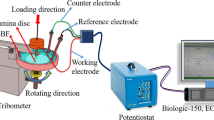
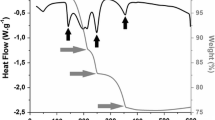
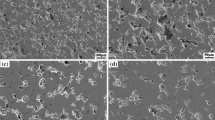
Abstract
Porous titanium (Ti) and its alloys are promising materials for orthopedic applications due to their low elastic modulus, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. In this study, the porous Ti–xNb–5Ag (x = 25, 30 and 35 wt%) alloys were synthesized using the powder metallurgy approach. The effects of Nb content on the porosity, mechanical properties, and electrochemical corrosion behavior of the alloys were investigated. XRD analysis revealed that the porous alloys mainly consist of α-Ti, β-Ti, intermetallic compound (Ti4Nb), and oxides of TiO2 and NbO phases. Porous alloys possess the porosity ranging from 57 to 65%, due to the addition of NH4HCO3 (45 wt%). Increase in Nb content lead to a reduction in the elastic modulus and compression strengths of the sintered porous Ti–xNb–5Ag alloys. All three developed porous Ti–xNb–5Ag alloys show the optimum combination of elastic modulus and compression strength, which is suitable for orthopedic applications. These porous alloys exhibit excellent electrochemical corrosion resistance in the simulated body fluids, and the samples having low porosity exhibit higher corrosion resistance than high-porosity samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geetha M, Singh A K, Asokamani R, and Gogia A K, Prog Mater Sci54 (2009) 397.
Spoerke E D, Murray N G, Li H, Brinson L C, Dunand D C, and Stupp S I, Acta Biomater.1 (2005) 523.
Gurappa I, Mater Charact49 (2002) 73.
Gao Z, Li Q, He F, Huang Y, and Wan Y, Mater Des42 (2012) 13.
Majumdar P, Singh S B, Dhara S, and Chakraborty M, Mater Sci Eng C46 (2015) 62.
Yang D, Guo Z, Shao H, Liu X, and Ji Y, Procedia Eng.36 (2012) 160.
Wang X, Li S, Jia M, Hao Y, Yang R, and Guo Z, Chin J Mater Res24 (2010) 378.
Aguilar C, Guerra C, Lascano S, Guzman D, Rojas P A, Thirumurugan M, Bejar L, and Medina A, Mater Sci Eng C58 (2016) 420.
Chen M, Zhang E, and Zhang L, Mater Sci Eng C. 62 (2016) 350.
Takahashi M, Kikuchi M, and Takada Y, Dent Mater J21 (2002) 270.
Lee C M, Ju C P, and Lin J H C, J Oral Reha29 (2002) 314.
Nazari K A, Nouri A, and Hilditch T, J Mech Beh Bio75 (2017) 33.
Liu Q, Meng Q, Guo S, and Zhao X, Prog Nat Sci Mater Inter23 (2013) 562.
Wang Y B, Zheng Y F, Mater Lett62 (2008) 269.
Xu L J, Chen Y Y, Liu Z G, and Kong F T, J Alloys Compd453 (2008) 320.
Hsu H-C, Wu S-C, Hsu S-K, Tsai M-S, Chang T-Y, and Ho W-F, Mater Des47 (2013) 21.
Yue-qin W, Jie T A O, Jin-long Z, and Tao W, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China.21 (2010) 1074.
Oliveira C S S, Griza S, de Oliveira M V, Ribeiro A A, and Leite M B, Powder Technol.281 (2015) 91.
Yılmaz E, Gökçe A, Findik F, Gulsoy H O, and İyibilgin O, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater87 (2018) 59.
Rao X, Chu C L, and Zheng Y Y, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater34 (2014) 27.
Murray N G D, and Dunand D C, Act Mater52 (2004) 2279.
Murr L E, Gaytan S M, Medina F, Martinez E, Martinez J L, Hernandez D H, Machado B I, Ramirez D A, and Wicker R B, Mater Sci Eng A. 527 (2010) 1861.
Wen C E, Mabuchi M, Yamada Y, Shimojima K, Chino Y, and Asahina T, Scr Mater.45 (2001) 1147.
Xu J L, Tao S C, Bao L Z, Luo J M, and Zheng Y F, Mater Sci Eng C.97 (2019) 156.
Li Y H, Chen N, Cui H T, and Wang F, J Alloys Compd723 (2017) 967.
Kokubo T, and Takadama H, Biomaterials27 (2006) 2907.
Dercz G, and Matuła I, Mater. Tehnol.51 (2017) 795.
Wen M, Wen C, Hodgson P, and Li Y, Mater Des.56 (2014) 629.
Staiger M P, Pietak A M, Huadmai J, and Dias G, Biomaterials.27 (2006) 1728.
Xie F, He X, Cao S, Mei M, and Qu X, Electrochim Acta.105 (2013) 121.
Bai Y, Li S J, Prima F, Hao Y L, and Yang R, Appl. Surf. Sci.258 (2012) 4035.
Lu J, Zhang Y, Huo W, Zhang W, Zhao Y, and Zhang Y, Appl Surf Sci.434 (2018) 63.
Acknowledgment
One of the authors Shivaram M.J wishes to acknowledge MHRD, Govt. of India, for providing research fellowship. The author expresses gratitude to Prof. Rajendra Udupa, Department of Metallurgical and Materials engineering, NITK Surathkal, for his technical inputs and suggestions. Authors also would like to thank Dr. R.B. Mane (MSME, IITH) for helping partially in developing alloys.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shivaram, M.J., Arya, S.B., Nayak, J. et al. Electrochemical Corrosion and Impedance Studies of Porous Ti–xNb–Ag Alloy in Physiological Solution. Trans Indian Inst Met 73, 921–928 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01904-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01904-0