Abstract
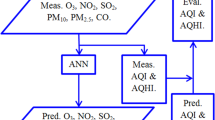
This study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between air pollutants (including nitrogen oxides [NO, NO2, NOX], sulfur dioxide [SO2], carbon monoxide [CO], ozone [O3], and particulate matter of median aerometric diameter <10 μm [PM10]) and hospital admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. The study had a case–crossover design which was conducted in Tabriz, Iran. Daily hospital admissions and air quality data from March 2009 to March 2011 were analyzed using the artificial neural networks (ANNs) and conditional logistic regression modeling. The results showed significant associations between gaseous air pollutants including NO2, O3, and NO and hospital admissions for cardiovascular disease. Gaseous air pollutants of NO2, NO, and CO were associated with hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, while PM10 was associated with hospitalizations due to respiratory infections. PM10 and O3 were also associated with asthmatic hospital admissions. There was no significant association between SO2 and studied health outcomes. Comparing the results of logistic regressions and ANNs confirmed the optimality of the ANNs for detection of the best predictors of hospital admissions caused by air pollution. Further research is required to investigate the effects of seasonal variations on air pollution-related health outcomes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asghari Jafarabadi M, Mohammadi S (2013) Statistical series: summarizing and displaying data. J Diabetes Lipid Disord 12:83–100
Bateson TF, Schwartz J (2004) Who is sensitive to the effects of particulate air pollution on mortality?: a case–crossover analysis of effect modifiers. Epidemiology 15:143–149
Bishop CM (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press, UK
Cai J, Zhao A, Zhao J, Chen R, Wang W, Ha S, Xu X, Kan H (2014) Acute effects of air pollution on asthma hospitalization in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 191:139–144
Cao J, Li W, Tan J, Song W, Xu X, Jiang C, Chen G, Chen R, Ma W, Chen B, Kan H (2009) Association of ambient air pollution with hospital outpatient and emergency room visits in Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 407:5531–5536
Chan C-C, Ng H-C (2011) A case–crossover analysis of Asian dust storms and mortality in the downwind areas using 14-year data in Taipei. Sci Total Environ 410–411:47–52
Chang C-C, Tsai S-S, Ho S-C, Yang C-Y (2005) Air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular disease in Taipei. Taiwan. Environ Res 98:114–119
Chen R, Chu C, Tan J, Cao J, Song W, Xu X, Jiang C, Ma W, Yang C, Chen B, Gui Y, Kan H (2010) Ambient air pollution and hospital admission in Shanghai, China. J Hazard Mater 181:234–240
Delong ER, Delong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44(3): 837–845
di Ciaula A (2012) Emergency visits and hospital admissions in aged people living close to a gas-fired power plant. Eur J Intern Med 23:e53–e58
Dreiseitl S, Ohno-Machado L (2002) Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: a methodology review. J Biomed Inform 35:352–359
Franck U, Leitte AM, Suppan P (2014) Multiple exposures to airborne pollutants and hospital admissions due to diseases of the circulatory system in Santiago de Chile. Sci Total Environ 468:746–756
Ge W, Chen R, Song W, Kan H (2011) Daily visibility and hospital admission in Shanghai, China. Biomed Environ Sci 24:117–121
Gleason JA, Bielory L, Fagliano JA (2014) Associations between ozone, PM2.5, and four pollen types on emergency department pediatric asthma events during the warm season in New Jersey: a case–crossover study. Environ Res 132:421–429
Guo Y, Jia Y, Pan X, Liu L, Wichmann HE (2009) The association between fine particulate air pollution and hospital emergency room visits for cardiovascular diseases in Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 407:4826–4830
Gurjar BR, Jain A, Sharma A, Agarwal A, Gupta P, Nagpure AS, Lelieveld J (2010) Human health risks in megacities due to air pollution. Atmos Environ 44:4606–4613
Hansen A, Bi P, Nitschke M, Pisaniello D, Ryan P, Sullivan T, Barnett AG (2012) Particulate air pollution and cardiorespiratory hospital admissions in a temperate Australian city: a case–crossover analysis. Sci Total Environ 416:48–52
Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S (2004) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York
Hosseinpoor AR, Forouzanfar MH, Yunesian M, Asghari F, Naieni KH, Farhood D (2005) Air pollution and hospitalization due to angina pectoris in Tehran, Iran: a time-series study. Environ Res 99:126–131
Kalantzi EG, Makris D, Duquenne MN, Kaklamani S, Stapountzis H, Gourgoulianis KI (2011) Air pollutants and morbidity of cardiopulmonary diseases in a semi-urban Greek peninsula. Atmos Environ 45:7121–7126
Kan H, Chen B (2003) A case–crossover analysis of air pollution and daily mortality in shanghai. J Occup Health 45:119–124
Khamutian R, Sharafi K, Najafi F, Shahhoseini M (2014) Association of air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular disease: a case study in Kermanshah, Iran. Zahedan J Res Med Sci 16:43–46
Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Neter J, Li W (2005) Applied linear statistical models, 4th edn. Irwin, Chicago
Kwon H-J, Cho S-H, Nyberg F, Pershagen G (2001) Effects of ambient air pollution on daily mortality in a cohort of patients with congestive heart failure. Epidemiology 12:413–419
Lee IM, Tsai S-S, Ho C-K, Chiu H-F, Wu T-N, Yang C-Y (2008) Air pollution and hospital admissions for congestive heart failure: are there potentially sensitive groups? Environ Res 108:348–353
Li S, Batterman S, Wasilevich E, Wahl R, Wirth J, Su F-C, Mukherjee B (2011) Association of daily asthma emergency department visits and hospital admissions with ambient air pollutants among the pediatric Medicaid population in Detroit: time-series and time-stratified case–crossover analyses with threshold effects. Environ Res 111:1137–1147
Lin S, Bell EM, Liu W, Walker RJ, Kim NK, Hwang S-A (2008) Ambient ozone concentration and hospital admissions due to childhood respiratory diseases in New York state, 1991–2001. Environ Res 108:42–47
Lin H, An Q, Luo C, Pun VC, Chan CS, Tian L (2013) Gaseous air pollution and acute myocardial infarction mortality in Hong Kong: a time-stratified case–crossover study. Atmos Environ 76:68–73
Liu HY, Bartonova A, Schindler M, Sharma M, Behera SN, Katiyar K, Dikshit O (2013) Respiratory disease in relation to outdoor air pollution in Kanpur, India. Arch Environ Occup Health 68:204–217
Qiu H, Yu ITS, Wang X, Tian L, Tse LA, Wong TW (2013) Season and humidity dependence of the effects of air pollution on COPD hospitalizations in Hong Kong. Atmos Environ 76:74–80
Qorbani M, Yunesian M, Fotouhi A, Zeraati H, Sadeghian S, Rashidi Y (2007) Relation between air pollution exposure and onset of acute coronary syndrome in Tehran heart center using a case–crossover design. Iran J Epidemiol 3:53–59
Qorbani M, Yunesian M, Fotouhi A, Zeraati H, Sadeghian S (2012) Effect of air pollution on onset of acute coronary syndrome in susceptible subgroups. East Mediterr Health J 18:550–555
Rodopoulou S, Chalbot M-C, Samoli E, Dubois DW, San Filippo BD, Kavouras IG (2014) Air pollution and hospital emergency room and admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in Doña Ana County, New Mexico. Environ Res 129:39–46
Rumelhart DE, McClelland JL, PDP Research Group (1988) Parallel distributed processing. Vol 1, IEEE
Rushworth A, Lee D, Mitchell R (2014) A spatio-temporal model for estimating the long-term effects of air pollution on respiratory hospital admissions in Greater London. Spat Spatio Temp Epidemiol 10:29–38
Tao Y, Mi S, Zhou S, Wang S, Xie X (2014) Air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou, China. Environ Pollut 185:196–201
Tobías A, Pérez L, Díaz J, Linares C, Pey J, Alastruey A, Querol X (2011) Short-term effects of particulate matter on total mortality during Saharan dust outbreaks: a case–crossover analysis in Madrid (Spain). Sci Total Environ 412–413:386–389
Villeneuve PJ, Johnson JYM, Pasichnyk D, Lowes J, Kirkland S, Rowe BH (2012) Short-term effects of ambient air pollution on stroke: who is most vulnerable? Sci Total Environ 430:193–201
Wendt JK, Symanski E, Stock TH, Chan W, Du XL (2014) Association of short-term increases in ambient air pollution and timing of initial asthma diagnosis among medicaid-enrolled children in a metropolitan area. Environ Res 131:50–58
Wilson AM, Salloway JC, Wake CP, Kelly T (2004) Air pollution and the demand for hospital services: a review. Environ Int 30:1109–1118
Wong MCS, Tam WWS, Wang HHX, Lao XQ, Zhang DD, Chan SWM, Kwan MWM, Fan CKM, Cheung CSK, Tong ELH, Cheung NT, Tse LA, Yu ITS (2014) Exposure to air pollutants and mortality in hypertensive patients according to demography: a 10 year case–crossover study. Environ Pollut 192:179–185
Yang C-Y, Chang C-C, Chuang H-Y, Tsai S-S, Wu T-N, Ho C-K (2004) Relationship between air pollution and daily mortality in a subtropical city: Taipei, Taiwan. Environ Int 30:519–523
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the help and support provided by the East Azerbaijan Environmental Office and the East Azerbaijan Bureau of Meteorology for supplying air data and also the hospitals including Ali Nasab, Amir Almomenin, Imam Reza, Madani, and Tabriz Children’s Hospital for supplying health data. There was no funding for this study. The authors also confirm that there is no competing interest for this research. The local ethical review committee of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences approved the study (Ethical No. 8509).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakerkhatibi, M., Dianat, I., Asghari Jafarabadi, M. et al. Air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiorespiratory diseases in Iran: artificial neural network versus conditional logistic regression. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3433–3442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0884-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0884-0