Abstract
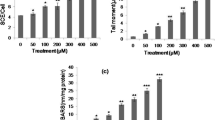
Chronic exposure of inorganic arsenic compounds is responsible for the manifestation of various tumours as well as other diseases. The principal mechanism behind arsenic toxicity is the induction of a strong oxidative stress with production of free radicals in cells. The present study was aimed to explore the shielding effect of anethole against oxidative damage induced by arsenic in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes and the effect of GSTO1 polymorphism. Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) frequency, comet tail moment and lipid peroxidation levels were used as biomarkers to assess the oxidative damage. Heparinised venous blood was collected from healthy individuals and treated with sodium arsenite (50 µM) in the presence of anethole (25 and 50 µM) for the analysis of shielding effect of anethole. For the genotyping of GSTO1, PCR RFLP method was adopted. A significant dose-dependent increase in the frequency of SCEs, tail moment and lipid peroxidation levels, was observed when lymphocytes were treated with sodium arsenite. Anethole in combination with sodium arsenite has shown a dose-dependent significant decrease in the frequency of SCEs, tail moment and lipid peroxidation levels. Genetic polymorphism of GSTO1 was found to effect individual susceptibility towards arsenic-mediated genotoxicity and was found insignificant when antigenotoxic effect of anethole was considered. GSTO1 mutant genotypes were found to have significant higher genotoxicity of sodium arsenite as compared to wild-type genotype. The results of the present study suggest ameliorative effects of anethole against arsenic-mediated genotoxic damage in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes. A significant effect of GSTO1 polymorphism was observed on genotoxicity of sodium arsenite.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham S (2001) Anti-genotoxicity of trans-anethole and eugenol in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 39:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(00)00156-3
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Tharakan ST, Sung B, Anand (2008) Potential of spice-derived phytochemicals for cancer prevention. Planta Med 74:1560–1569. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1074578
Amkiss S, Dallouh A, Idaomar M, Amkiss B (2013) Genotoxicity and anti-genotoxicity of fennel plant (Foeniculum vulgare Mill) fruit extracts using the somatic mutation and recombination test (SMART). Afr J Food Sci 7(8):193–197. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJFS13.0999
Avani G, Rao MV (2009) In vitro genotoxicity assays to evaluate the role of vitamin A on arsenic in human lymphocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(2):635–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.03.011
Buchet JP, Lauwerys R (1987) Study of factors influencing the in vivo methylation of inorganic arsenic in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 91:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008X(87)90194-3
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid, peroxidation. In: Flesicher S, Packer L (eds) Methods enzymol, vol 52. Academic, New York, pp 302–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(78)52032-6
Chen JW, Wang SL, Wang YH, Sun CW, Huang YL, Chen CJ, Li WF (2012) Arsenic methylation, GSTO1 polymorphisms, and metabolic syndrome in an arseniasis endemic area of Southwestern Taiwan. Chemosphere 88:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.059
Chen Y, Wu F, Liu M, Parvez F, Slavkovich V, Eunus M (2013) A prospective study of arsenic exposure, arsenic methylation capacity, and risk of cardiovascular disease in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 121:832–838. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205797
Cimbaljevic S, Suvakov S, Matic M, ljesa-Ercegovac M, Pekmezovic T, Radic T, Coric V, Damjanovic T, Dimkovic N, Markovic R, Savic-Radojevic A, Simic T (2016) Association of GSTO1 and GSTO2 polymorphism with risk of end-stage renal disease development and patient survival. J Med Biochem 35(3):302–311. https://doi.org/10.1515/jomb-2016-0009
Collins AR (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: principles, applications, and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261. https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:26:3:249
Eder E, Wacker M, Wanek P (2008) Lipid peroxidation-related 1, N2-propandodeoxyguanosine-DNA adducts induced by endogenously formed 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in organs of female rats fed diets supplemented with sunflower, rapeseed live or coconut oil. Mutat Res 654:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.04.010
Faita F, Cori L, Bianchi F, Andreassi MJ (2013) Arsenic-induced genotoxicity and genetic susceptibility to arsenic-related pathologies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:1527–1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10041527
Ferreccio C, Smith AH, Durán V, Barlaro T, Benítez H, Valdés R, Aguirre JJ, Moore LE, Acevedo J, Vásquez MI, Pérez L, Yuan Y, Liaw J, Cantor KP, Steinmaus C (2013) Case–control study of arsenic in drinking water and kidney cancer in uniquely exposed Northern Chile. Am J Epidemiol 178:813–818. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt059
Flora SJ (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 51:257–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008
Hsieh YC, Lien LM, Chung WT, Hsieh FI, Hsieh PF, Wu MM, Tseng HP, Chiou HY, Chen CJ (2011) Significantly increased risk of carotid atherosclerosis with arsenic exposure and polymorphisms in arsenic metabolism genes. Environ Res 111:804–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2011.05.003
Hsu L, Chen WP, Yang TY, Chen YH, Lo WC, Wang YH, Liao YT, Hsueh YM, Chiou HY, Wu MM, Chen C (2011) Genetic polymorphisms in glutathione S-transferase (GST) superfamily and risk of arsenic-induced urothelial carcinoma in residents of Southwestern Taiwan. J Biomed Sci 18:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-18-51
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2004) Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Human. 84:1–477. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol84/
IMG Report (2015) Report of the Inter-Ministerial Group (IMG) for arsenic mitigation. Ministry of Water resources India. http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in
International Agency for Research on Cancer Arsenic, metals, fibres, and dusts (2012) IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Human 100C:1–526 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK304375/
James KA, Byers T, Hokanson JE, Meliker JR, Zerbe OG, Marshall JA (2015) Association between lifetime exposure to inorganic arsenic in drinking water and coronary heart disease in colorado residents. Environ Health Perspect 123:2. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1307839
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1649
Kaur R, Arora S (2015) Alkaloids-important therapeutic secondary metabolites of plant origin. J Crit Rev 2(3):1–8. https://innovareacademics.in/journals/index.php/jcr/article/view/6756/5256
Kumar M, Chauhan LK, Paul BN, Agarwal SK, Goel SK (2009) GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 polymorphism in north Indian population and its influence on the hydroquinone-induced in vitro genotoxicity. Toxicol Mech Met 19(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376510802399057
Lesseur C, Diamond DG, Andrew AS, Ekstrom RM, Li Z, Kelsey TK, Marsit CJ, Karagas MR (2012) A case-control study of polymorphisms in xenobiotic and arsenic metabolism genes and arsenic-related bladder cancer in New Hampshire. Toxicol Lett 210(1):100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.01.015
Marahatta SB, Punyarit P, Bhudisawasdi V, Paupairoj A, Wongkham S, Petmitr S (2006) Polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase omega gene and risk of cancer. Cancer Lett 236:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2005.05.020
Moorhead PS, Nowell PC, Mellmam WJ, Battips DM, Hungerford DA (1960) Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res 20:613–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5
Newberne P, Smith RL, Doull J, Goodman JI, Munro IC, Portoghese PS, Wagner BM, Weil CS, Woods LA, Adams TB, Lucas CD, Ford RA (1999) The FEMA GRAS assessment of trans-anethole used as a flavouring substance. Food Chem Toxicol 37(7):789–811. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00037-X
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Park HS, Kwan-Hee Eun-HH, Yun-Chul L H (2002) Benzo [a] pyrene-induced DNA-protein crosslinks in cultured human lymphocytes and the role of the GSTM1 and GSTT1 genotypes. J Korean Med Sci 17:316–321. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2002.17.3.316
Perry P, Wolff S (1974) New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature 251(5471):156–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/251156a0
Pierce BL, Kibriya MG, Tong L, Jasmine F, Argos M, Roy S, Paul-Brutus R, Rahaman R, Rakibuz-Zaman M, Parvez (2012) Genome-wide association study identifies chromosome 10q24.32 variants associated with arsenic metabolism and toxicity phenotypes in Bangladesh. PLoS Genet 8:e1002522. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002522
Sankar P, Telang AG, Kalaivanan R, Karunakaran V, Suresh S, Kesavan M (2013) Oral nanoparticulate curcumin combating arsenic-induced oxidative damage in kidney and brain of rats. Toxicol Ind Health 32(3):410–421. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713498455
Shahat AA, Ibrahim AY, Hendawy SF, Omer EA, Hammouda FM, Abdel- Rahman FH, Saleh MA (2011) Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of essential oils from organically cultivated fennel cultivars. Molecules 16:1366–1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16021366
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Sonoda E, Sasaki MS, Morrison C, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Takata MT (1999) Sister chromatid exchanges are mediated by homologous recombination in vertebrate cells. Mol Cell Biol 19:5166–5516 (PMCID: PMC84359)
Whitbread AK, Tetlow N, Eyre HJ, Sutherland GR, Board PG (2003) Characterization of the human Omega class glutathione transferase genes and associated polymorphisms. Pharmacogenetics 13:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.fpc.0000054062.98065.6e
Wu F, Molinaro P, Chen Y (2014) Arsenic exposure and subclinical endpoints of cardiovascular disease. Curr Environ Rep 1:148–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-014-0011-2
Zablotska LB, Chen Y, Graziano JH, Parvez F, Geen AV, Howe GR, Ahsan H (2008) Protective effects of B vitamins and antioxidants on the risk of arsenic-related skin lesions in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 116:1056–1062. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10707
Zakharyan RA, Sampayo-Reyes A, Healy SM, Tsaprailis G, Board PG, Liebler DC, Aposhian HV (2001) Human monomethylarsonic acid (MMA (V)) reductase is a member of the glutathione-S-transferase superfamily. Chem Res Toxicol 14:1051–1057. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx010052h
Acknowledgements
The present work was purposed and guided by Dr. Anita Yadav. The work was performed in Animal Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra (Haryana), India. We are thankful to all the blood donors for their valuable contribution in our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of the present work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, S., Yadav, A., Verma, N. et al. Shielding effect of anethole against arsenic induced genotoxicity in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes and effect of GSTO1 polymorphism. 3 Biotech 8, 232 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1263-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1263-6