Abstract
Aim
To determinate the prognostic significance of low serum C3 at the time of diagnosis of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV).
Methods
Our cohort included 75 consecutive patients with AAV diagnosed from January 2005 to December 2015. C3 levels were measured at the time of diagnosis. Patients were divided into two groups, those with low serum C3 levels (< 0.9 g/l) and those with normal serum C3 levels (0.9–1.8 g/l). We analysed association between serum C3 levels and both combined and singularly patient and renal survival (ESRD). Small number of relapsed patients did not allow for the statistical analysis to be performed as to weather the low serum C3 is associated with relapse rate in AAV patients.
Results
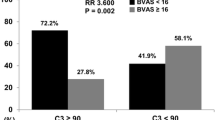
Low serum C3 levels were significantly associated with worse combined end-point patient and renal survival (HR 3.079; 95% CI 1.231–7.701; p = 0.016), and on multivariate adjusted analysis association remained significant (HR 2.831; 95% CI 1.093–7.338; p = 0.032). For both end-points individually low serum C3 levels were significantly associated with poorer patient survival (HR 6.378; 95% CI 2.252–18.065; p < 0.001; on multivariate adjusted analysis HR 4.315 95% CI 1.350–13.799; p = 0.014) and renal survival (HR 3.207; 95% CI 1.040–9.830; p = 0.043; on multivariate adjusted analysis HR 3.679; 95% CI 1.144–11.827; p = 0.029). In our study there was no significant association between serological and patohistological phenotypes and serum C3 levels.
Conclusion
Lower serum C3 levels at the diagnosis is associated with poorer patient and renal outcomes in AAV patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F et al (2013) 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65(1):1–1
Binda V, Moroni G, Messa P (2017) ANCA-associated vasculitis with renal involvement. J Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-017-0412-z
Mukhtyar C, Flossmann O, Hellmich B, Bacon P, Cid M, Cohen-Tervaert JW et al (2008) Outcomes from studies of antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody associated vasculitis: a systematic review by the European League Against Rheumatism systemic vasculitis task force. Ann Rheum Dis 67(7):1004–1010
Hauer HA, Bajema IM, Van Houwelingen HC, Ferrario F, Noël LH, Waldherr R et al (2002) Determinants of outcome in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis: a prospective clinico-histopathological analysis of 96 patients. Kidney Int 62(5):1732–1742
Neumann I, Kain R, Regele H, Soleiman A, Kandutsch S, Meisl FT (2005) Histological and clinical predictors of early and late renal outcome in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 20:96–104
Hilhorst M, Wilde B, Van Breda VP, Van Paassen P, Tervaert JWC (2013) Estimating renal survival using the ANCA-associated GN classification. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1371–1375
Diaz-Crespo F, Villacorta J, Acevedo M, Cavero T, Guerrero C, Díaz EG et al (2016) The predictive value of kidney biopsy in renal vasculitis: a multicenter cohort study. Hum Pathol 52:119–127
Córdova-Sánchez BM, Mejía-Vilet JM, Morales-Buenrostro LE, Loyola-Rodríguez G, Uribe-Uribe NO, Correa-Rotter R (2016) Clinical presentation and outcome prediction of clinical, serological, and histopathological classification schemes in ANCA-associated vasculitis with renal involvement. Clin Rheumatol 35:1805–1816
Flossmann O, Berden A, de Groot K, Hagen C, Harper L, Heijl C et al (2011) Long-term patient survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 70(3):488–494
De Joode AAE, Sanders JAF, Stegeman CA (2013) Renal survival in proteinase 3 and myeloperoxidase ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8(10):1709–1717
Hilhorst M, van Paassen P, van Rie H, Bijnens N, Heerings-Rewinkel P, van Breda Vriesman P et al (2017) Complement in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 32(8):1302–1313
Gou SJ, Yuan J, Chen M, Yu F, Zhao MH (2013) Circulating complement activation in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Kidney Int 83(1):129–137
Augusto JF, Langs V, Demiselle J, Lavigne C, Brilland B, Duveau A, Poli C, Chevailler A, Crou A, Tollis F, Sayegh J, Subra JF. Low serum complement C3 levels at diagnosis of renal ANCA-associated vasculitis is associated with poor prognosis. PloS One 11(7): e0158871
Manenti L, Vaglio A, Gnappi E, Maggiore U, Allegri L, Allinovi M et al (2015) Association of serum C3 concentration and histologic signs of thrombotic microangiopathy with outcomes among patients with ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10(12):2143–2151
Berden AE, Ferrario F, Hagen EC, Jayne DR, Jennette JC, Joh K et al (2010) Histopathologic classification of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(10):1628–1636
Huugen D, van Esch A, Xiao H, Peutz-Kootstra CJ, Buurman WA, Tervaert JW et al (2007) Inhibition of complement factor C5 protects against anti-myeloperoxidase antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis in mice. Kidney Int 71(7):646–654
Xiao H, Schreiber A, Heeringa P, Falk RJ, Jennette JC (2007) Alternative complement pathway in the pathogenesis of disease mediated by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies. Am J Pathol 170(1):52–64
Gou SJ, Yuan J, Wang C, Zhao MH, Chen M (2013) Alternative complement pathway activation products in urine and kidneys of patients with ANCA-associated GN. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8(11):1884–1891
Molad Y, Tovar A, Ofer-Shiber S (2014) Association of low serum complement C3 with reduced patient and renal survival in antimyeloperoxidase-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Nephron Clin Pract 126(1):67–74
Magen E, Mishal J, Paskin J, Glick Z, Yosefy C, Kidon M, Schlesinger M (2008) Resistant arterial hypertension is associated with higher blood levels of complement C3 and C-reactive protein. J Clin Hypertens 10(9):677–683
Barbour T, Johnson S, Cohney S, Hughes P (2012) Thrombotic microangiopathy and associated renal disorders. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27(7):2673–2685
Sethi S, Fervenza FC, Zhang Y, Zand L, Vrana JA, Nasr SH, Theis JD, Dogan A, Smith RJ (2012) C3 glomerulonephritis: clinicopathological findings, complement abnormalities, glomerular proteomic profile, treatment, and follow-up. Kidney Int 82(4):465–473
Alexander MP, Fervenza FC, De Vriese AS, Smith RJH, Nasr SH, Cornell LD, Herrera Hernandez LP, Zhang Y, Sethi S (2016) C3 glomerulonephritis and autoimmune disease: more than a fortuitous association? J Nephrol 29(2):203–209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Since this is a retrospective study formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
All of the authors: Matija Crnogorac, Ivica Horvatic, Patricia Kacinari, Danica Galesic Ljubanovic and Kresimir Galesic declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crnogorac, M., Horvatic, I., Kacinari, P. et al. Serum C3 complement levels in ANCA associated vasculitis at diagnosis is a predictor of patient and renal outcome. J Nephrol 31, 257–262 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-017-0445-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-017-0445-3