Abstract
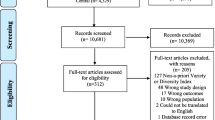
This systematic review examines the relationship between diet quality and weight gain in adults over time and is an update of our previous review of the same topic. The goal was to synthesise the best available current evidence on diet quality and weight change within longitudinal analyses. The inclusion criteria were case-control or cohort studies, and adults aged ≥18 years. The dependent variable was diet quality indexes and the independent variable was any measurement of body weight. The current systematic review identified 16 studies published between 1970 and 2014. Of these, eight were published since our last review. The findings of these recent studies confirm the results of our previous review, that higher diet quality is associated with relatively lower prospective weight gain, as well as a lower risk of becoming overweight or obese, compared with poor diet quality. Across the 16 studies, it appears that the diet quality indexes based on foods alone, or food and nutrient components, are more predictive of weight change. However, further research is needed to confirm this. Additionally, high-quality analyses that assess change in diet quality over time are needed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
McCarron D, Reusser M. The power of food to improve multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2000;2:482–6.
Hu FB. Dietary pattern analysis: a new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002;13:3–9.
Wirt A, Collins CE. Diet quality–what is it and does it matter? Public Health Nutr. 2009;12:2473–92.
Slattery ML. Analysis of dietary patterns in epidemiological research This paper is one of a selection of papers published in the CSCN–CSNS 2009 Conference, entitled Are dietary patterns the best way to make nutrition recommendations for chronic disease prevention? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2010;35:207–10.
Waijers PMCM, Feskens EJM, Ocké MC. A critical review of predefined diet quality scores. Br J Nutr. 2007;97:219–31.
Appel LJ. Lifestyle modification as a means to prevent and treat high blood pressure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:S99–S102.
World Health Organization. Nutrition,Controlling the global obesity epidemic 2013: Available from: http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/obesity/en/. This article provides global information and statistics regarding public health issues including obesity.
Togo P, Osler M, Sørensen TI, Heitmann BL. Food intake patterns and body mass index in observational studies. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord J Int Assoc Study Obes. 2001;25:1741–51.
Aljadani H, Patterson A, Sibbritt D, Collins CE. The association between dietary patterns and weight change in adults over time: a systematic review of studies with follow up. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Rep. 2013;11.
Aljadani HM, Patterson A, Sibbritt D, Collins CE. The association between diet quality and weight change in adults over time: a systematic review in perspective studies. In: Preedy LLaVP VR, editor. Diet quality- an evidence approach. New York: Springer; 2013. p. 3–27.
Aljadani HM, Sibbritt D, Patterson A, Collins CE. The Australian Recommended Food Score did not predict weight gain in mid-age Australian women during six year of follow-up. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2013;37:322–8.
Aljadani HM, Patterson A, Sibbritt D, Hutchesson MJ, Jensen ME, Collins CE. Diet quality, measured by fruit and vegetable intake, predicts weight change in young women. J Obes. 2013;2013:10. This reference analysed a subgroup of disease-free women with plausible energy intake and found a relationship with the frequency and variety of fruit and vegetable intake (FAVI).
Arabshahi S, van der Pols JC, Williams GM, Marks GC, Lahmann PH. Diet quality and change in anthropometric measures: 15-year longitudinal study in Australian adults. Br J Nutr. 2012;107:1376–85.
Asghari G, Mirmiran P, Rashidkhani B, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Mehran M, Azizi F. The association between diet quality indices and obesity: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Arch Iran Med. 2012;15:599–605.
Beunza J-J, Toledo E, Hu FB, Bes-Rastrollo M, Serrano-Martínez M, Sánchez-Villegas A, et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet, long-term weight change, and incident overweight or obesity: the Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra (SUN) cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010.
Boggs DA, Rosenberg L, Rodríguez-Bernal CL, Palmer JR. Long-term diet quality is associated with lower obesity risk in young African American Women with normal BMI at baseline. J Nutr. 2013;143:1636–41. Little is known about maintaining high diet quality during follow-up period and its effect on weight change over time. This reference explored the association between maintaining higher diet quality and weight changes over time.
Forget G, Doyon M, Lacerte G, Labonté M, Brown C, Carpentier AC, et al. Adoption of American Heart Association 2020 ideal healthy diet recommendations prevents weight gain in young adults. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2013;113:1517–22.
Kimokoti RW, Newby PK, Gona P, Zhu L, Jasuja GK, Pencina MJ, et al. Diet quality, physical activity, smoking status, and weight fluctuation are associated with weight change in women and men. J Nutr. 2010;140:1287–93.
Lassale C, Fezeu L, Andreeva VA, Hercberg S, Kengne AP, Czernichow S, et al. Association between dietary scores and 13-year weight change and obesity risk in a French prospective cohort. Int J Obes. 2012. This study examined the association between various diet quality indexes, not just the MDP scores but also other indexes such as DGI and DQI-I with weight changes and the incidence of obesity among men and women. In addition, dietary intake data was derived from 24-h records.
Mendez MA, Popkin BM, Jakszyn P, Berenguer A, Tormo MJ, Sanchez MJ, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is associated with reduced 3-year incidence of obesity. J Nutr. 2006;136:2934–8.
Quatromoni PA, Pencina M, Cobain MR, Jacques PF, D'Agostino RB. Dietary quality predicts adult weight gain: findings from the Framingham Offspring Study. Obesity. 2006;14:1383–91.
Romaguera D, Norat T, Vergnaud A, Mouw T, May AM, Agudo A, et al. Mediterranean dietary patterns and prospective weight change in participants of the EPIC-PANACEA project. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:912–21.
Sanchez-Villegas A, Bes-Rastrollo M, Martinez-Gonzalez M, Serra-Majem L. Adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern and weight gain in a follow-up study: the SUN cohort. Int J Obes. 2006;30:350–8.
Wolongevicz DM, Zhu L, Pencina MJ, Kimokoti RW, Newby PK, D'Agostino RB, et al. Diet quality and obesity in women: the Framingham Nutrition Studies. Br J Nutr. 2010;103:1223–9.
Yannakoulia M, Panagiotakos D, Pitsavos C, Lentzas Y, Chrysohoou C, Skoumas I, et al. Five-year incidence of obesity and its determinants: the ATTICA Study. Public Health Nutr. 2009;12:36–43.
Zamora D, Gordon-Larsen P, Jacobs DR, Popkin BM. Diet quality and weight gain among black and white young adults: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study (1985–2005). Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:784–93. This article looked at the impact of race on diet quality and the risk of weight gain over a long period of follow-up.
Guenther PM, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM. Development of the healthy eating index-2005. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108:1896–901.
Trichopoulou A, Costacou T, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2599–608.
Kim S, Haines PS, Siega-Riz AM, Popkin BM. The Diet Quality Index-International (DQI-I) provides an effective tool for cross-national comparison of diet quality as illustrated by China and the United States. J Nutr. 2003;133:3476–84.
Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Stefanadis C. Dietary patterns: a Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and biological markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16:559–68.
Lorefat B, Ganowiak W, Wissing U, Granerus AK, Unosson M. Food habits and intake of nutrients in elderly patients with Parkinson's disease. Gerontology. 2006;52:160–8.
Acknowledgements
Haya Aljadani received funding from the King Abdul-Aziz University and Ministry of Higher Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, to allow her to study at the University of Newcastle.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Haya Aljadani, Amanda Patterson, David Sibbritt, and Clare E. Collins declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Dietary Patterns and Behavior
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aljadani, H., Patterson, A., Sibbritt, D. et al. Diet Quality and Weight Change in Adults Over Time: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Curr Nutr Rep 4, 88–101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-014-0115-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-014-0115-1