Abstract
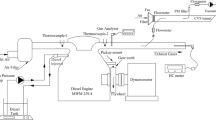
This work investigates a diesel engine operating with diesel oil containing 7% biodiesel (B7) and hydrous ethanol with concentrations varying from 5 to 30%. The experiments were conducted in a 49-kW diesel power generator, equipped with an electronic ethanol injection unit installed in the intake manifold and without any modifications in the diesel oil injection system. The results showed a decrease of in-cylinder pressure and net heat release rate with the use of ethanol at low loads and an increase at high loads, in comparison with B7. Increasing ethanol injection caused increased ignition delay and decreased combustion duration. Fuel conversion efficiency was raised up to 13% with the use of ethanol. The use of 30% ethanol in the fuel caused a reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions up to 12% and nitric oxide up to 53%. Carbon monoxide, total hydrocarbons and oxides of nitrogen (NO X ) emissions increased with ethanol addition. The replacement of 20% of diesel fuel by ethanol showed the lowest penalties on NO X emissions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu L, Cheung CS, Zhang WG, Huang Z (2010) Emissions characteristics of a diesel engine operating on biodiesel and biodiesel blended with ethanol and methanol. Sci Total Environ 408:914–921. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.078
Brito RF, Martins CA (2014) Experimental analysis of a diesel engine operating in diesel–ethanol dual-fuel mode. Fuel 134:140–150. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2014.05.010
Surawski NC, Ristovski ZD, Brown RJ, Situ R (2012) Gaseous and particle emissions from an ethanol fumigated compression ignition engine. Energy Convers Manag 54:145–151. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2011.10.011
Franco ALC, Cherubin MR, Cerri CC, Pavinato PS, Cerri CEP, Six J, Davies CA (2015) Soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus changes under sugarcane expansion in Brazil. Sci Total Environ 515–516:30–38. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.025
Boretti A (2012) Advantages of converting diesel engines to run as dual fuel ethanol–diesel. Appl Therm Eng 47:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.04.037
Zhang ZH, Cheung CS, Yao CD (2013) Influence of fumigation methanol on the combustion and particulate emissions of a diesel engine. Fuel 111:442–448. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.05.014
Kwanchareon P, Luengnaruemitchai A, Jai-In S (2007) Solubility of a diesel-biodiesel-ethanol blend, its fuel properties, and its emission characteristics from diesel engine. Fuel 86:1053–1061. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2006.09.034
Lapuerta M, Armas O, Garcia-Contreras R (2007) Stability of diesel–bioethanol blends for used in diesel engines. Fuel 86:1351–1357. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2006.11.042
Chauhan BS, Kumar N, Pal SS, Jun YD (2011) Experimental studies on fumigation of ethanol in a small capacity diesel engine. Energy 36:1030–1038. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2010.12.005
Sahin Z, Durgun O (2007) Theoretical investigation of effects of light fuel fumigation on diesel engine performance and emissions. Energy Convers Manag 48:1952–1964. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2007.01.027
Bodisco T, Brown RJ (2013) Inter-cycle variability of in-cylinder pressure parameters in an ethanol fumigated common rail diesel engine. Energy 52:55–65. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.12.032
He BQ, Shuai SJ, Wang JX, He H (2003) The effect of ethanol blended diesel fuels on emissions from a diesel engine. Atmos Environ 37:4965–4971. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.08.029
Tsang KS, Zhang ZH, Cheung CS, Chan TL (2010) Reducing emissions of a diesel engine using fumigation ethanol and a diesel oxidation catalyst. Energy Fuel 24:6156–6165. doi:10.1021/ef100899z
Padala S, Woo C, Kook S, Hawkes ER (2013) Ethanol utilization in a diesel engine using dual-fueling technology. Fuel 109:597–607. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.03.049
Zhang ZH, Tsang KS, Cheung CS, Chan TI, Yao CD (2011) Effect of fumigation methanol and ethanol on the gaseous and particulate emissions of a direct-injection diesel engine. Atmos Environ 45:2001–2008. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.12.019
Tutak W (2014) Bioethanol E85 as a fuel for dual fuel diesel engine. Energy Convers Manag 86:39–48. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2014.05.016
Britto Júnior RF, Martins CA (2015) Emissions analysis of a diesel engine operating in diesel–ethanol dual-fuel mode. Fuel 148:191–201. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2015.01.008
De Oliveira A, Santos ECM, Botelho GC, Valente OS, Sodré JR (2013) Hydrogen electronic injection system for a diesel power generator. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.04.118
Morais AM, Justino MAM, Valente OS, Hanriot SM, Sodré JR (2013) Hydrogen impacts on performance and CO2 emissions from a diesel power generator. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:6857–6864. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.119
International Organization for Standardization ISO 3046-1 (2002) Reciprocating internal combustion engines—performance—part 1: declarations of power, fuel and lubricating oil consumptions, and test methods—additional requirements for engines for general use. ISO, Switzerland, p 7
Heywood JB (2003) Internal combustion engine fundamental, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, Singapore
Katrasnik T, Trenc F, Opresnik SR (2006) A new criterion to determine the start of combustion in diesel engines. Trans ASME J Eng Gas Turbine Power 128:928–933. doi:10.1115/1.2179471
Zhu L, Cheung CS, Zhang WG (2011) Combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a DI diesel engine fueled with ethanol–biodiesel blends. Fuel 90:1743–1750. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2011.01.024
Hansdah D, Murugan S (2014) Bioethanol fumigation in a DI diesel engine. Fuel 130:324–333. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2014.04.047
Zhu L, Cheung CS, Zhang WG, Fang JH, Huang Z (2013) Effects of ethanol-biodiesel blends and diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) on particulate and unregulated emissions. Fuel 113:690–696. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2013.06.028
Abu-Qudais M, Haddad O, Qudaisat M (2000) The effect of alcohol fumigation on diesel engine performance and emissions. Energy Convers Manag 41:389–399. doi:10.1016/S0196-8904(99)00099-0
Yao CD, Zhang ZH, Cheung CS, Xu GL (2010) Experimental study on the effect of gaseous and particulate emission from an ethanol fumigated diesel engine. Sci China Technol Sci 53:3294–3301. doi:10.1007/s11431-010-3187-1
Armas O, García-Contreras R, Ramos A (2014) Pollutant emissions from New European driving cycle with ethanol and butanol diesel blends. Fuel Process Technol 122:64–71. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.01.023
Tadano YS, Borillo GC, Godoi AFL, Cichon A, Silva TOB, Yamamoto CI, Godoi RHM (2014) Gaseous emissions from a heavy-duty engine equipped with SCR aftertreatment system and fuelled with diesel and biodiesel: assessment of pollutant dispersion and health risk. Sci Total Environ 500–501:64–71. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.100
Jiang J, Li D (2016) Theoretical analysis and experimental confirmation of exhaust temperature control for diesel vehicle NOx emissions reduction. Appl Energy 174:232–244. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.096
Asad U, Kumar R, Zheng M, Tjong J (2015) Ethanol-fueled low temperature combustion: a pathway to clean and efficient diesel engine cycles. Appl Energy 157:838–850. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.01.057
Palash SM, Masjuki HH, Kalam MA, Masum BM, Sanjid A, Abedin MJ (2013) State of the art of NOx mitigation technologies and their effect on the performance and emission characteristics of biodiesel-fueled compression ignition engines. Energy Convers Manag 76:400–420. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2013.07.059
Divekar PS, Chen X, Tjong J, Zheng M (2016) Energy efficiency impact of EGR on organizing clean combustion in diesel engines. Energy Convers Manag 112:369–381. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.042
Hebbar GS, Bhat AK (2013) Control of NOx from a DI diesel engine with hot EGR and ethanol fumigation: an experimental investigation. Int J Autom Technol 14(3):333–341. doi:10.1007/s12239-013-0037-8
Park SH, Youn IM, Lee CS (2010) Influence of two-stage injection and exhaust gas recirculation on the emissions reduction in an ethanol-blended diesel-fueled four-cylinder diesel engine. Fuel Process Technol 91:1753–1760. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2010.07.016
Guo M, Fu Z, Ma D, Ji N, Song C, Liu Q (2015) A short review of treatment methods of marine diesel engine exhaust gases. Procedia Eng 121:938–943. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2015.09.059
Stein HJ (1996) Diesel oxidation catalysts for commercial vehicle engines: strategies on their application for controlling particulate emissions. Appl Catal B 10(1–3):69–82. doi:10.1016/0926-3373(96)00024-0
Resitoglu IA, Altinisik K (2015) The pollutant emissions from diesel-engine vehicles and exhaust aftertreatment systems. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:15–27. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0793-9
Zervas E (2008) Impact of different configurations of a diesel oxidation catalyst on the CO and HC tail-pipe emissions of a Euro4 passenger car. Appl Therm Eng 28:962–966. doi:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2007.06.033
Zhang ZH, Cheung CS, Chan TL, Yao CD (2010) Experimental investigation on regulated and unregulated emissions of a diesel/methanol compound combustion engine with and without diesel oxidation catalyst. Sci Total Environ 408(4):865–872. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.060
Zhang ZH, Cheung CS, Chan TL, Yao CD (2009) Emission reduction from diesel engine using fumigation methanol and diesel oxidation catalyst. Sci Total Environ 407(15):4497–4505. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.036
Wei L, Yao C, Wang Q, Pan W, Han G (2015) Combustion and emission characteristics of a turbocharged diesel engine using high premixed ratio of methanol and diesel fuel. Fuel 140:156–163. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2014.09.070
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), the National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq) research project number 304114/2013-8, the Foundation of Support Research of the State of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) research projects number TEC PPM 00136-13 and TEC PPM 0385-15, and VALE/FAPEMIG research Project Number TEC RDP 00198-10 for the financial support to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Luis Fernando Figueira da Silva.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, A., de Morais, A.M., Valente, O.S. et al. Combustion, performance and emissions of a diesel power generator with direct injection of B7 and port injection of ethanol. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 1087–1096 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0667-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0667-7