Abstract
Objective
The objective of the study was to report mature outcomes in patients treated on a prospective feasibility study of helical tomotherapy-based craniospinal irradiation.
Methods
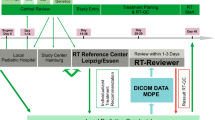
Patients needing craniospinal irradiation were accrued, treated, and followed up longitudinally for survival and toxicity on an institutional review board-approved study.
Results
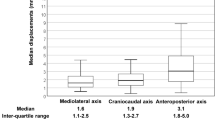
Twenty patients (median age of 15 years) constituted the study cohort. Tomotherapy-based craniospinal irradiation was well tolerated with self-limiting and reversible acute toxicity. Four (20 %) patients needed growth factor or platelet support during craniospinal irradiation. Significant late neuro-toxicity was seen in only one (5 %) patient. None of the patients developed symptomatic radiation pneumonitis or second new malignancy. At a median follow-up of 62 months (inter-quartile range 24–71 months), the 5-year progression-free survival and overall survival for the entire cohort was 50 and 55 %, respectively. Outcomes within the cohort varied significantly; patients with favorable biology disease had good outcomes while patients with high-risk, metastatic, or recurrent disease fared poorly reflecting inherently aggressive biology.
Conclusions
Helical tomotherapy is an ideal platform for planning, verification, and delivery of supine craniospinal irradiation in clinical practice resulting in moderate, self-limiting, reversible acute toxicity and modest delayed toxicity. Patterns of failure and survival outcomes are largely dependent upon disease biology and are not any different compared to conventional techniques.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samkari A, Hwang E, Packer RJ (2012) Medulloblastoma/Primitive neuroectodermal tumor and germ cell tumors: the uncommon but potentially curable primary brain tumors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 26(4):881–895. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2012.04.002
McGovern SL, Grosshans D, Mahajan A (2014) Embryonal brain tumors. Cancer J 20(6):397–402. doi:10.1097/PPO.0000000000000081
Wei RL, Nguyen ST, Yang JN, Wolff J, Mahajan A (2012) Salvage craniospinal irradiation with an intensity modulated radiotherapy technique for patients with disseminated neuraxis disease. Practical radiation oncology 2(4):e69–75. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2012.01.004
Fossati P, Ricardi U, Orecchia R (2009) Pediatric medulloblastoma: toxicity of current treatment and potential role of protontherapy. Cancer Treat Rev 35(1):79–96. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.09.002
Jefferies S, Rajan B, Ashley S, Traish D, Brada M (1998) Haematological toxicity of cranio-spinal irradiation. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 48(1):23–27
Christopherson KM, Rotondo RL, Bradley JA, Pincus DW, Wynn TT, Fort JA, Morris CG, Mendenhall NP, Marcus RB Jr, Indelicato DJ (2014) Late toxicity following craniospinal radiation for early-stage medulloblastoma. Acta Oncol 53(4):471–480. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2013.862596
Scott RL (2013) An overview of craniospinal axis fields and field matching. Med Dosim: Off J Am Assoc Med Dosimetrists 38(4):424–429. doi:10.1016/j.meddos.2013.05.005
Hideghety K, Cserhati A, Nagy Z, Varga Z, Fodor E, Vincze V, Szanto E, Maraz A, Thurzo L (2012) A prospective study of supine versus prone positioning and whole-body thermoplastic mask fixation for craniospinal radiotherapy in adult patients. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 102(2):214–218. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2011.07.003
Verma J, Mazloom A, Teh BS, South M, Butler EB, Paulino AC (2015) Comparison of supine and prone craniospinal irradiation in children with medulloblastoma. PRO 5(2):93–98. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2014.05.004
Michalski JM, Klein EE, Gerber R (2002) Method to plan, administer, and verify supine craniospinal irradiation. J Appl Clin Med Phys/ Am College Med Physics 3(4):310–316. doi:10.1120/1.1508013
Parker WA, Freeman CR (2006) A simple technique for craniospinal radiotherapy in the supine position. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 78(2):217–222. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2005.11.009
Wilkinson JM, Lewis J, Lawrence GP, Lucraft HH, Murphy E (2007) Craniospinal irradiation using a forward planned segmented field technique. Br J Radiol 80(951):209–215. doi:10.1259/bjr/61306844
Pai Panandiker A, Ning H, Likhacheva A, Ullman K, Arora B, Ondos J, Karimpour S, Packer R, Miller R, Citrin D (2007) Craniospinal irradiation with spinal IMRT to improve target homogeneity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68(5):1402–1409. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.02.037
Parker W, Filion E, Roberge D, Freeman CR (2007) Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for craniospinal irradiation: target volume considerations, dose constraints, and competing risks. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 69(1):251–257. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.04.052
Penagaricano JA, Papanikolaou N, Yan Y, Youssef E, Ratanatharathorn V (2005) Feasibility of cranio-spinal axis radiation with the Hi-Art tomotherapy system. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 76(1):72–78. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2005.06.013
Bedford JL, Lee YK, Saran FH, Warrington AP (2012) Helical volumetric modulated arc therapy for treatment of craniospinal axis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(3):1047–1054. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.07.039
Chen JCC, Atwood TF et al (2012) Volumetric modulated arc therapy planning method for supine craniospinal irradiation. J Radiat Oncol 1:291–297
Kunos CA, Dobbins DC, Kulasekere R, Latimer B, Kinsella TJ (2008) Comparison of helical tomotherapy versus conventional radiation to deliver craniospinal radiation. Technol Cancer Res Treat 7(3):227–233
Sharma DS, Gupta T, Jalali R, Master Z, Phurailatpam RD, Sarin R (2009) High-precision radiotherapy for craniospinal irradiation: evaluation of three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy and helical TomoTherapy. Br J Radiol 82(984):1000–1009. doi:10.1259/bjr/13776022
Studenski MT, Shen X, Yu Y, Xiao Y, Shi W, Biswas T, Werner-Wasik M, Harrison AS (2013) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy for adult craniospinal irradiation—a comparison with traditional techniques. Med Dosim: Offi J Am Assoc Med Dosimetrists 38(1):48–54. doi:10.1016/j.meddos.2012.05.006
Myers PA, Mavroidis P, Papanikolaou N, Stathakis S (2014) Comparing conformal, arc radiotherapy and helical tomotherapy in craniospinal irradiation planning. J Appl Clin Med Phys/ Am College Med Physics 15(5):4724. doi:10.1120/jacmp.v15i5.4724
Petersson K, Gebre-Medhin M, Ceberg C, Nilsson P, Engstrom P, Knoos T, Kjellen E (2014) Haematological toxicity in adult patients receiving craniospinal irradiation—indication of a dose-bath effect. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 111(1):47–51. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2014.01.020
Welsh JS, Patel RR, Ritter MA, Harari PM, Mackie TR, Mehta MP (2002) Helical tomotherapy: an innovative technology and approach to radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat 1(4):311–316
Al-Wassia R, Bahig H, Poon E, Parker W, Freeman C (2013) Daily setup uncertainty analysis for craniospinal irradiation using helical tomotherapy. PRO 3(4):349–355. doi:10.1016/j.prro.2012.07.005
Gupta T, Upasani M, Master Z, Patil A, Phurailatpam R, Nojin S, Kannan S, Godasastri J, Jalali R (2015) Assessment of three-dimensional set-up errors using megavoltage computed tomography (MVCT) during image-guided intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for craniospinal irradiation (CSI) on helical tomotherapy (HT). Technol Cancer Res Treat 14(1):29–36. doi:10.7785/tcrt.2012.500391
Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF (1995) Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31(5):1341–1346. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(95)00060-C
Wolden SL (2013) Protons for craniospinal radiation: are clinical data important? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(2):231–232. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.036
Yoon M, Shin DH, Kim J, Kim JW, Kim DW, Park SY, Lee SB, Kim JY, Park HJ, Park BK, Shin SH (2011) Craniospinal irradiation techniques: a dosimetric comparison of proton beams with standard and advanced photon radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(3):637–646. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.06.039
Moeller BJ, Chintagumpala M, Philip JJ, Grosshans DR, McAleer MF, Woo SY, Gidley PW, Vats TS, Mahajan A (2011) Low early ototoxicity rates for pediatric medulloblastoma patients treated with proton radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 6:58. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-6-58
Jimenez RB, Sethi R, Depauw N, Pulsifer MB, Adams J, McBride SM, Ebb D, Fullerton BC, Tarbell NJ, Yock TI, Macdonald SM (2013) Proton radiation therapy for pediatric medulloblastoma and supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors: outcomes for very young children treated with upfront chemotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(1):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.017
Barney CL, Brown AP, Grosshans DR, McAleer MF, de Groot JF, Puduvalli V, Tucker SL, Crawford CN, Gilbert MR, Brown PD, Mahajan A (2014) Technique, outcomes, and acute toxicities in adults treated with proton beam craniospinal irradiation. Neuro-Oncology 16(2):303–309. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not155
Sethi RV, Giantsoudi D, Raiford M, Malhi I, Niemierko A, Rapalino O, Caruso P, Yock TI, Tarbell NJ, Paganetti H, MacDonald SM (2014) Patterns of failure after proton therapy in medulloblastoma; linear energy transfer distributions and relative biological effectiveness associations for relapses. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88(3):655–663. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.11.239
Johnstone PA, McMullen KP, Buchsbaum JC, Douglas JG, Helft P (2013) Pediatric CSI: are protons the only ethical approach? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(2):228–230. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.05.037
Penagaricano J, Moros E, Corry P, Saylors R, Ratanatharathorn V (2009) Pediatric craniospinal axis irradiation with helical tomotherapy: patient outcome and lack of acute pulmonary toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75(4):1155–1161. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.083
Sugie C, Shibamoto Y, Ayakawa S, Mimura M, Komai K, Ishii M, Miyamoto A, Oda K (2011) Craniospinal irradiation using helical tomotherapy: evaluation of acute toxicity and dose distribution. Technol Cancer Res Treat 10(2):187–195
Mesbah L, Matute R, Usychkin S, Marrone I, Puebla F, Minguez C, Garcia R, Garcia G, Beltran C, Marsiglia H (2011) Helical tomotherapy in the treatment of pediatric malignancies: a preliminary report of feasibility and acute toxicity. Radiat Oncol 6:102. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-6-102
Lopez Guerra JL, Marrone I, Jaen J, Bruna M, Sole C, Sanchez-Reyes A, Rivin E, Ortiz MJ, Calvo F, Matute R (2014) Outcome and toxicity using helical tomotherapy for craniospinal irradiation in pediatric medulloblastoma. Clin Transl Oncol: Off Pub Federation Spanish Oncol Soc National Cancer Institute Mexico 16(1):96–101. doi:10.1007/s12094-013-1048-7
Qu B, Du L, Huang Y, Yu W, Cai B, Xu S, Ma L (2014) Clinical analysis of intracranial germinoma’s craniospinal irradiation using helical tomotherapy. Chin J Cancer Res 26(3):247–254. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.05.02
Skowronska-Gardas A, Chojnacka M, Morawska-Kaczynska M, Perek D, Perek-Polnik M (2007) Patterns of failure in children with medulloblastoma treated with 3D conformal radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol: J Euro Soc Therapeutic Radiology Oncol 84(1):26–33. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2007.05.018
Lee DS, Cho J, Kim SH, Kim DS, Shim KW, Lyu CJ, Han JW, Suh CO (2014) Patterns of failure following multimodal treatment for medulloblastoma: long-term follow-up results at a single institution. Breast Cancer Res Treat : Off J Korean Cancer Asso. doi:10.4143/crt.2014.067
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was partially funded by a competitive intramural research grant (IRB Project No. 197) provided by Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was duly approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, T., Zade, B., Upasani, M. et al. Helical tomotherapy-based craniospinal irradiation: mature outcomes of a prospective feasibility study. J Radiat Oncol 5, 221–230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-015-0235-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-015-0235-2