxicillin, cephalexin, tetracycline and penicillin G from aqueous solutions using activated carbon nanoparticles prepared from vine wood. J Water Process Eng 1:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.03.006
Pourjaafar M (2017) M. Pourjaafar supervisors: B. Anvaripour, M. Motavassel. Petroleum University of Technology
Qaiser S, Saleemi AR, Umar M (2009) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solution by Ficus religiosa leaves: batch and column study. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):998–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.003
Rahmani A, Mousavi HZ, Fazli M (2010) Effect of nanostructure alumina on adsorption of heavy metals. Desalination 253(1–3):94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.11.027
Ramasamy V, Anand P, Suresh G (2017) Biomimetic synthesis and characterization of polymer template Mn @ CaCO3 nanomaterials using natural carbonate sources. Int J Mater Sci 10(7):563–569
Tang S et al (2008) Effect of nano-SiO2 on the performance of starch/polyvinyl alcohol blend films. Carbohydr Polym 72(3):521–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.09.019
Wang J, Chen C (2006) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a review. Biotechnol Adv 24(5):427–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.03.001
Wang SG et al (2007) Removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto manganese oxide-coated carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 58(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.07.006
Zamani AA et al (2013) Adsorption of lead, zinc and cadmium ions from contaminated water onto Peganum harmala seeds as biosorbent. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0107-x
Acknowledgements
This article was supported by the Petroleum University of Technology, Abadan, Iran (Project No.: 2146-3242).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahmaleki, A.A., Motevassel, M., Isari, A.A. et al. An effective approach for the adsorptive removal of lead from an aqueous medium using nano Prosopis Cineraria leaf ash (NPCLA): characterization, operational effects, and recyclability. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 6, 139–149 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00666-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00666-z