Abstract
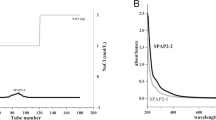
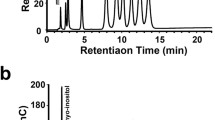
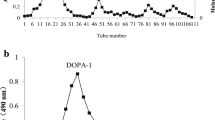
In this study, a water-soluble longan seed polysaccharide (WLSP), with a molecular weight of 57 kDa, was isolated from longan seed. Gas chromatography (GC) analysis showed that WLSP was composed mainly of rhamnose (Rha), mannose (Man), arabinose (Ara), galactose (Gal), and glucose (Glc), with molar ratios of 2.4:1.5:2.3:5.6:6.5. The result in 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay showed that WLSP showed a dose-dependent antiproliferative effect on the proliferation of A549 human lung cancer cells, which is consistent with the amount of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from A549 cells. Prompted by this antiproliferative effect, we further examined its antiproliferative mechanism and in vivo anticancer effect. Our results showed that WLSP had the ability to cause cell cycle arrest in G1 phase, activation of caspases 3 and 9, and cleavage of poly[ADP (ribose)] polymerase (PARP) in A549 cells. The result of this in vivo study showed that WLSP could suppress the growth of xenograft A549 tumors and induce apoptosis. Taken together, these results indicate that WLSP exert an anticancer effect in vitro and in vivo and may be useful for the prevention of lung tumorigenesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Worasuttayangkurn L, Watcharasit P, Rangkadilok N, Suntararuks S, Khamkong P, Satayavivad J. Safety evaluation of longan seed extract: acute and repeated oral administration. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50:3949–55.
Jiang YM, Zhang ZQ, Joyce DC, Ketsa S. Postharvest biology and handling of longan fruit (Dimocarpus longan Lour.). Postharvest Biol Technol. 2002;26:241–52.
Xiao G, Huang R, Zeng Q, Chen W, Liu X, Rui H. Nutrition composition of longan seeds. Shi Pin Ke Ji. 2004;1:93–4.
Zheng G, Wei X, Xu L, Li Z, Liu G, Zhang X. A new natural lactone from Dimocarpus longan Lour. seeds. Molecules. 2012;17:9421–5.
Rangkadilok N, Sitthimonchai S, Worasuttayangkurn L, Mahidol C, Ruchirawat M, Satayavivad J. Evaluation of free radical scavenging and antityrosinase activities of standardized longan fruit extract. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45:328–36.
Zheng SQ, Jiang F, Gao HY, Zheng JG. Preliminary observations on the antifatigue effects of longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seed polysaccharides. Phytother Res. 2010;24:622–4.
Chung YC, Lin CC, Chou CC, Hsu CP. The effect of longan seed polyphenols on colorectal carcinoma cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40:713–21.
Huang RQ, Zou XY, Liu XM. Study on the hypoglycemic effect of longan seed extract. Nat Prod Res Dev. 2006;18:991–2.
Soong YY, Barlow PJ. Isolation and structure elucidation of compounds from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seed by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2005;1085:270–7.
Rangkadilok N, Worauttayngkurn L, Bennett RN, Satayavivad J. Identification and quantification of polyphenolic compounds in longan (Euphoria longana Lam.) fruit. J Agric Food Chem. 2005;53:1387–92.
Minakata H, Komura H, Tamura SY, Ohfune Y, Nakanishi K, Kada T. Anti-mutagenic unusual amino acids from plants. Experientia. 1985;41:1621–2.
Jiang G, Wen L, Chen F, Wu F, Lin S, Yang B, et al. Structural characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from longan seed. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92:758–64.
Wen LR, Lin LZ, You LJ, Yang B, Jiang GX, Zhao MM. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and structural identification of polysaccharides from Isodon lophanthoides var. gerardianus (Bentham) H. Hara. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;85:541–7.
Staub AM. Removal of protein: Sevag method. Methods Carbohydr Chem. 1965;5:5–6.
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem. 1956;28:350–6.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Chem. 1976;72:248–54.
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973;54:484–9.
Luo AX, He XJ, Zhou S, Fan YJ, Luo AS, Chun Z. Purification, composition analysis and antioxidant activity of the polysaccharides from Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;79:1014–9.
Zhai Q, Li X, Yang Y, Yu L, Yao Y. Antitumor activity of a polysaccharide fraction from Laminaria japonica on U14 cervical carcinoma-bearing mice. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:117–22.
Lee TH, Chuang LY, Hung WC. Tamoxifen induces p21Waf1 and p27Kip1 expression in estrogen receptor-negative lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 1999;18:4269–74.
Sawaoka H, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Gunawan ES, Sasaki Y, Kawano S, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors suppress angiogenesis and reduce tumor growth in vivo. Lab Invest. 1999;79:1469–77.
Waheed Roomi M, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T, Niedzwiecki A, Rath M. In vivo and in vitro antitumor effect of a unique nutrient mixture on lung cancer cell line A-549. Exp Lung Res. 2006;32:441–53.
Yin X, Zhou J, Jie C, Xing D, Zhang Y. Anticancer activity and mechanism of Scutellaria barbata extract on human lung cancer cell line A549. Life Sci. 2004;75:2233–44.
Punathil T, Katiyar SK. Inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer cell migration by grape seed proanthocyanidins is mediated through the inhibition of nitric oxide, guanylate cyclase, and ERK1/2. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:232–42.
Choi WH, Chu JP, Jiang MH, Baek SH, Park HD. Effects of fraction obtained from Korean Corni Fructus extracts causing anti-proliferation and p53-dependent apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 2011;63:121–9.
Houghton PJ. The role of plants in traditional medicine and current therapy. J Altern Complement Med. 1995;1:131–43.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31100656).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, X., Li, Y. et al. Antitumor activity of a polysaccharide from longan seed on lung cancer cell line A549 in vitro and in vivo. Tumor Biol. 35, 7259–7266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1927-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1927-8