Abstract
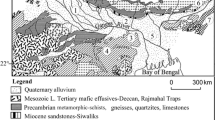
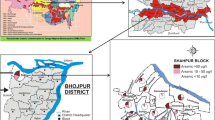
The authors’ survey of the Ganga–Meghna–Brahmaputra (GMB) plain (area 569,749 km2; population >500 million) over the past 20 years and analysis of more than 220,000 hand tube-well water samples revealed groundwater arsenic contamination in the floodplains of the Ganga–Brahmaputra river (Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Assam) in India and the Padma–Meghna–Brahmaputra river in Bangladesh. On average, 50 % of the water samples contain arsenic above the World Health Organization guideline value of 10 μg/L in India and Bangladesh. More than 100 million people in the GMB plain are potentially at risk. The authors’ medical team screened around 155,000 people from the affected villages and registered 16,000 patients with different types of arsenical skin lesions. Arsenic neuropathy and adverse pregnancy outcomes have been recorded. Infants and children drinking arsenic-contaminated water are believed to be at high risk. About 45,000 biological samples analyzed from arsenic-affected villages of the GMB plain revealed an elevated level of arsenic present in patients as well as non-patients, indicating that many are sub-clinically affected. In West Bengal and Bangladesh, there are huge surface water in rivers, wetlands, and flooded river basins. In the arsenic-affected GMB plain, the crisis is not over water scarcity but about managing the available water resources.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed S, Sengupta MK, Mukherjee A, Hossain MA, Das B, Nayak B, Pal A, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Dutta RN, Chatterjee G, Mukherjee A, Srivastava R, Chakraborti D (2006a) Groundwater arsenic contamination in middle Ganga plain, Uttar Pradesh-India: a future danger? Sci Total Environ 370:310–332
Ahamed S, Sengupta MK, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Mukherjee A, Hossain MA, Das B, Nayak B, Zafar A, Kabir S, Islam TS, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman MM, Chakraborti D (2006b) An eight-year study report on groundwater arsenic contamination and health effect in Eruani village, Bangladesh and an approach for its mitigation. J Health Popul Nutr 24(2):129–141
Ahmad S, Sayed MH, Barua S, Khan MH, Faruquee MH, Jalil A, Hadi SA, Talukder HK (2001) Arsenic in drinking water and pregnancy outcome. Environ Health Perspect 109(6):629–631
Aschengrau A, Zierler S, Cohen A (1989) Quality of community drinking water and the occurrence of spontaneous abortion. Arch Environ Health 44:283–290
Bhattacharya P, Chatterjee D, Jacks G (1997) Occurrence of arsenic-contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from the Delta plain, Eastern India: options for a safe drinking water supply. Water Res Dev 13:79–92
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Paul K, Chowdhury UK, Sengupta MK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Saha KC, Mukherjee SC (2002) Arsenic calamity in the Indian sub-continent—what lessons have been learned? Talanta 58:3–22
Chakraborti D, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Sengupta MK, Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Chakraborty AK, Basu GK (2003) Arsenic groundwater contamination in middle Ganga plain, Bihar, India: a future danger. Environ Health Perspect 111(9):1194–1201
Chakraborti D, Sengupta MK, Rahman MM, Ahamed S, Chowdhury UK, Hossain MA, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Saha KC, Dutta RN, Quamruzzaman Q (2004) Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in the Ganga–Meghna–Brahmaputra plain. J Environ Monit 6:75N–83N
Chakraborti D, Singh EJ, Das B, Hossain MA, Shah BA, Nayak B, Ahamed S, Sengupta MK, Singh NR (2008) Groundwater arsenic contamination in Manipur, one of the seven North Eastern Hill state in India: a future danger. Environ Geol 56:381–390
Chakraborti D, Das B, Rahaman MM, Chowdhury UK, Biswas B, Goswami AB, Nayak B, Pal A, Sengupta MK, Ahamed S, Hossain A, Basu G, Roy Chowdhury T, Das D (2009) Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in the state of West-Bengal, India: a 20 years study report. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:542–551
Chowdhury UK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury TR, Samanta G, Mandal BK, Basu GK, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Saha KC, Mukherjee SC, Roy S, Kabir S, Quamruzzaman Q, Chakraborti D (2000) Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh and West Bengal India. Environ Health Perspect 108(5):393–396
Datta DV, Kaur MK (1976) Arsenic content of tubewell water in villages in northern India. A concept of arsenicosis. J Assoc Physicians India 24:599–604
Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE), Bangladesh (1999). Groundwater studies for arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Rapid Investigation Phase Final Report. Report prepared by Mott MacDonald Ltd. and the British Geological Survey for the Department of Public Health Engineering (Bangladesh) and the Department for International Development (UK)
Dhar RK, Biswas BK, Samanta G, Mandal BK, Chakraborti D, Roy S, Jafar A, Islam A, Ara G, Kabir S, Khan AW, Ahmed SA, Hadi SA (1997) Groundwater arsenic calamity in Bangladesh. Curr Sci 73(1):48–59
Feldman RG, Niles CA, Kelly-Hayes M, Sax DS, Dixon WJ, Thomson DJ, Landau E (1979) Peripheral neuropathy in arsenic smelter workers. Neurology 29:939–944
Galer BS (1998) Painful polyneuropathy. In: Backonja MM (ed) Neuropathic Pain Syndromes, vol 16. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 91–811
Garai R, Chakraborti AK, Dey SB, Saha KC (1984) Chronic arsenic poisoning from tubewell water. J Ind Med Assoc 82(1):34–35
Harvey CF, Swartz CH, Badruzzaman ABM, Keon-Blute N, Yu W, Ali MA, Jay J, Beckie R, Niedan V, Brabander D, Oates PM, Ashfaque KN, Islam S, Hemond HF, Ahmed MF (2002) Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 98:1602–1606
Islam FS, Gault AG, Boothman C, Polya DA, Charnok JM, Chatterjee D, Lloyd JR (2004) Role of metal reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature 430:68–71
Mandal BK, Roy Chowdhury T, Samanta G, Basu GK, Chowdhury PP, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Karan NK, Dhar RK, Tamili DK, Das D, Saha KC, Chakraborti D (1996) Arsenic in groundwater in seven districts of West Bengal, India-the biggest arsenic calamity in the world. Curr Sci 170:976–986
Mukherjee SC, Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Sengupta MK, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Saha KC, Chakraborti D (2003) Neuropathy in arsenic toxicity from groundwater arsenic contamination in West Bengal-India. J Environ Sci Health A38(1):165–183
Mukherjee SC, Saha KC, Pati S, Dutta RN, Rahman MM, Sengupta MK, Ahamed S, Lodh D, Das B, Hossain MA, Nayak B, Palit SK, Kaies I, Barua AK, Asad KA, Mukherjee A, Chakraborti D (2005) Murshidabad—one of the nine groundwater arsenic affected districts of West Bengal, India. Part II: dermatological neurological and obstetric findings. Clin Toxicol 43:835–848
Nickson R, McArthur J, Burgess W, Ahmed KM, Ravenscroft P, Rahman M (1998) Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature 395:338
Nordstrom S, Beckman L, Nordenson I (1979) Occupational and environmental risks in and around a smelter in northern Sweden. V. Spontaneous abortion among female employees and decreased birth weight in their offspring. Hereditas 90:291–296
NRC (National Research Council) (2001) Arsenic in drinking water, Prepublication Copy, National Academy Press, Washington DC
NRC National Research Council) (1993) Arsenic in drinking water, National Academy Press, Washington DC; National Research Council, USA
Post Conference Report (1995) Experts opinion, recommendation and future planning for groundwater problem of West Bengal: school of environmental studies. Jadavpur University, Calcutta
Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Mukherjee SC, Mondal BK, Paul K, Lodh D, Chanda CR, Basu GK, Saha KC, Roy S, Das R, Palit SK, Quamruzzaman Q, Chakraborti D (2001) Chronic arsenic toxicity in Bangladesh and West Bengal-India—a review and commentary. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 39(7):683–700
Roy Chowdhury T, Basu GK, Mandal BK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury UK, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Roy SL, Saha KC, Roy S, Kabir S, Zaman QQ, Chakraborti D (1999) Arsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta. Nature 401:545–546
Saha KC (2003) Diagnosis of arsenicosis. J Environ Sci Health A38:255–272
Shrestha RR, Surestha MP, Upadhyay NP, Pradhan R, Maskey A, Maharjan M, Tuladhar S, Dahal BM, Shrestha K (2003) Groundwater arsenic contamination its health impact and mitigation program in Nepal. J Environ Sci Health 38(1):185–200
Yang CY, Chang CC, Tsai SS, Chuang HY, Ho CK, Wu TN (2003) Arsenic in drinking water and adverse pregnancy outcome in an arseniasis-endemic area in northeastern Taiwan. Environ Res 91:29–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborti, D., Rahman, M.M., Das, B. et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination in Ganga–Meghna–Brahmaputra plain, its health effects and an approach for mitigation. Environ Earth Sci 70, 1993–2008 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2699-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2699-y