Abstract
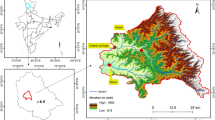
Mendoza is the province that has the largest irrigated area in Argentina where water resources depend mainly on snowmelt and glacier melting in the closed Andes Mountain. In this region the Blanco River Basin is one of the most important, covering about 300 km2 flowing from the highest peaks to Potrerillos Dam (1300 masl). The objective of this work was to make a preliminary characterization of stable isotopes in surface and groundwater, ice and snowmelt to contribute to a better understanding of the hydrologic cycle in the region, using a Los Gatos DLT-100 analyzer. Hydrochemical analyses were performed on 157 samples. The isotopic composition of rain water is more enriched than streamwater, clearly indicating that the stream recharge sources are at higher altitude. The discharge regime of the streams indicates that snowmelt is the main water origin, and considering the theoretical evolution of isotopes in meltwater, the composition of streams corresponds to the first meltwater, without fractionation. Then, it is more depleted than the original snow. The ice isotopic composition is more enriched than streamwater, indicating that snowmelt is the main recharge source. The hydrochemical results indicate the importance of geology in determining streamwater composition, which is integrated with isotopic data to achieve a better comprehension of the hydrological system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott MD, Lini A, Bierman PR (2000) δ18O, δD and 3H measurement constrain groundwater recharge patterns in an upland fracture bedrock aquifer, Vermont, USA. J Hydrol 228:101–112
Aggarwal PK, Gat JR, Froehlich KFO (2005) Isotopes in the water cycle: past, present and future of a developing science. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Netherlands
Alvarez A, Fasciolo G, Barbazza C, Lorenzo F, Balanza ME (2008) Impactos en el agua subterránea de un sistema de aprovechamiento de efluentes para riego. El sistema Paramillo. Lavalle Mendoza. Rev Fac Cienc Agrar 40:61–81
Alvarez A, D’Elía M, Paris M, Fasciolo G, Barbazza C (2011) Evaluación de la contaminación de acuíferos producida por actividades de saneamiento y re-uso de efluentes en el norte de la provincia de Mendoza. Rev Fac Cienc Agrar 43:19–39
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Auge MP (2004) Regiones hidrogeológicas. República Argentina y provincias de Buenos Aires, Mendoza y Santa Fe. La Plata. http://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/bitstream/handle/10915/15909/Documento_completo.pdf?sequence=1. Accessed 22 May 2015
Blasch K, Bryson J (2007) Distinguishing sources of ground water recharge by using δ2H and δ18O. Ground Water 45:294–308
Cambalach and Waterloo Hydrogeologic (2003) Water quality data analysis, plotting and modeling; Aquachem user’s manual v.4.0, Co. Developed by Lukas Calmbach and Waterloo Hydrogeologic Inc., USA
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Press/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Congjian S, Weihong L, Yaning C, Xingong L, Yuhui Y (2015) Isotopic and hydrochemical composition of runoff in the Urumqi River, Tianshan Mountains, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, in press. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4144-x
Cortés JM (2000) Fallas cuaternarias oblicuas al frente montañoso en la Cordillera Frontal de Mendoza (34º–34º30′S). Revista Cuaternario y Ciencias Ambientales Special Paper 4:57–62
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Dapeña C (2008) Isótopos Ambientales Livianos: su aplicación en hidrología e hidrogeología. PhD Tesis, University of Buenos Aires
Drovandi A, Zuluaga J, Filippini M, Cónsoli D, Valdes A, Nacif C, Dediol C, Morsucci A (2010) Evaluación de la calidad del agua en el Embalse Potrerillos y Cuenca del Río Blanco, Provincia de Mendoza. III Congreso Internacional sobre Gestión y Tratamiento Integral del Agua. Córdoba, Argentina. Proceedings: 1–39
Edjah AKM, Akiti TT, Osae S, Adotey D, Glover ET (2015) Hydrogeochemistry and isotope hydrology of surface water and groundwater systems in the Ellembelle district, Ghana, West Africa. Appl Water Sci, in press. doi: 10.1007/s13201-015-0273-3
Frisbee M, Phillips F, Campbell A, Hendrickx J, Engle E (2010) Modified passive capillary samplers for collecting samples of snowmelt infiltration for stable isotope analysis in remote, seasonally inaccessible watersheds 2: field evaluation. Hydrol Process 24:834–849
Gonfiantini R (1978) Standards for stable isotopes measurements in natural compounds. Nature 271:534–536
Harvey FE, Sibray SS (2001) Delineating groundwater recharge from leaking irrigation canals using water chemistry and isotopes. Groundwater 39:408–421
Hem J (1992) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. USGS, Water Supply paper, Virginia, p 2254
Heredia N, Farias P, García-Sansegundo J, Giambiagi L (2012) The basement of the Andean frontal cordillera in the Cordón del Plata (Mendoza, Argentina): geodynamic evolution. Andean Geol 39:242–257
Hernández J, Martinis N (2006) Particularidades de las cuencas hidrogeológicas explotadas con fines de riego en la Provincia de Mendoza, Instituto Nacional del Agua-Centro Regional Andino, Mendoza. http://www.riegoyfertirriego.com.ar/III_Jornadas/Trabajospresentados/Hernandez.pdf. Accessed 23 May 2015
Kendall C, McDonnell JJ (1998) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier Science BV, Amsterdam
Kirchner JW (2003) A double paradox in catchment hydrology and geochemistry. Hydrol Process 17:871–874
Klaus J, McDonnell JJ (2013) Hydograph separation using stable isotopes: review and evaluation. J Hydrol 505:47–64
Kurás P, Weiler M, Alila Y (2008) The spatiotemporal variability of runoff generation and groundwater dynamics in a snow-dominated catchment. J Hydrol 352:50–66
Lee J, Feng X, Faiia A, Posmentier E, Kirchner J, Osterhuber R, Taylor S (2010) Isotopic evolution of a seasonal snowcover and its melt by isotopic exchange between liquid water and ice. Chem Geol 270:126–134
Lis G, Wassenaar LI, Hendry MJ (2008) High-precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Anal Chem 80:287–293
Mcdonell JJ (2003) Where does water goes when it rains? Moving beyond the variable source are concept of rainfall runoff response. Hydrol Process 17:1869–1875
Morabito JA, Hernandez R, Salatino SE, Mirabile CM (2009) Calculo de las necesidades de riego de los principales cultivos del oasis Sur. Mendoza, Argentina. INA Papers. http://www.ina.gob.ar/pdf/CRA-RYD-22_Morabito_ETc_zona_sur.pdf. Accessed 26 May 2015
Panarello H, Dapeña C (1996) Mecanismos de recarga y salinización en las Cuencas de los Rios Mendoza y Tunuyan, República Argentina. Proceedings of XII Congreso Geologico de Bolivia 2:1–18
Panarello H, Dapeña C, Garcia E, Alvarez, A (1993) Estudio isotópico e hidroquímico de los acuíferos de la Cuenca Norte mendocina, Rios Mendoza y Tunuyan. Proceedings of XII Congreso Geologico Argentino, Mendoza
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)-A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations: U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259
Penna D, Ahmad M, Birks SJ, Bouchaou L, Brenčič M, Butt S, Holko L, Jeelani G, Martínez DE, Melikadze G, Shanley J, Sokratov SA, Stadnyk T, Sugimoto A, Vreča P (2014) A new method of snowmelt sampling for water stable isotopes. Hydrol Process 28:5637–5644
Polanski J (1963) Estratigrafía, neotectónica y geomorfología del Pleistoceno pedemontano entre los ríos Diamante y Mendoza. Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina 17:127–349
Qian H, Wu J, Zhou Y, Li P (2014) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol Process 28:3554–3562
Ramos VA (1988) The tectonic of the Central Andes: 30–33˚ S latitude. In: Clark S, Burchfiel D (ed) Processes in continental litospheric deformation, Geological Society of America, Special Paper 218:31–54
Tekleab S, Wenninger J, Uhlenbrook S (2013) Identifying residence times and streamflow generation processes using 18O and 2H in meso-scale catchments in the Abay/Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc Dis 10:10333–10377
Yeh HF, Lee CH, Hsu KC (2011) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes for the characteristics of groundwater recharge: a case study from the Chih-Pen Creek basin, Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 62:393–402
Zuluaga J, Filippini M, Drovandi A, Berrmejillo A, Morsucci A, Valdés A, Cónsoli D (2008) Caracterización de lo contaminantes del Río Blanco previo a su descarga en el Embalse Potrerillos. Proceedings of V Congreso Argentino de Embalses y Aprovechamiento Hidroelectrico, Tucumán
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) for the financial support (CRP 16202/RO) and specially thank Eng. Enrique Montero from “Departamento General de Irrigación” of Mendoza province for the sampling of wells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on "3RAGSU", guest edited by Daniel Emilio Martinez.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massone, H., Martinez, D., Vich, A. et al. Snowmelt contribution to the sustainability of the irrigated Mendoza’s Oasis, Argentina: an isotope study. Environ Earth Sci 75, 520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5141-9