Abstract
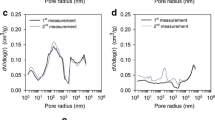
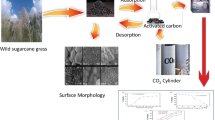
Activated carbons (ACs) with a highly developed porosity have been prepared from a lignocellulosic precursor (coffee husk) for environmental pollutant adsorption. Characterization results show that these materials exhibit a high amount oxygen groups and high specific surface area with micro mesopores. From SEM results we can see the collapse of large pores at longer activation times. The ACs obtained from coffee husk waste is a promising adsorbent material, with high adsorption capacity for the methylene blue dye (MB). Thus, the use of the coffee husk for AC preparation, with porosity development, showed as a good alternative for the waste transformation. Results also showed that the adsorption of MB by the AC-1/1 was much better than commercial AC from Merck.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsh, H., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.: Activated carbon. Elsevier, New York (2006)
Aworn, A., Thiravetyan, P., Nakbanpote, W.: Preparation of CO2 activated carbon from corncob for monoethylene glycol adsorption. Colloids Surf. A 333, 19–25 (2009)
Yang, J., Qiu, K.: Development of high surface area mesoporous activated carbons from herb residues. Chem. Eng. J. 167, 148–154 (2011)
Foo, K.Y., Hameed, B.H.: Coconut husk derived activated carbon via microwave induced activation: effects of activation agents, preparation parameters and adsorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 184, 57–65 (2012)
Nahil, M.A., Williams, P.T.: Characterization of activated carbons with high surface area and variable porosity produced from agricultural cotton waste by chemical activation and co-activation. Waste Biomass Valoriz 2, 117–130 (2012)
Oliveira, L.C.A., Pereira, E., Guimaraes, I.R., Vallone, A., Pereira, M., Mesquita, J.P., Sapag, K.: Preparation of activated carbons from coffee husks utilizing FeCl3 and ZnCl2 as activating agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 165, 87–94 (2009)
Jaramillo, J., Gómez-Serrano, V., Álvarez, P.M.: Enhanced adsorption of metal ions onto functionalized granular activated carbons prepared from cherry stones. J. Hazard. Mater. 161, 670–676 (2009)
Reddy, K.S.K., Shoaibi, A.A., Srinivasakannan, C.: Activated carbon from date palm seed: process optimization using response surface methodology. Waste Biomass Valoriz 2, 149–156 (2012)
Benaddi, H., Bandosz, T.J., Jagiello, J., Schwarz, J.A., Rouzaud, J.N., Legras, D., Béguin, F.: Surface functionality and porosity of activated carbons obtained from chemical activation of wood. Carbon 38, 669–674 (2000)
Kalderis, D., Koutoulakis, D., Paraskeva, P., Diamadopoulos, E., Otal, E., Valle, J.O., Fernández-Pereira, C.: Adsorption of polluting substances on activated carbons prepared from rice husk and sugarcane bagasse. Chem. Eng. J. 144, 42–50 (2008)
Oliveira, L.C.A., Guerreiro, M.C., Gonçalves, M., Oliveira, D.Q.L., Costa, L.C.M.: Preparation of activated carbon from leather waste: a new material containing small particle of chromium oxide. Mater. Lett. 62, 3710–3712 (2008)
Ramos, P.H., Guerreiro, M.C., Resende, E.C., Gonçalves, M.: Produção e caracterização de carvão ativado produzido a partir do defeito preto, verde, ardido (PVA) do café. Quim. Nova 32, 1139–1143 (2009)
Brum, S.S., Bianchi, M.L., Silva, V.L., Gonçalves, M., Guerreiro, M.C., Oliveira, L.C.A.: Preparação e caracterização de carvão ativado produzido a partir de resíduos do beneficiamento do café. Quim. Nova 31, 1048–1052 (2008)
CONAB-Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento. http://www.conab.gov.br/OlalaCMS/uploads/arquivos/12_05_10_08_56_04_boletim_cafe_-_maio_2012.pdf. Accessed 2012-08-20
Avelar, F.F., Bianchi, M.L., Gonçalves, M., Mota, E.G.: The use of piassava fibers (Attalea funifera) in the preparation of activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 4639–4645 (2010)
El-Hendawy, A.N.A.: Influence of HNO3 oxidation on the structure and adsorptive properties of corncob-based activated carbon. Carbon 41, 713–722 (2003)
Boonamnuayvitaya, V., Sae-ung, S., Tanthapanichakoon, W.: Preparation of activated carbons from coffee residue for the adsorption of formaldehyde. Sep. Purif. Technol. 42, 159–168 (2005)
Sing, K.S.W., Everett, D.H., Haul, R.A.W., Moscou, L., Pierotti, R.A., Rouquerol, J., Siemieniewska, T.: Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Int. Union Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 603–619 (1985)
Boonamnuayvitaya, V., Chaiya, C., Tanthapanichakoon, W.: The preparation and characterization of activated carbon from coffee residue. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 37, 1504–1512 (2004)
Figueiredo, J.L., Pereira, M.F.R., Freitas, M.M.A., Órfão, J.J.M.: Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 37, 1379–1389 (1999)
Menéndez, J.A., Phillips, J., Xia, B., Radovic, L.R.: On the modification and characterization of chemical surface properties of activated carbon: in the search of carbons with stable basic properties. Langmuir 12, 4404–4410 (1996)
Dandekar, A., Baker, R.T.K., Vannice, M.A.: Characterization of activated carbon, graphitized carbon fibers and synthetic diamond powder using TPD and DRIFTS. Carbon 36, 1821–1831 (1998)
Rey, A., Zazo, J.A., Casas, J.A., Bahamonde, A., Rodriguez, J.J.: Influence of the structural and surface characteristics of activated carbon on the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Catal. A 402, 146–155 (2011)
Zhuang, Q.-L., Kyotani, T., Tomita, A.: DRIFT and TK/TPD analyses of surface oxygen complexes formed during carbon gasification. Energy Fuels 8, 714–718 (1994)
Simoncic, P., Armbruster, T.: Cationic methylene blue incorporated into zeolite mordenite-Na: a single crystal X-ray study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 81, 87–95 (2005)
Dural, M.U., Cavas, L., Papageorgiou, S.K., Katsaros, F.K.: Methylene blue adsorption on activated carbon prepared from Posidonia oceanica (L.) dead leaves: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chem. Eng. J. 168, 77–85 (2011)
Girgis, B.S., Smith, E., Louis, M.M., El-Hendawy, A.N.A.: Pilot production of activated carbon from cotton stalks using H3PO4. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 86, 180–184 (2009)
Stavropoulos, G.G., Zabaniotou, A.A.: Production and characterization of activated carbons from olive-seed waste residue. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 82, 79–85 (2005)
Ahmed, M.J., Dhedan, S.K.: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics modeling of methylene blue adsorption on agricultural wastes-based activated carbons. Fluid Phase Equilib. 317, 9–14 (2012)
Acknowledgments
To CAPQ, FAPEMIG, CNPq and to CAPES for the financial support and analysis conduction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, M., Guerreiro, M.C., Oliveira, L.C.A. et al. Micro Mesoporous Activated Carbon from Coffee Husk as Biomass Waste for Environmental Applications. Waste Biomass Valor 4, 395–400 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-012-9163-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-012-9163-1