Abstract
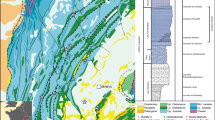
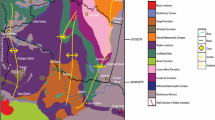
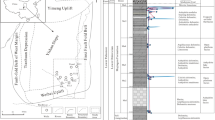
In this study, we systemically investigated the petrological features and geochemical compositions of dolostones in various sedimentary facies, to provide more understanding on the effects of facies-dependent diagenesis and hydrothermal reworking during the post-deposition stage. Microscopic observations and XRD analyses of carbonate were performed as well as analyses of C–O–Sr isotopic and elemental concentrations. Multiple evidence demonstrated that dolostones in the studied section underwent meteoric diagenesis and hydrothermal alterations. Effects of meteoric diagenesis were represented by meteoric dissolution, dedolomitization and calcite cementation, and varied along the downward migration of meteoric flow. Generally, meteoric dissolution mainly occurred in the exposure ooid shoal complex in the lower Triassic and accounted for the formation of mold pore, while in the underlying reef dolostones of the upper Permian, interparticle pores and cavities were mostly blocked by sparry calcite cement. Ooid dolostone layers in the lower Triassic exhibited low 87Sr/86Sr ratios and high Ba concentrations with saddle dolomite cement rimmed around the pore, demonstrating the relatively intense hydrothermal reworking. We inferred that high-permeability layers produced by early meteoric dissolution facilitated the migration of hydrothermal fluid and water–rock interaction in the burial stage. Petrologic observations indicated the hydrothermal reworking rearranged pore systems via regional transformation from dissolution to precipitation along the migration of fluid flows, and further enhanced the heterogeneity of the dolostone reservoir. Generally, the effects of early diagenesis and hydrothermal reworking in dolostones varied in dolostones of sedimentary facies, and high-quality dolostones reservoirs for oil and nature gas in this area formed as a result of the combined effects of early meteoric dissolution and hydrothermal reworking.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams A, Diamond LW (2017) Early diagenesis driven by widespread meteoric infiltration of a Central European carbonate ramp: a reinterpretation of the upper Muschelkalk. Sediment Geol 362:37–52
Al-Aasm IS, Lonnee J, Clarke J (2002) Multiple fluid flow events and the formation of saddle dolomite: case studies from the Middle Devonian of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Mar Pet Geol 19:209–217
Andrieu S, Brigaud B, Barbarand J, Lasseur E (2017) Linking early diagenesis and sedimentary facies to sequence stratigraphy on a prograding oolitic wedge: the Bathonian of western France (Aquitaine Basin). Mar Pet Geol 81:169–195
Archie GE (1952) Classification of carbonate reservoir rocks and petrophysical considerations. AAPG Bull 36:278–298
Banner JL (1995) Application of the trace element and isotope geochemistry of strontium to studies of carbonate diagenesis. Sedimentology 42:805–824
Becker S, Reuning L, Amthor JE, Kukla PA (2019) Diagenetic processes and reservoir heterogeneity in salt-encased microbial carbonate reservoirs (Late Neoproterozoic, Oman). Geofluids 2019:1–19
Bialik OM, Wang X, Zhao S, Waldmann ND, Frank R, Li W (2018) Mg isotope response to dolomitization in hinterland-attached carbonate platforms: outlook of δ26Mg as a tracer of basin restriction and seawater Mg/Ca ratio. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 235:189–207
Brand U, Veizer J (1980) Chemical diagenesis of a multicomponent carbonate system: 1, trace elements. J Sediment Res 50:1219–1236
Budd DA (1997) Cenozoic dolomites of carbonate islands: their attributes and origin. Earth-Sci Rev 42:1–47
Cai C, Li K, Li H, Zhang B (2008) Evidence for cross formational hot brine flow from integrated 87Sr/86Sr, REE and fluid inclusions of the Ordovician veins in Central Tarim, China. Appl Geochem 23:2226–2235
Cai C, He W, Jiang L, Li K, Xiang L, Jia L (2014) Petrological and geochemical constraints on porosity difference between lower Triassic sour- and sweet-gas carbonate reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. Mar Pet Geol 56:34–50
Cao CQ, Yang YC, Shen SZ, Wang W, Zheng QF, Summons RE (2010) Pattern of δ13Ccarb and implications for geological events during the Permian–Triassic transition in South China. Geol J 45:186–194
Chen H, Zhong Y, Hou M, Lin L, Dong G, Liu J (2009) Sequence styles and hydrocarbon accumulation effects of carbonate rock platform in the Changxing–Feixianguan formation in the northeastern Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol 30:539–547 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Chen Q, Hu W, Li Q, Zhu J (2012) Characteristics and genesis of dolomitization in Changxing and Feixianguan formations in Panlongdong, northeastern Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol 33:84–93 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Chen L, Lu Y, Fu X, Xing F, Wang C, Luo C (2017) Oolitic shoal complexes characterization of the lower Triassic Feixianguan formation in the Yuanba gas field, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 83:35–49
Davies GR, Smith LB (2006) Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: an overview. AAPG Bull 90:1641–1690
Dawns JM, Swart PK (1988) Textural and geochemical alternations in Late Cenozoic Bahamian dolomites. Sedimentology 35:385–404
Debruyne D, Hulsbosch N, Muchez P (2016) Unraveling rare earth element signatures in hydrothermal carbonate minerals using a source–sink system. Ore Geol Rev 72:232–252
Della Porta G, Webb GE, McDonald I (2015) REE patterns of microbial carbonate and cements from Sinemurian (Lower Jurassic) siliceous sponge mounds (Djebel Bou Dahar, High Atlas, Morocco). Chem Geol 400:65–86
Dickson JAD (1966) Carbonate identification and genesis as revealed by staining. J Sediment Res 36:494–505
Dong S, Chen D, Qing H, Zhou X, Wang D, Guo Z, Jiang M, Qian Y (2013) Hydrothermal alteration of dolostones in the Lower Ordovician, Tarim Basin, NW China: multiple constraints from petrology, isotope geochemistry and fluid inclusion microthermometry. Mar Pet Geol 46:270–286
Dong S, Chen D, Zhou X, Qian Y, Tian M, Qing H, Hollis C (2017) Tectonically driven dolomitization of Cambrian to lower Ordovician carbonates of the Quruqtagh area, north-eastern flank of Tarim Basin, north-west China. Sedimentology 64:1079–1106
Dudás FÖ, Yuan DX, Shen SZ, Bowring SA (2017) A conodont-based revision of the 87Sr/86Sr seawater curve across the Permian–Triassic boundary. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 470:40–53
Elburg M, Vroon P, Vanderwagt B, Tchalikian A (2005) Sr and Pb isotopic composition of five USGS glasses (BHVO-2G, BIR-1G, BCR-2G, TB-1G, NKT-1G). Chem Geol 223:196–207
Elderfield H (1986) Strontium isotope stratigraphy. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 57:71–90
Feng M, Wu P, Qiang Z, Liu X, Duan Y, Xia M (2017) Hydrothermal dolomite reservoir in the Precambrian Dengying formation of central Sichuan Basin, Southwestern China. Mar Pet Geol 82:206–219
Frisia S, Borsato A, Hellstrom J (2018) High spatial resolution investigation of nucleation, growth and early diagenesis in speleothems as exemplar for sedimentary carbonates. Earth-Sci Rev 178:68–91
Gao P, Li S, He Z, Wo Y, Han Y, Li X (2020) Tectonic-sedimentary evolution of Guangyuan–Liangping paleo-rift in Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol 41:784–799 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Giorgioni M, Iannace A, D’Amore M, Dati F, Galluccio L, Guerriero V, Mazzoli S, Parente M, Strauss C, Vitale S (2016) Impact of early dolomitization on multi-scale petrophysical heterogeneities and fracture intensity of low-porosity platform carbonates (Albian-Cenomanian, southern Apennines, Italy). Mar Pet Geol 73:462–478
Godet A, Durlet C, Spangenberg JE, Föllmi KB (2016) Estimating the impact of early diagenesis on isotope records in shallow-marine carbonates: a case study from the Urgonian platform in western Swiss Jura. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 454:125–138
Hu Z, Hu W, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang L, Liao Z, Li W (2017) Resetting of Mg isotopes between calcite and dolomite during burial metamorphism: outlook of Mg isotopes as geothermometer and seawater proxy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 208:24–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.03.026
Hu Z, Hu W, Liu C, Sun F, Liu Y, Li W (2019) Conservative behavior of Mg isotopes in massive dolostones: from diagenesis to hydrothermal reworking. Sediment Geol 381:65–75
Hu Z, Bialik OM, Hohl SV, Xia Z, Waldmann ND, Liu C, Li W (2021) Response of Mg isotopes to dolomitization during fluctuations in sea level: constraints on the hydrological conditions of massive dolomitization systems. Sediment Geol 420:105922
Huo F, Wang X, Wen H, Xu W, Huang H, Jiang H, Li Y, Li B (2020) Genetic mechanism and pore evolution in high quality dolomite reservoirs of the Changxing-feixianguan formation in the northeastern Sichuan Basin China. J Petrol Sci Eng 194:107511
Jiang L, Worden RH, Cai C, Li K, Xiang L, Cai L, He X (2014) Dolomitization of gas reservoirs: the upper Permian Changxing and lower Triassic feixianguan formations, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. J Sediment Res 84:792–815
Jiang L, Worden RH, Cai CF, Shen AJ, He XY, Pan LY (2018) Contrasting diagenetic evolution patterns of platform margin limestones and dolostones in the lower Triassic feixianguan formation, Sichuan Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 92:332–351
Jiu B, Huang W, Mu N, He M (2020) Effect of hydrothermal fluids on the ultra-deep Ordovician carbonate rocks in Tarim Basin, China. J Pet Sci Eng 194:107445
Kaufmann B, Wendt J (2000) Calcite cement successions in middle Devonian (Givetian) carbonate mud buildups of the southern Ahnet Basin (Algerian Sahara). Carbonates Evaporites 15:149–161
Khodaei N, Rezaee P, Honarmand J, Abdollahi-Fard I (2021) Controls of depositional facies and diagenetic processes on reservoir quality of the Santonian carbonate sequences (Ilam formation) in the Abadan plain. Carbonates Evaporites, Iran, p 36
Land LS (1985) The origin of massive dolomite. J Geol Edu 33:112–125
Li Z, Goldstein RH, Franseen EK (2017) Meteoric calcite cementation: diagenetic response to relative fall in sea-level and effect on porosity and permeability, Las Negras area, southeastern Spain. Sediment Geol 348:1–18
Luo Z, Sun W, Han J (2012) Effect of Emei mantle plume on the conditions of Permian accumulation in middle-upper Yangtze area. Earth Sci Front 19:144–154 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma Y, Guo T, Zhao X, Cai X (2008) The formation mechanism of high-quality dolomite reservoir in the deep of Puguang gas field. Sci China Ser D 51:53–64
Ma X, Yang Y, Wen L, Luo B (2019) Distribution and exploration direction of medium- and large-sized marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petrol Explor Dev 46:1–15
Machel HG, Mountjoy EW (1986) Chemistry and environments of dolomitization—a reappraisal. Earth-Sci Rev 23:175–222
McCormack JM, Bahr A, Gerdes A, Tütken T, Prinz-Grimm P (2015) Preservation of successive diagenetic stages in Middle Triassic bonebeds: evidence from in situ trace element and strontium isotope analysis of vertebrate fossils. Chem Geol 410:108–123
McHargue TR, Price RC (1982) Dolomite from clay in argillaceous or shale-associated marine carbonates. J Sediment Res 52:873–886
Moore CH (2001) Carbonate reservoirs: porosity evolution and diagenesis in a sequence stratigraphic framework-charpter 7 diagenesis in the meteoric environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 145–183
Moore CH, Wade WJ (2013) Summary of early diagenesis and porosity modification of carbonate reservoirs in a sequence stratigraphic and climatic framework-charpter 9. Develop Sedimentol 67:207–238
Mou CL, Tan QY, Yu Q, Wang LQ (2003) The late Permian organic reefal oil pool section in Panlongdong, Xuanhan, Sichuan. Sediment Geol Tethyan Geol 23:60–64 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Mu S, Zhou M, Hua Y (1994) Dolomite genetic types in Feixianguan formation of lower Triassic series in northeast area of Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind 14(3):23–26 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Pan L, Hu A, Liang F, Jiang L, Hao Y, Feng Y, Shen A, Zhao J (2021) Diagenetic conditions and geodynamic setting of the middle Permian hydrothermal dolomites from southwest Sichuan Basin, SW China: insights from in situ U-Pb carbonate geochronology and isotope geochemistry. Mar Pet Geol 129:105080
Qiao Z, Janson X, Shen A, Zheng J, Zeng H, Wang X (2016) Lithofacies, architecture, and reservoir heterogeneity of tidal-dominated platform marginal oolitic shoal: an analogue of oolitic reservoirs of lower Triassic Feixianguan formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Mar Pet Geol 76:290–309
Qiu X, Mingyi HU, Zhonggui HU, Zhao E (2011) Analysis on sedimentary facies of Changxing formation reefs profile of Panlongdong in Xuanhan, Northeastern Sichuan Basin. Offshore Oil 31:39–44 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Raczek I, Jochum KP, Hofmann AW (2003) Neodymium and strontium isotope data for USGS reference materials BCR-1, BCR-2, BHVO-1, BHVO-2, AGV-1, AGV-2, GSP-1, GSP-2 and eight MPI-DING reference glasses. Geostand Newsl 27:173–179
Sequero C, Aurell M, Bádenas B (2019) Sedimentary evolution of a shallow carbonate ramp (Kimmeridgian NE Spain): unravelling controlling factors for facies heterogeneities at reservoir scale. Mar Pet Geol 109:145–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.018
Sibley DF (1982) The origin of common dolomite fabrics: clues from the Pliocene. J Sediment Res 52:1087–1100
Sibley DF (1991) Secular changes in the amount and texture of dolomite. Geology 19:151–154
Soleimani B, Moradi M, Ghabeishavi A, Mousavi A (2018) Permeability variation modeling and reservoir heterogeneity of Bangestan carbonate sequence, Mansouri oilfield, SW Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 34:143–157
Song H, Wignall PB, Tong J, Song H, Chen J, Chu D, Tian L, Luo M, Zong K, Chen Y, Lai X, Zhang K, Wang H (2015) Integrated Sr isotope variations and global environmental changes through the late Permian to early late Triassic. Earth Planet Sci Lett 424:140–147
Swart PK, Melim LA (2000) The origin of dolomites in tertiary sediments from the margin of Great Bahama Bank. J Sediment Res 70:738–748
Veizer J, Ala D, Azmy K, Bruckschen P, Buhl D, Bruhn F, Carden GAF, Diener A, Ebneth S, Godderis Y, Jasper T, Korte C, Pawellek F, Podlaha OG, Strauss H (1999) 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater. Chem Geol 161:59–88
Wang SY, Jiang XQ, Guan HL, Bao YJ (2009) Pore evolution of reservoirs of Feixianguan formation in Puguang gas field in northeasteen Sichuan. Pet Geol & Experi 31(1):26–30 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wang L, Hu W, Wang X, Cao J, Chen Q (2014) Seawater normalized REE patterns of dolomites in Geshan and Panlongdong sections, China: implications for tracing dolomitization and diagenetic fluids. Mar Pet Geol 56:63–73
Wang G, Li P, Hao F, Zou H, Yu X (2015) Origin of dolomite in the third member of Feixianguan formation (lower Triassic) in the Jiannan area, Sichuan Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol 63:127–141
Wei W, Chen D, Qing H, Qian Y (2017) Hydrothermal dissolution of deeply buried Cambrian dolomite rocks and porosity generation: integrated with geological studies and reactive transport modeling in the Tarim Basin, China. Geofluids 2017:1–19
Wu Q, Peng JN (2013) Burial and thermal histories of northeastern Sichuan Basin: a case study of well Puguang 2. Pet Geol & Experi 35(2):133–138 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Wu YS, Jiang HX, Liu LJ, Zhao R (2015) Revised sedimentary facies and lithostratigraphy of the upper Permian CHANGXING formation at Panlongdong, Xuanhan, Sichuan province. Acta Geol Sin 89:412–424 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Yin H, Jiang H, Xia W, Feng Q, Zhang N, Shen J (2014) The end-Permian regression in South China and its implication on mass extinction. Earth-Sci Rev 137:19–33
Zevin LS (1977) A method of quantitative phase analysis without standards. J Appl Crystallogr 10:147–150
Zhang P, Liu G, Cai C, Li M, Chen R, Gao P, Xu C, Wan W, Zhang Y, Jiang M (2019) Alteration of solid bitumen by hydrothermal heating and thermochemical sulfate reduction in the Ediacaran and Cambrian dolomite reservoirs in the Central Sichuan Basin, SW China. Precambrian Res 321:277–302
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M681379 to Z. Hu), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2021CDJQY-028 to Z. Liao) and the National Science Foundation of China (grants 41830425 to W. Hu; grants 41702129 to Z. Liao). This manuscript benefits from constructive comments and suggestions from two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Hu, W., Liao, Z. et al. Facies-dependent early diagenesis and hydrothermal reworking in dolostones: a case study on upper Permian and lower Triassic in northeast Sichuan Basin. Carbonates Evaporites 36, 63 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00730-9
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00730-9