Abstract
Justification
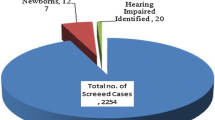
Hearing impairment is one of the most critical sensory impairments with significant social and psychological consequences. Evidence-based, standardized national guidelines are needed for professionals to screen for hearing impairment during the neonatal period.
Process
The meeting on formulation of national consensus guidelines on developmental disorders was organized by Indian Academy of Pediatrics in Mumbai, on 18th and 19th December, 2015. The invited experts included Pediatricians, Developmental Pediatricians, Pediatric Neurologists and Clinical Psychologists. The participants framed guidelines after extensive discussions.
Objective
To provide guidelines on newborn hearing screening in India.
Recommendations
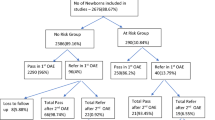
The first screening should be conducted before the neonate’s discharge from the hospital–if it ‘fails’, then it should be repeated after four weeks, or at first immunization visit. If it ‘fails’ again, then Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) audiometry should be conducted. All babies admitted to intensive care unit should be screened via ABR. All babies with abnormal ABR should undergo detailed evaluation, hearing aid fitting and auditory rehabilitation, before six months of age. The goal is to screen newborn babies before one month of age, diagnose hearing loss before three months of age and start intervention before six months of age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stevenson J, McCann D, Watkin P, Worsfold S, Kennedy C. The relationship between language development and behaviour problems in children with hearing loss. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010;51:77–83
Yoshinaga-Itano C, Sedey AL, Coulter DK, Mehl AL. Language of early-and later-identified children with hearing loss. Pediatrics. 1998;102:1161–71.
Dominguez M, Becker S, Bruce I, Read H. A spiking neuron model of cortical correlates of sensorineural hearing loss: Spontaneous firing, synchrony and tinnitus. Neural Comput. 2006;18:2942:2958.
Wynbrandt J, Ludman MD. The Encyclopaedia of Genetic Disorders and Birth Defects. New York, USA: Infobase Publishing;2009.
Berg AL, Spitzer JB, Towers HM, Bartosiewicz C, Diamond BE. Newborn hearing screening in the NICU: profile of failed auditory brainstem response/passed otoacoustic emission. Pediatrics. 2005;116:933–98.
Al-Kandar JM, Alshuaib WB. Newborn hearing screening in Kuwait. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;47:305–13.
Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 Position Statement: Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:898–921.
Jones KL. Smith’s Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation 6th Edition, Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier;2009.
Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram. Available from http://nrhm.gov.in/nrhm-components/rmnch-a/child-healthimmunization/rashtriya-bal-swasthya-karyakram-rbsk/background.html. Accessed on February 6, 2015.
Kemp DT. Otoacoustic emissions, their origin in cochlear function, and use. Br Med Bull. 2002;63:223–41.
Hunter MF, Kimm L, Cafarlli DD, Kennedy CR, Thornton AR. Feasibility of otoacoustic emission detection followed by ABR as a universal neonatal screening test for hearing impairment. Br J Audiol. 1994;28:47–51.
Paul AK. Early identification of hearing loss and centralized newborn hearing screening facility-the Cochin experience. Indian Pediatr. 2011;48:355–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, A., Prasad, C., Kamath, S.S. et al. Consensus statement of the Indian Academy of Pediatrics on newborn hearing screening. Indian Pediatr 54, 647–651 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1128-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1128-9