Abstract
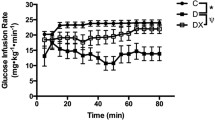
We hypothesized that a part of therapeutic effects of endurance training on insulin resistance is mediated by increase in cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial lactate transporter, monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1). Therefore, we examined the effect of 7 weeks endurance training on the mRNA and protein expression of MCT1 and MCT4 and their chaperon, CD147, on both sarcolemmal and mitochondrial membrane, separately, in healthy and type 2 diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced by injection of low dose of streptozotocin and feeding with high-fat diet. Insulin resistance was confirmed by homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance index and accuracy of two membranes separation was confirmed by negative control markers (glucose transporter 1 and cytochrome c oxidase. Real-time PCR and western blotting were used for mRNA and protein expression, respectively. Diabetes dramatically reduced MCT1 and MCT4 mRNA and their expression on sarcolemmal membrane whereas the reduction in MCT1 expression was less in mitochondrial membrane. Training increased the MCT1 mRNA and protein expression in both membranes and decreased insulin resistance as an adaptive consequence. In both tissues increase in CD147 mRNA was only parallel to MCT1 expression. The response of MCT1 on sarcolemmal and mitochondrial membranes was different between cardiac and skeletal muscles which indicate that intracellular lactate kinetic is tissue specific that allows a tissue to coordinate whole organism metabolism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew PH, Nigel TP (1999) The proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) family: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 343:281–299
Becker-immermann K, Berger M, Berchtold P, Gries FA, Herberg L, Schewenen M (1982) Treadmill training improves intravenous glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in fatty Zuckerrats. Diabetologia 22:468–474
Benton CR, Yoshida Y, Lally J, Han XX, Hatta H, Bonen A (2008) PGC-1α increases skeletal muscle lactate uptake by increasing the expression of MCT1 but not MCT2 or MCT4. Physiol Genomics 35:45–54
Bloomgarden MD (2005) Concepts of Insulin Resistance. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 3:284–293
Bonen A (2001) The expression of lactate transporters (MCT1 and MCT4) in heart and muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:6–11
Bonen A, Mio T, Dragana M, Catherine H, John JH, Andrew P (2000) Isoform-specific regulation of the lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 by contractile activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E1131–E1138
Brooks GA (2009) Cell-cell and intracellular lactate shuttles. J Physiol 23:5591–5600
Brooks GA, Dubouchaud H, Brown M, Sicurello JP, Butz CE (1999) Role of mitochondrial lactate dehydrogenase and lactate oxidation in the intracellular lactate shuttle. J Physiol 96:1129–1134
Brooks GA, Brown MA, Butz CE, Sicurello JP, Dubouchaud H (1999) Cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondria have a monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. J Appl Physiol 87(5):1713–1718
Butz CE, McClelland GB, Brooks GA (2004) MCT1 confirmed in rat striated muscle mitochondria. J Appl Physiol 97:1059–1066
Choi CS, Kim YB, LeeFN ZJM, Kahn BB, Youn JH (2002) Lactate induces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by suppressing glycolysis and impairing insulin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E233–E240
Defronzo RA, Simonson D, Ferrannini E (1982) Hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance: a common feature of type 2 (non-insulin dependent) and type 1 (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 23:313–319
Deora AA, Philp N, Hu J, Bok D, Rodriguez-Boulan E (2005) Mechanisms regulating tissue-specific polarity of monocarboxylate transporters and their chaperone CD147 in kidney and retinal epithelia. PNAS 45:16245–16250
DiGirolamo M, Newby FD, Lovejoy J (1992) Lactate production in adipose tissue: a regulated function with extraadipose implications. FASEB J 6:2405–2412
Dubouchaud H, Butterfield GE, Wolfel EE, Bergman BC, Brooks GA (2000) Endurance training, expression and physiology of LDH, MCT1 and MCT4 in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E571–E579
Dubouchaud H, Granier P, Mercier J, Le Peuch C, Prefaut C (1996) Lactate uptake by skeletal muscle sarcolemmal vesicles decreases after 4 wk of hindlimb unweighting in rats. J Appl Physiol 80:416–421
Enoki T, Yoshida Y, Hatta H, Bonen A (2003) Exercise training alleviates MCT1 and MCT4 reductions in heart and skeletal muscles of STZ induced diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol 94:2433–2438
Enoki T, Yoshida Y, Lally J, Hatta H, Bonen A (2006) Testosterone increases lactate transport, monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 and MCT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 1:433–443
Frøsig C, Rose AJ, Treebak JT, Kiens B, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF (2007) Effects of endurance exercise training on insulin signaling in human skeletal muscle: interactions at the level of PI3-K, Akt and AS160. Diabetes 56:2093–2102
Goodyear LJ, Hirshman MF, Knutson SM, Horton ED, Horton ES (1974) Effect of exercise training on glucose homeostasis in normal and insulin-deficient diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol 65:844–851
Gutmann L, Wahlefeld AW (1974) l-lactate determination with lactate dehydrogenase and NAD. Meth Enzym Anal 1464–1472
Hashimoto T, Hussien R, Cho HS, Kaufer D, Brooks GA (2008) Evidence for the mitochondrial lactate oxidation complex in rat neurons: demonstration of an essential component of brain lactate shuttles. PLoS One 3(8):e2915
Kelley KM, Hamann JJ, Navarre C, Gladden LB (2002) Lactate metabolism in resting and contracting canine skeletal muscle with elevated lactate concentration. J Appl Physiol 93:865–872
Kirk P, Wilson MC, Heddle C, Brown MH, Barclay AN, Halestrap AP (2000) CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression. EMBO J 19(15):3896–904
Kraniou GN, Cameron-Smith D, Hargreaves M (2006) Acute exercise and GLUT4 expression in human skeletal muscle: influence of exercise intensity. J Appl Physiol 101:934–937
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−Delta Delta C(T). Method 25:402–408
Liu H, Colavitti R, Rovira II, Finkel T (2005) Redox-dependent transcriptional regulation. Circ Res 97:967–974
Lombardi AM, Fabris R, Bassetto F, SerrR LA, Federspil G, Girard J, Vettor R (1999) Hyperlactatemia reduces muscle glucose uptake and GLUT-4 mRNA while increasing (E1a)PDH gene expression in rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 39:E922–E929
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
McCullagh KJ, Bonen A (1995) Reduced lactate transport in denervated rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 268:R884–R888
Metz L, Sirvent P, Py G, Brun JF, Fédou C, Raynaud E, Mercier J (2005) Relationship between blood lactate concentration and substrate utilization during exercise in type 2 diabetic postmenopausal women metabolism. Clin Exp 54:1102–1107
Miyamoto S, Chiorini JA, Urcelay E, Safer B (1996) Regulation of gene expression for translation initiation factor eIF-2 alpha: importance of the 3′ untranslatedregion. Biochem J 315:791–798
Mondon CE, Jones IR, Azhar S, Hollenbeck CB, Reaven GM (1992) Lactate production and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in fat and skeletal muscle from diabetic rats. Diabetes 41:1547–1554
O’Gorman DJ, Karlsson HK, McQuaid S, Yousif O, Rahman Y, Gasparro D, Glund S, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR, Nolan JJ (2006) Exercise training increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and GLUT4 (SLC2A4) protein content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 49:2983–2992
Pérez de Heredia F, Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2010) Hypoxia stimulates lactate release and modulates monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1, MCT2, and MCT4) expression in human adipocytes. Pflugers Arch-Eur J Physiol 459:509–518
Philp NJ, Ochrietor JD, Rudoy C, Muramatsu T, Linser PJ (2003) Loss of MCT1, MCT3, and MCT4 expression in the retinal pigment epithelium and neural retina of the 5A11/basigin-null mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1305–1311
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA (1963) The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1:785–789
Reed MJ, Meszaros K, Entes LJ, Claypool MD, Pinkett JG, Gadbois TM, Reaven GM (2000) A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism 49:1390–1394
Russell AP, Feilchenfeldt J, Schreiber S, Praz M, Crettenand A, Gobelet C, Meier CA, Bell DR, Kralli A, Giacobino JP, Deriaz O (2003) Endurance training in humans leads to fiber type-specific increases in levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 52:2874–2881
Schneiderhan W, Scheler M, Holzmann KH, Marx M, Gschwend JE, Bucholz M, Gress TM, Seufferlein T, Adler G, Oswald F (2009) CD147 silencing inhibits lactate transport and reduces malignant potential of pancreatic cancer cells in in vivo and in vitro models. Gut 58:1391–1398
Schwoch C, Pasoow H (1984) preparation and properties of human erythrocyte ghosts. Mol Cell Biochem 152(2):197–218
Sharma AK, Srinivasan BP (2009) Triple verses glimepiride plus metformin therapy on cardiovascular risk biomarkers and diabetic cardiomyopathy in insulin resistance type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Eur J Pharm Sci 38:433–444
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening Srinivasan. Pharmacol Res 52:313–320
Terada S, Tabata I (2004) Effects of acute bouts of running and swimming exercise on PGC-1alpha protein expression in rat epitrochlearis and soleus muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286:E208–E216
Ullah MS, Davies AJ, Halestrap AP (2006) The plasma membrane lactate transporter MCT4, but not MCT1, is up-regulated by hypoxia through a HIF-1-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem 281:9030–9037
Valenti D, de Bari L, Atlante A, Passarella S (2002) l-lactate transport into rat heart mitochondria and reconstruction of the l-lactate/pyruvate shuttle. Biochem J 364:101–104
Vettor R, Lombardi AM, Fabris R, Pagano C, Cusin I, Rohner JF, Federspil G, Jeanrenaud B (1997) Lactate Infusion in anesthetized rats produces insulin resistance in heart and skeletal muscles. Metabolism 46:684–690
Wincey C, Marks V (1961) A micro-method for measuring glucose using the autoanalyzer and glucose-oxidase. J Clin Pathol 14:558–559
Wright DC, Geiger PC, Han DH, Jones TE, Holloszy JO (2007) Calcium induces increases in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha and mitochondrial biogenesis by a pathway leading to p38 mitogen activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 82:18793–18799
Zhang F, Ye C, Li G, Ding W, Zhou W, Zhu H, Chen G, Luo T, Guang M, Liu Y, Zhang D, Zheng S, Yang J, Gu Y, Xie X, Luo M (2003) The rat model of type 2 diabetic mellitus and its glycometabolism character. Exp Anim 52(5):401–407
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Centre grant from the Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center of Tehran University of Medical Sciences. We also acknowledge all our collaborators.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikooie, R., Rajabi, H., Gharakhanlu, R. et al. Exercise-induced changes of MCT1 in cardiac and skeletal muscles of diabetic rats induced by high-fat diet and STZ. J Physiol Biochem 69, 865–877 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0263-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0263-6