Abstract
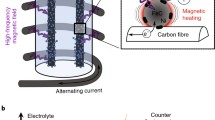
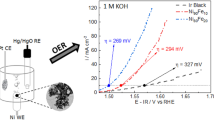
Today, hydrogen mainly originates from fossil sources (gas, oil, and coal). Room temperature water electrolysis is an interesting alternative for renewable electricity storage, even if it is well-known that high-temperature systems are more efficient. To address this issue, we studied different non-platinum group metal (non-PGM) catalysts for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) by recording cyclic voltamperograms with a rotating disk electrode set up. Physicochemical characterizations of Ni-based and FeNi3-based catalysts were performed using transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Ni synthesized by the hot injection method is a good catalyst for HER, yet still less active than Pt/C. FeNi3 with and without a Ni surface doping is very good OER catalysts, slightly better than commercial unsupported IrO2. Electrochemical tests under alternating magnetic field (AMF) using these nanoparticles are ongoing, as these materials are compatible with AMF activation.

Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00642-1
References
P.C.K. Vesborg, T.F. Jaramillo, Addressing the terawatt challenge: Scalability in the supply of chemical elements for renewable energy. RSC Adv. 2(21), 7933 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra20839c
I. Dincer, Environmental and sustainability aspects of hydrogen and fuel cell systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 31(1), 29–55 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/er.1226
S. Ehsan, M.A. Wahid, Hydrogen production from renewable and sustainable energy resources: Promising green energy carrier for clean development. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 57, 850–866 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.112
K. Zeng, D. Zhang, Recent progress in alkaline water electrolysis for hydrogen production and applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 36(3), 307–326 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2009.11.002
U. Bossel, Does a hydrogen economy make sense? IEEE. 94(10), 1826–1837 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2006.883715
J. Chi, H. Yu, Water electrolysis based on renewable energy for hydrogen production. Chin. J. Catal. 39(3), 390–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62949-8
L.F.L. Oliveira, S. Laref, E. Mayousse, A.A. Franco, A multiscale physical model for the transient analysis of PEM water electrolyzer anodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(29), 10215–10224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp23300b
S. Cherevko, T. Reier, A.R. Zeradjanin, Z. Pawolek, P. Strasser, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, Stability of nanostructured iridium oxide electrocatalysts during oxygen evolution reaction in acidic environment. Electrochem. Commun. 48, 81–85 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.08.027
S. Cherevko, S. Geiger, O. Kasian, N. Kulyk, J.P. Grote, A. Savan, B.R. Shrestha, S. Merzlikin, B. Breitbach, A. Ludwig, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, Oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions on Ru, RuO2, Ir, and IrO2 thin film electrodes in acidic and alkaline electrolytes: A comparative study on activity and stability. Catal. Today 262, 170–180 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.08.014
S. Geiger, O. Kasian, A.M. Mingers, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, S. Cherevko, Stability limits of tin-based electrocatalyst supports. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 3–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04079-9
O. Kasian, S. Geiger, M. Schalenbach, A.M. Mingers, A. Savan, A. Ludwig, S. Cherevko, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, Using instability of a non-stoichiometric mixed oxide oxygen evolution catalyst as a tool to improve its electrocatalytic performance. Electrocatalysis. 9(2), 139–145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-017-0394-6
F. Claudel, Degradation mechanisms of oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts: A combined identical-location transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. ACS Catal. 9(5), 4688–4698 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b00280
L. Sola-Hernandez, F. Claudel, F. Maillard, C. Beauger, Doped tin oxide aerogels as oxygen evolution reaction catalyst supports. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 4(45), 24331–24341 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.152
A. Damien, Hydrogène par électrolyse de l’eau, Tech. l’Ingénieur. (1992)
C. Niether, S. Faure, A. Bordet, J. Deseure, M. Chatenet, J. Carrey, B. Chaudret, A. Rouet, Improved water electrolysis using magnetic heating of FeC–Ni core–shell nanoparticles. Nat. Energy 3(6), 476–483 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-018-0132-1
A. Bordet, L. Lacroix, P. Fazzini, J. Carrey, K. Soulantica, B. Chaudret, Heterogeneous catalysis hot paper magnetically induced continuous CO2 hydrogenation using composite iron carbide nanoparticles of exceptionally high heating power. Communications. 55(51), 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201609477
J. Carrey, B. Mehdaoui, M. Respaud, Simple models for dynamic hysteresis loop calculations of magnetic single-domain nanoparticles: Application to magnetic hyperthermia optimization. J. Appl. Phys. 109(8), 083921 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3551582
M. Schalenbach, O. Kasian, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, An alkaline water electrolyzer with nickel electrodes enables efficient high current density operation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 43(27), 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.219
M. Görlin, P. Chernev, J. Ferreira, D. Arau, T. Reier, S. Dresp, B. Paul, R. Kra, H. Dau, P. Strasser, Oxygen evolution reaction dynamics, faradaic charge efficiency, and the active metal redox states of Ni−Fe oxide water splitting electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 5603–5614 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b00332
M. Görlin, J. Ferreira, D. Arau, H. Schmies, D. Bernsmeier, S. Dresp, M. Gliech, Z. Jusys, P. Chernev, R. Kraehnert, H. Dau, P. Strasser, Tracking catalyst redox states and reaction dynamics in Ni−Fe oxyhydroxide oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts: The role of catalyst support and electrolyte pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(5), 2070–2082 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b12250
M. Görlin, P. Chernev, P. Paciok, C.-W. Tai, F.A. de Jorge, T. Reier, M. Heggen, R. Dunin-Borkowski, P. Strasser, H. Dau, Formation of unexpectedly active Ni–Fe oxygen evolution electrocatalysts by physically mixing Ni and Fe oxyhydroxydes. Chem. Commun. 55, 818–821 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc06410e
F. Moureaux, P. Stevens, G. Toussaint, M. Chatenet, Development of an oxygen-evolution electrode from 316L stainless steel: Application to the oxygen evolution reaction in aqueous lithium e air batteries. J. Power Sources 229, 123–132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.11.133
F. Moureaux, P. Stevens, G. Toussaint, M. Chatenet, Environmental timely-activated 316L stainless steel: A low cost , durable and active electrode for oxygen evolution reaction in concentrated alkaline environments. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 258, 117963 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117963
D. De Masi, J.M. Asensio, P. Fazzini, L. Lacroix, B. Chaudret, Engineering iron–nickel nanoparticles for magnetically induced CO2 methanation in continuous flow. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(15), 1–6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201913865
R. Chattot, O. Le Bacq, V. Beermann, S. Kühl, J. Herranz, S. Henning, L. Kühn, T. Asset, L. Guétaz, G. Renou, J. Drnec, P. Bordet, A. Pasturel, A. Eychmüller, T.J. Schmidt, P. Strasser, L. Dubau, F. Maillard, Surface distortion as a unifying concept and descriptor in oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 17(9), 827–833 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-018-0133-2
G. Cognard, G. Ozouf, C. Beauger, G. Berthomé, D. Riassetto, L. Dubau, R. Chattot, M. Chatenet, F. Maillard, Benefits and limitations of Pt nanoparticles supported on highly porous antimony-doped tin dioxide aerogel as alternative cathode material for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 201, 381–390 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.010
Y. Garsany, J. Ge, J. St-Pierre, R. Rocheleau, K.E. Swider-Lyons, Standardizing thin-film rotating disk electrode measurements of the oxygen reduction activity of Pt/C. ECS Trans. 58(1), 3–14 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1149/05801.0003ecst
Y. Garsany, J. Ge, J. St-pierre, R. Rocheleau, Analytical procedure for accurate comparison of rotating disk electrode results for the oxygen reduction activity of Pt/C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161(5), 628–640 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.036405jes
Y. Garsany, I.L. Singer, K.E. Swider-lyons, Impact of film drying procedures on RDE characterization of Pt/VC electrocatalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 662(2), 396–406 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.09.016
B.G. Pollet, J.T.E. Goh, The importance of ultrasonic parameters in the preparation of fuel cell catalyst inks. Electrochim. Acta 128, 292–303 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.160
B.G. Pollet, Let’s not ignore the ultrasonic effects on the preparation of fuel cell materials. Electrocatalysis. 5(4), 330–343 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-014-0211-4
H.A. El-sayed, A. Weiß, L.F. Olbrich, G.P. Putro, H.A. Gasteiger, OER catalyst stability investigation using RDE technique: A stability measure or an artifact ? J. Electrochem. Soc. 166(8), 458–464 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0301908jes
A. Zadick, L. Dubau, N. Sergent, G. Berthomé, M. Chatenet, Huge instability of Pt/C catalysts in alkaline medium. ACS Catal. 5(8), 4819–4824 (2015) 1–9
F. Arteaga-cardona, K. Rojas-rojas, R. Costo, M.A. Mendez-rojas, Improving the magnetic heating by disaggregating nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 663, 636–644 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.285
M. Schalenbach, O. Kasian, M. Ledenecker, F.D. Speck, A.M. Mingers, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, S. Cherevko, The electrochemical dissolution of noble metals in alkaline media. Electrocatalysis. 9(2), 153–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-017-0438-y
E.S. Davydova, S. Mukerjee, D.R. Dekel, Electrocatalysts for hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline electrolytes. ACS Catal. 8(7), 6665–6690 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b00689
Y. Qiu, L. Xin, W. Li, Electrocatalytic oxygen evolution over supported small amorphous Ni−Fe nanoparticles in alkaline electrolyte. ACS Pub. 30(26), 7893–7901 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/la501246e
N. Danilovic, R. Subbaraman, D. Strmcnik, K. Chang, A.P. Paulikas, V.R. Stamenkovic, N.M. Markovic, Enhancing the alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction activity through the bifunctionality of Ni(OH)2/metal catalysts**. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(50), 12495–12498 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201204842
Acknowledgments
The LPCNO authors thank ERC Advanced Grant (MONACAT 2015-694159). The LPCNO is acknowledged for the NP syntheses. Christian Beauger, from the PERSEE group of ARMINES in Sophia Antipolis, is greatly acknowledged for having provided the ATO support used herein.
Funding
This work has been performed in the frame of the Hy-WalHy project, funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR-1-CE05-0017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vivien Gatard did all the electrochemical tests, the TEM pictures of the Ni-based catalysts with the help of Marian Chatenet, and helped doing ICP-MS measurements with Vincent Martin. Déborah De Masi and Irene Mustieles Marin did the FeNi3 and the FeNi3@Ni syntheses while Pier-Francesco Fazzini characterized them with TEM pictures. Raphaël Chattot designed and performed the Ni-based material syntheses. Juan Manuel Asensio Revert did the FeC@Ni synthesis. Thierry Encinas performed all the XRD measurements. VG, JD, and MC essentially wrote and reviewed the contribution, with the help of Stéphane Faure, Julian Carrey, and Bruno Chaudret.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatard, V., De Masi, D., Chattot, R. et al. FeNi3 and Ni-Based Nanoparticles as Electrocatalysts for Magnetically Enhanced Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Electrocatalysis 11, 567–577 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-020-00616-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-020-00616-9