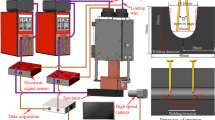
Abstract
Among the factors that influence welding defects, arc interruption is an important and unavoidable problem. When the welding torch swings during narrow gap pulsed gas metal arc welding (P-GMAW), arc interruption phenomenon always occurs at the same position along the torch trajectory and is therefore governed by some concrete conditions. Prior to arc interruption, the arc exhibits a distinct shape and the voltage signals fluctuate significantly. Internal causes of the distinct arc shape were investigated, and it was found that narrowness of the gap played an important role. As the metal vapor is easily ionized, the arc rises along with the rising vapor plume, expanding beyond the end of the wire and forming an approximately parabolic shape. The effect of narrow grooves on the droplets and weld beads, especially when the torch deviates from the groove center, will be beneficial for the generation and collection of metal vapor. Since the arc will always be prolonged prior to interruption and the voltage will fluctuate, the arc interruption of this kind can be predicted and eliminated, thus improving the welding quality of narrow gap.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek D, Moon HS, Park SH (2017) Development of an automatic orbital welding system with robust weaving width control and a seam-tracking function for narrow grooves. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):767–777
Lan H, Zhang HJ, Zhao DL, Chen AJ, Lin SY (2015) Effects of arc-sidewall distance on arc appearance in narrow gap MAG welding. In: Tarn TJ, Chen SB, Chen XQ (eds) Robotic welding, intelligence and automation. RWIA 2014: advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 363, pp 35–45
Li W, Gao K, Wu J (2014) SVM-based information fusion for weld deviation extraction and weld groove state identification in rotating arc narrow gap MAG welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74(9–12):1355–1364
Liu WJ, Li LY, Yue JF, Yan PJ, Liu XH (2017) Research on the “jump sidewall” behavior and its signal characteristics in narrow gap p-mag welding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(1–4):1189–1196
Shelyagin V, Khaskin V, Bernatskyi A, Siora A, Sydorets VN, Chinakhov DA (2018) Multi-pass laser and hybrid laser-arc narrow-gap welding of steel butt joints. Mater Sci Forum 927:64–71
Wang J, Sun Q, Zhang T, Zhang S, Liu Y, Feng J (2018) Arc characteristics in alternating magnetic field assisted narrow gap pulsed GTAW. J Mater Process Technol 254:254–264
Zhang G, Shi Y, Zhu M, Fan D (2017) Arc characteristics and metal transfer behavior in narrow gap gas metal arc welding process. J Mater Process Technol 245:15–23
Funding
The Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1733125), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (CN) (No. 18JCYBJC19100), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (CN) (No. 17JCZDJC38700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51705361), and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. 2017KJ080) provided the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Study Group 212 - The Physics of Welding
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Jia, Z., Yue, J. et al. Arc interruption phenomena and internal causes in narrow gap P-GMAW. Weld World 64, 1779–1787 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00957-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-020-00957-5