Abstract
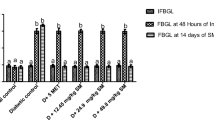
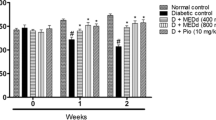
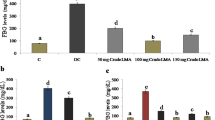
Chronic hyperglycemic condition leads to development of diabetic nephropathy (DN). Basella alba is an important edible vegetable in India. Present study was conducted to inquire the effects of methanol extract from Basella alba leaf (MEBA) against diabetic nephropathy in rats. A single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (55 mg/kg) was given to Wistar albino rats to induce diabetes. After 4 weeks of diabetes induction, the rats were divided into normal control group, disease DN group, MEBA treatment groups (200 and 400 mg/kg), metformin treatment group (150 mg/kg) and the treatment was continued for next 3 weeks. In MEBA treated groups there were marked improvements in blood glucose, ALP, ALT, total protein, serum lipid profile such as total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL levels and renal functions such as urine volume, urinary protein excretion, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine clearance as compared to non-treated DN group. There was significant rise in malonaldehyde level, and decline in acivites of superoxide dismutase and reduced Glutathione (GSH) of kidney in diabetic rats as compared to normal control group rats. The MEBA treated groups showed dose dependent restoration of altered oxidative stress parameters. Moreover, from renal histopathology it was evident that the abnormal thickening of Glomerular basement membrane in kidney of diabetic rats were improved in MEBA treated rats. From the present study it can be concluded that, Basella alba leaf has marked protective effect against diabetic nephropathy and proteinuria in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboonabi A, Rahmat A, Fauziah O (2014) Effect of pomegranate on histopathology of liver and kidney on generated oxidative stress diabetic induced rats. J Cytol Histol 6:294
Adhikari R, Kumar HNN, Shruthi SD (2012) A review on medicinal importance of Basella alba L. Int J Pharm Sci Drug Res 4:110–114
Afshari AT, Shirpoor A, Farshid A, Saadatian R, Rasmi Y, Saboory E, Ilkhanizadeh B, Allameh A (2007) The effect of ginger on diabetic nephropathy, plasma antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Food Chem 101:148–153
Anonymous (2008) Guidelines for the testing of chemicals/Section 4: health effects test No. 425: acute oral toxicity: up-and-down procedure, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development Publishing, Paris
Anusuya N, Gomathi R, Manian S, Sivaram V, Menon A (2012) Evaluation of Basella rubra L., Rumex nepalensis Spreng. and Commelina benghalensis L. for antioxidant activity. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:714–720
Arokoyo DS, Oyeyipo IP, Plessis SSD, Aboua YG (2018) Antioxidant activities of Basella alba aqueous leave extract in blood, pancreas, and gonadal tissues of diabetic male Wistar rats. Pharmacogn Res 10:31–36
Bamidele O, Arokoyo DS, Akinnuga AM, Oluwarole AO (2014) Antidiabetic effect of aqueous extract of Basella alba leaves and metformin in alloxan-induced diabetic albino rats. Afr J Biotechnol 13:2455–2458
Bhattacharya S (2011) Natural antimutagens: a review. Res J Med Plants 5:116–126
Bhattacharya S (2017) Medicinal plants and natural products in amelioration of arsenic toxicity: a short review. Pharm Biol 55:349–354
Bhattacharya S (2018a) The role of medicinal plants and natural products in melioration of cadmium toxicity. Orient Pharm Exp Med 18:177–186
Bhattacharya S (2018b) Medicinal plants and natural products can play a significant role in mitigation of mercury toxicity. Interdiscip Toxicol 11:247–254
Bhattacharya S (2019) Probiotics against alleviation of lead toxicity: recent advances. Interdiscip Toxicol 12:89–92
Biswas M, Kar B, Bhattacharya S, Kumar RBS, Ghosh AK, Haldar PK (2011) Antihyperglycemic activity and antioxidant role of Terminalia arjuna leaf in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 49:335–340
Chakraborty M, Bala A, Bhattacharya S, Haldar PK (2018) Hypoglycemic effect of ethyl acetate fraction of methanol extract from Campylandra aurantiaca rhizome on high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacogn Mag 14:539–545
Creutzfeldt W (1999) Effects of the α-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose on the development of long-term complications in diabetic animals: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:289–296
Dabla PK (2010) Renal function in diabetic nephropathy. World J Diabetes 1:48–56
Das S, Bhattacharya S, Prasanna A, Kumar RBS, Pramanik G, Haldar PK (2011) Preclinical evaluation of antihyperglycemic activity of Clerodendron infortunatum leaf against streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Ther 2:92–100
Dronavalli S, Duka I, Bakris GL (2008) The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4:444–452
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Gross JJL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T (2005) Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Diabetes Care 28:164–176
Harborne JB (1998) Phytochemical methods, a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. Chapman & Hall, London
Hovind P, Rossing P, Tarnow L, Smidt UM, Parving HH (2001) Progression of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 59:702–709
Kakkar P, Das B, Vishwanathan PN (1984) A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21:130–132
Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner EI, Chen S, Chugh S, Danesh FR (2008) Diabetic nephropathy: mechanism of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med 233:4–11
Krishna CB (2012) Anti Inflammatory activity of Basella alba Linn. in albino rats. J Appl Pharm Sci 2:87–89
Kumar A, Lingadurai S, Shrivastava TP, Bhattacharya S, Haldar PK (2011) Hypoglycemic activity of Erythrina variegata leaf in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 49:577–582
Nathan DM (1993) Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 328:1676–1685
Nirmala A, Saroja S, Devi GG (2011) Antidiabetic activity of Basella rubra and its relationship with the antioxidant property. British Biotechnol J 1:1–9
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oyewole OA, Al-Khalil S, Kalejaiye OA (2012) The antimicrobial activities of ethanolic extracts of Basella alba on selected micro organisms. Int Res J Pharm 3:71–73
Pandey MM, Rastogi S, Rawat AKS (2013) Indian traditional Ayurvedic system of medicine and nutritional supplementation. Evid Complement Alternat Med 2013:376327
Patra S, Bhattacharya S, Bala A, Haldar PK (2020) Antidiabetic effect of Drymaria cordata leaf against streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 11:44–52
Raptis AE, Viberti G (2001) Pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109:S424–S437
Reshmi SK, Aravindhan KM, Devi PS (2012) Antioxidant analysis of betacyanin extracted from Basella alba fruit. Int J Pharm Tech Res 4:900–913
Rodda R, Kota A, Sindhuri T, Kumar SA, Gnananath K (2012) Investigation on anti-inflammatory property of Basella alba Linn leaf extract. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:452–454
Saleh A (2011) Protective effect of Basella alba L. on nephrotoxicity induced by gentamycin in rats. Clin Exp Med J 5:225–233
Sen K, Goel A, Rawal S, Mahajan N, Baboo S, Alok S (2010) Antimicrobial activity of Basella rubra leaves. Int J Pharm Sci Res 1:88–91
Somani R, Singhai AK, Shivgunde P, Jain D (2012) Asparagus racemosus Willd. (Liliaceae) ameliorates early diabetic nephropathy in STZ induced diabetic rats. Indian J Exp Biol 50:469–475
Sun SZ, Wang Y, Li Q, Tian YJ, Liu MH, Yu YH (2006) Effects of benazepril on renal function and kidney expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in diabetic rats. Chin Med J 119:814–821
Telagari M, Hullatti K (2015) In-vitro α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of Adiantum caudatum Linn. and Celosia argentea Linn. extracts and fractions. Indian J Pharmacol 47:425–429
Tesch GH, Allen TJ (2007) Rodents models of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol 12:261–266
Tiwari BK, Pandey KB, Abidi AB, Rizvi SI (2013) Markers of oxidative stress during diabetes mellitus. J Biomark 2013:378790
Vaziri ND (2006) Dyslipidemia of chronic renal failure: the nature, mechanisms, and potential consequences. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F262–F272
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE), New Delhi, India and RUSA 2.0, MHRD, Govt. of India for financial supports and Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, Jadavpur University, Kolkata 700032, India for providing necessary facilities related to the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statements
Mentioned under materials and methods section.
Conflict of interest
Reshma Kumari has no conflict of interest. Waquar Ahmed Goldar has no conflict of interest. Subhodeep Mondal has no conflict of interest. Susmita Patra has no conflict of interest. Sanjib Bhattacharya has no conflict of interest. Pallab Kanti Haldar has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, R., Goldar, W.A., Mondal, S. et al. Protective effect of Basella alba leaf against diabetic nephropathy in rats. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 21, 111–119 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00458-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00458-2