Abstract
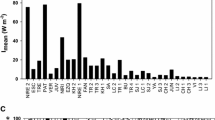
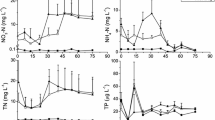
The ecological relevance of shallow lakes has been largely documented. The Pampean plain (Argentina) holds one of the main wetlands of South America, constituted by thousands of shallow lakes which provide valuable ecosystem services, and can be found in any of three regimes: clear-vegetated, inorganic-turbid or phytoplankton-turbid. Since these lakes play an important role in the global carbon balance, metabolism studies encompassing phytoplankton and periphyton under different regimes become relevant. Here, we analyzed the primary production (PP) of phytoplankton and periphyton in three Pampean shallow lakes representing the main types mentioned. The relative contribution of each algal community to the joint PP was different in each lake and related to their regime. The periphyton contribution was higher in the clear-vegetated lake than in the turbid lakes. The phytoplankton-turbid lake exhibited the highest PP for both communities. The inorganic-turbid lake presented the highest light limitation; nonetheless, the efficiency of periphyton in this lake showed an increasing trend with depth, suggesting light acclimation. Although phytoplankton dominated the PP in the three lakes, periphyton contribution was also important, particularly in the clear-vegetated lake. Our results emphasize that the PP of attached communities should be considered to estimate the PP of the whole lake.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allende L, Tell G, Zagarese H, Torremorell A, Pérez G, Bustingorry J, Escaray R, Izaguirre I (2009) Phytoplankton and primary production in clear-vegetated, inorganic-turbid, and algal-turbid shallow lakes from the pampa plain (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 624:45–60
APHA American Public Health Association (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewaters, 21 st edn. AWWA/APWA/WEF, Washington DC
Ask J, Karlsson J, Persson L, Ask P, Byström P, Jansson M (2009) Terrestrial organic matter and light penetration: effects on bacterial and primary production in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 54:2034–2040
Burkholder JM (1996) Interaction of benthic algae with their substrata. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 253–298
Cano MG, Casco MA, Claps MC (2013) Vertical distribution of epiphyton biomass and diversity in a shallow lake during contrasting ecosystem regimes. Aquatic Botany 110:38–47
Casco MA, Mac Donagh ME, Cano MG, Solari LC, Claps MC, Gabellone NA (2009) Phytoplankton and Epipelon responses to clear and turbid phases in a seepage Lake (Buenos Aires, Argentina). International Review of Hydrobiology 94:153–168
Cole JJ, Prairie YT, Caraco NF, McDowell WH, Tranvik LJ, Striegl RG, Duarte CM, Kortelainen P, Downing JA, Middelburg JJ, Melack J (2007) Plumbing the global carbon cycle: integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 10:172–185
Diovisalvi N, Bohn VY, Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Baigún C, Zagarese HE (2015) Shallow lakes from the Central Plains of Argentina: an overview and worldwide comparative analysis of their basic limnological features. Hydrobiologia 752:5–20
Esquius KS, Escalante AH (2012). Periphyton assemblages and their relationships with environmental variables in a eutrophic shallow lake from pampa plain, Argentina. Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences 7: 57–72
Falkowski PG, LaRoche J (1991) Acclimation to spectral irradiance in algae. Journal of Phycology 27:8–14
Genkai-kato AM, Vadeboncoeur Y, Liboriussen L, Jeppesen E (2016) Benthic-planktonic coupling, regime shifts, and whole-lake primary production in shallow lakes. Ecology 93:619–631
Goldsborough LG, Robinson GGC (1996) Pattern in wetlands. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 77–117
Hansson L-A (1988) Effects of competitive interactions on the biomass development of planktonic and periphytic algae in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 33:121–128
Hansson L-A (1992) Factors regulating periphytic algal biomass. Limnology and Oceanography 37:322–328
Havens KE, Hauxwell J, Tyler AC, Thomas S, McGlathery KJ, Cebrian J, Valiela I, Steinman AD, Hwang SJ (2001) Complex interactions between autotrophs in shallow marine and freshwater ecosystems: implications for community responses to nutrient stress. Environmental Pollution 113:95–107
Hill W (1996) Effects of light. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 121–148
Holm-Hansen O, Helbling EW (1995) Técnicas para la medición de la productividad primaria en el fitoplancton. In: Alvear K, Ferrario ME, Oliveira EC, Sar E (eds) Manual de Métodos Ficológicos. Universidad de Concepción, Concepción, pp. 329–350
Huisman J, Jonker RR, Zonneveld C, Weissing FJ (1999) Competition for light between phytoplankton species: experimental test of mechanistic theory. Ecology 80:211–222
Izaguirre I, Allende L, Escaray R, Bustingorry J, Pérez G, Tell G (2012) Comparison of morpho-functional phytoplankton classifications in human-impacted shallow lakes with different stable states. Hydrobiologia 698:203–216
Jäger CG, Diehl S (2014) Resource competition across habitat boundaries: asymmetric interactions between benthic and pelagic producers. Ecological Monographs 84:287–302
Jespersen AM, Christoffersen K (1987) Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 109:445–454
Kalff J (2003) Limnology: inland waters ecosystems. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Kirk JTO (2011) Light & Photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems, 3rd edn. University Press, Cambridge
Kosten S, Vernooij M, Van Nes EH, Sagrario MA, Clevers JGPW, Scheffer M (2012) Bimodal transparency as an indicator for alternative states in south American lakes. Freshwater Biology 57:1191–1201
Liboriussen L, Jeppesen E (2003) Temporal dynamics in epipelic, pelagic and epiphytic algal production in a clear and turbid shallow lake. Freshwater Biology 48:418–431
Lowe R (1996) Periphyton patterns in lakes. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 57–76
Mackereth FJH, Heron J, Talling JF (1978) Water analysis: some revised methods for limnologists. Freshwater Biological Associations, Cumbria
Pérez GL, Torremorell A, Bustingorry J, Escaray R, Pérez P, Diéguez M, Zagarese H (2010) Optical characteristics of shallow lakes from the pampa and Patagonia regions of Argentina. Limnologica 40:30–39
Quirós R, Rennella AM, Boveri MB, Rosso JJ, Sosnovsky A (2002) Factores que afectan la estructura y el funcionamiento de las lagunas pampeanas. Ecología Austral 12:175–185
Quirós R, Boveri MB, Petracchi CA, Renella AM, Rosso J, Sosnovsky A, von Bernard HT (2006) Los efectos de la agriculturización del humedal pampeano sobre la eutrofización de sus lagunas. In: Tundisi JG, Matsumura-Tundisi T, Sidagis Galli C (eds) Eutrofização na América do Sul:Causas,conseqüências e tecnologías de gerenciamento e controle, Instituto Internacional de Ecologia, Instituto Internacional de Ecologia e Gerenciamento Ambiental, Academia Brasileira de Ciências, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico. Inter Academy Panel on International Issues, Inter American Network of Academies of Sciences, Brasil. pp 1–16
Reynolds C (2006) Ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, New York
Rodríguez P, Pizarro H (2015) Phytoplankton and periphyton production and its relation to temperature in a humic lagoon. Limnologica 55:9–12
Rodríguez P, Vera MS, Pizarro H (2012) Primary production of phytoplankton and periphyton in two humic lakes of a south American wetland. Limnology 13:281–287
Sánchez ML, Pizarro H, Tell G, Izaguirre I (2010) Relative importance of periphyton and phytoplankton in turbid and clear vegetated shallow lakes from the pampa plain (Argentina): a comparative experimental study. Hydrobiologia 646:271–280
Sánchez ML, Pérez GL, Izaguirre I, Pizarro H (2013) Influence of underwater light climate on periphyton and phytoplankton communities in shallow lakes from the pampa plain (Argentina) with contrasting steady states. Journal of Limnology 72:62–78
Scheffer M (1998) Ecology of shallow lakes. Chapman & Hall, London
Scheffer M (2009) Critical transitions in nature and society. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer M-L, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 8:275–279
Schrier-Uijl AP, Veraart AJ, Leffelaar PA, Berendse F, Veenendaal EM (2011) Release of CO2 and CH4 from lakes and drainage ditches in temperate wetlands. Biogeochemistry 102:265–279
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry: chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Torremorell A, Llames ME, Pérez GL, Escaray R, Bustingorry J, Zagarese H (2009) Annual pattern of phytoplankton density and primary production in a large shallow lake: the central role of light. Freshwater Biology 54:437–449
Tranvik LJ, Downing JA, Cotner JB, Loiselle SA, Striegl RG, Ballatore TJ, Dillon P, Finlay K, Fortino K, Knoll LB, Kortelainen PL, Kutser T, Larsen S, Laurion I, Leech DM, McCallister SL, McKnight DM, Melack JM, Overholt E, Porter JA, Prairie Y, Renwick WH, Roland F, Sherman BS, Schindler DW, Sobek S, Tremblay A, Vanni MJ, Verschoor AM, von Wachenfeldt E, Weyhenmeyer GA (2009) Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnology and Oceanography 54:2298–2314
Utermöhl M (1958) Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen phytoplankton Methodik. Mitteilungen Internationale Vereinigung für Limnologie 9:1–38
Vadeboncoeur Y, Steinman AD (2002) Periphyton function in lake ecosystems. Scientific World Journal 2:1449–1468
Vadeboncoeur Y, Jeppesen E, Vander Zanden MJ, Schierup H-H, Cristoffersen K, Lodge DM (2003) From Greenland to green lakes: cultural eutrophication and the loss of benthic pathways in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 48:1408–1418
Vadeboncoeur Y, Kalff J, Christoffersen K, Jeppesen E (2006) Substratum as a driver of variation in periphyton chlorophyll and productivity in lakes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25:379–392
Vadeboncoeur Y, Peterson G, Vander Zanden MJ, Kalff J (2008) Benthic algal production across lake size gradients: interactions among morphometry, nutrients, and light. Ecology 89:2542–2552
Vadeboncoeur Y, Devlin SP, Mcintyre PB, Vander Zanden MJ (2014) Is there light after depth ? Distribution of periphyton chlorophyll and productivity in lake littoral zones. Freshwater Science 33:524–536
Wetzel RG (2005) Limnology: Lake and river ecosystems, 4th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (2000) Limnological analyses, 3rd edn. Springer, USA
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Roberto Escaray and the members of Laboratorio de Ecología y Fotobiología Acuática from Instituto de Investigaciones Biotecnológicas- Instituto Tecnológico de Chascomús (Chascomús, Buenos Aires, Argentina) for their field support. This research was supported by a grant of the University of Buenos Aires (UBACyT X838) and PAMPA2 Project (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, M.L., Rodríguez, P., Torremorell, A.M. et al. Phytoplankton and Periphyton Primary Production in Clear and Turbid Shallow Lakes: Influence of the Light Environment on the Interactions between these Communities. Wetlands 37, 67–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-016-0840-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-016-0840-x