Abstract
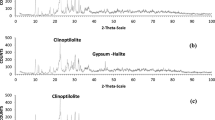
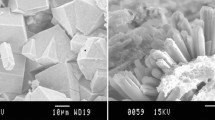
The removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution by two Brazilian rocks that contain zeolites—amygdaloidal dacite (ZD) and sandstone (ZS)—was examined by batch experiments. ZD contains mordenite and ZS, stilbite. The effects of contact time, concentration of metal in solution and capacity of Na+ to recover the adsorbed metals were evaluated at room temperature (20°C). The sorption equilibrium was reached in the 30 min of agitation time. Both materials removed 100% of Pb2+ from solutions at concentrations up to 50 mg/L, and at concentrations larger than 100 mg/L of Pb2+, the adsorption capacity of sandstone was more efficient than that of amygdaloidal dacite due to the larger quantities and the type of zeolites (stilbite) in the cement of this rock. All adsorbed Pb2+ was easily replaced by Na+ in both samples. The analysis of the adsorption models using nonlinear regression revealed that the Sips and the Freundlich isotherms provided the best fit for the ZS and ZD experimental data, respectively, indicating the heterogeneous adsorption surfaces of these zeolites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed IAM, Young SD, Crout NMJ (2006) Time-dependent sorption of Cd2+ on CaX zeolite: experimental observations and model predictions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:4850–4861. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2006.07.011
Álvarez-Ayuso E, García-Sánchez A, Querol X (2003) Purification of metal electroplating waste waters using zeolites. Water Res 37:4855–4862. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.08.009
An HK, Park BY, Kim DS (2001) Crab shell for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Water Res 35(15):3551–3556
Armbruster T, Gunter ME (2001) Crystal structures of natural zeolites. In: Bish DL, Ming DW (ed) Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 45. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, DC, pp 1–67
Bailey SE, Olin TJ, Bricka M, Adrian DD (1999) A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res 33(11):2469–2479
Barrer RM (1978) Zeolites and clay minerals as sorbents and molecular sieves. Academic Press, London
Bektas N, Kara S (2004) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by natural clinoptilolite: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Separ Purif Tech 39:189–200. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2003.12.001
Bosso ST, Enzweiler J (2002) Evaluation of heavy metal removal from aqueous solution onto scolecite. Water Res 36:4795–4800
Breck DW (1984) Zeolite Molecular Sieve. John Wiley and Son, New York
Castaldi P, Santona L, Enzo S, Melis P (2008) Sorption processes and XRD analysis of a natural zeolite exchanged with Pb2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ cations. J Hazard Mater 156(1–3):428–434. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.040
Chabani M, Amrane A, Bensmaili A (2009) Equilibrium sorption isotherms for nitrate on resin Amberlite IRA 400. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):27–33. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.08.091
Chen Z, Ma W, Han M (2008) Biosorption of nickel and cooper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): application of isotherm and kinetic models. J Hazard Mater 155:327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.064
Colella C (1996) Ion-exchange equilibria in zeolite minerals. Miner Deposita 31:554–562
Çoruh S (2008) The removal of zinc ions by natural and conditioned clinoptilolites. Desalination 225:41–57
Curkovic L, Cerjan-Stefanovic S, Filipan T (1997) Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites. Water Res 31:1379–1382
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interf Sci 280:309–314. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.028
Habuda-Stanic M, Kuleš M, Kalajdžca B, Romic Z (2007) Quality of groundwater in eastern Croatia. The problem of arsenic pollution. Desalination 210:157–162. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.05.040
Han R, Zou W, Li H, Li Y, Shi J (2006) Copper(II) and lead(II) removal from aqueous solution in fixed-bed columns by manganese oxide coated zeolite. J Hazard Mater B137:934–942. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.016
Ho YS, Porter JF, McKay G (2002) Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 141:1–33
Janasi VA, Negri FA, Montanheiro TJ, Freitas VA, Rocha BC, Reis PM (2007) Geochemistry of the eocretacic basalt magmatism in the Piraju-Ourinhos region, SE Brazil, and implications to the stratigraphy of the Serra Geral Formation. Rev Bras Geoc 37:148–162
Kinniburgh DG (1986) General purpose adsorption isotherms. Environ Sci Tech 20:895–904. doi:10.1021/es00151a008
Kocaoba S, Orhan Y, Akyüz T (2007) Kinetics and equilibrium studies of heavy metal ions removal by use of natural zeolite. Desalination 214:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.09.023
Leppert D (1990) Heavy metal sorption with clinoptilolite zeolite: alternatives for treating contaminated soil and water. Min Eng 42:604–608
Monte MBM, Resende NGAM (2004) Zeolitas Naturais. In: COPM (coord.) Rochas & Minerais industriais: usos e especificações. CETEM/MCT, Rio de Janeiro, 33, pp 699–720
Ouki SK, Kavannagh M (1997) Performance of natural zeolites for the treatment of mixed metal-contaminator effluents. Waste Manag Res 15:383–394
Pabalan RT, Bertetti FP (2001) Cation-exchange properties of natural zeolites. In: Bish DL, Ming DW (ed) Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 45. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, DC, pp 453–518
Pansini M, Colella C (1990) Dynamic data on lead uptake from water by chabazite. Desalination 78:287–295
Pansini M, Colella C, Caputo D, De Gennaro M, Langella A (1996) Evaluation of phillipsite as cation exchanger in lead removal from water. Micropor Mater 5:357–364
Pitcher SK, Slade RCT, Ward NI (2004) Heavy metal removal from motorway stormwater using zeolites. Sci Total Environ 334–335:161–166. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.035
Rezende NGAM (2002) A zona zeolítica da Formação Corda—Bacia do Parnaíba. Dissertation, Federal University of Pará, Brasil
Shinzato MC, Montanheiro TJ, Negri FA, Janasi VA, Andrade S, Yamamoto JK (2008) Caracterização tecnológica das zeólitas naturais associadas às rochas eruptivas da Formação Serra Geral, na região de Piraju-Ourinhos (SP). Rev Bras Geoc 38(3):525–532
Shinzato MC, Montanheiro TJ, Janasi VA, Andrade S, Yamamoto JK (2009) Remoção de Pb2+ e Cr3+ em solução por zeólitas naturais associadas a rochas eruptivas da Formação Serra Geral, Bacia Sedimentar do Paraná (SP). Quim Nova 32(8):1989–1994
Simoncic P, Armbruster T (2004) Peculiarity and defect structure of the natural and synthetic zeolite mordenite: a single-crystal study. Am Miner 89:421–431
Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk AP, Namiesnik J (2006) Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J Colloid Interf Sci 304:21–28. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.07.068
Svilovic S, Rusic D, Zanetic R (2008) Thermodynamics and adsorption isotherms of copper ions removal from solutions using synthetic zeolite X. Chem and Biochem Eng Q 22(3):299–305
Turan M, Mart U, Yüksel B, Çelik MS (2005) Lead removal in fixed-bed columns by zeolite and sepiolite. Chemosphere 60:1487–1492. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.036
Vijayaraghavan K, Padmesh TVN, Palanivelu K, Velan M (2006) Biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J Hazard Mater B133:304–308. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.016
Yuan G, Seyama H, Soma M, Theng BKG, Tanaka A (1999) Adsorption of some heavy metals by natural zeolites: XPS and batch studies. J. Environ Sci Health A Environ Sci Eng 34(3):625–648
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (process 03/06259-4). N.G.A.M. Rezende provided the sandstone from the Corda Formation (Parnaíba Basin). We wish to thank the anonymous referees for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinzato, M.C., Montanheiro, T.J., Janasi, V.A. et al. Removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solutions using two Brazilian rocks containing zeolites. Environ Earth Sci 66, 363–370 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1245-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1245-z