Abstract
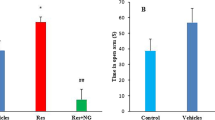
Reserpine (RES)-induced orofacial dyskinesia (OD) has been used as an animal model for human tardive dyskinesia (TD) for decades, due to its strong pathophysiological association with striatal oxidative stress and neural cytoarchitecture alteration. L-Theanine (LT), one of the major amino acid components in green tea, has potent antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects. In this study, we examined the potential protective effects of LT on RES-induced behavioral and neurochemical dysfunction in rats. RES treatment (1 mg/kg s.c., 3 injections 1 day apart) induced significant increases (p < 0.001) in the frequency of vacuous chewing movements (VCM), tongue protrusion (TP), as well as the duration of facial twitching (FT). LT treatment (100, 300 mg/kg orally for 14 days, starting 10 days before RES injection) was able to prevent most of the RES-induced OD. Moreover, LT treatment reduced the RES-induced lipid peroxidation (LPO) production, increased the antioxidation power and catecholamines in the striatum, and significantly reduced the levels of neuroinflammatory and apoptotic markers. Our results indicated that LT was able to counteract the increased oxidative damage, neurotransmitter deficiency, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis induced by RES, and these results have demonstrated the possible neuroprotective effects of LT against RES-induced OD, including antioxidation, neurochemical deficiency prevention, antineuroinflammation, and antiapoptosis. These findings, therefore, suggest a potential role for LT to have a clinically relevant therapeutic effect in delaying or treating human TD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
catalase
- DA:
-
dopamine
- FT:
-
facial twitching
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- LPO:
-
lipid peroxidation
- MAO:
-
monoamine oxidase
- NE:
-
norepinephrine
- OD:
-
orofacial dyskinesia
- PD:
-
Parkinson disease
- RES:
-
reserpine
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- LT:
-
L-theanine
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric acid-reactive substance
- TD:
-
tardive dyskinesia
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
- TP:
-
tongue protrusion
- VCM:
-
vacuous chewing movements
- VMAT:
-
vesicular monoamine transporter
- 5-HT:
-
serotonin
References
Abílio VC, Silva RH, Carvalho RC, Grassl C, Calzavara MB, Registro S, D’Almeida V, Ribeiro Rde A, Frussa-Filho R (2004) Important role of striatal catalase in aging- and reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 47(2):263–272
Andreassen OA, Ferrante RJ, Beal MF, Jørgensen HA (1998) Oral dyskinesias and striatal lesions in rats after long-term co-treatment with haloperidol and 3-nitropropionic acid. Neuroscience 87(3):639–648
Beers RF Jr, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195(1):133–140
Bilska A, Dubiel M, Sokołowska-Jezewicz M, Lorenc-Koci E, Włodek L (2007) Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 146(4):1758–1771
Burger ME, Alves A, Callegari L, Athayde FR, Nogueira CW, Zeni G, Rocha JB (2003) Ebselen attenuates reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and oxidative stress in rat striatum. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27(1):135–140
Calvente PR, Araujo CC, Bergamo M, Abilio VC, D’Almeida V, Ribeiro Rde A, Frussa FR (2002) The mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid aggravates reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia in rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26(2):401–405
Cunha AS, Matheus FC, Moretti M, Sampaio TB, Poli A, Santos DB, Colle D, Cunha MP, Blum-Silva CH, Sandjo LP, Reginatto FH, Rodrigues AL, Farina M, Prediger RD (2016) Agmatine attenuates reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia in mice: role of oxidative stress, nitric oxide and glutamate NMDA receptors. Behav Brain Res 312:64–76
Datta S, Jamwal S, Deshmukh R, Kumar P (2016) Beneficial effects of lycopene against haloperidol induced orofacial dyskinesia in rats: possible neurotransmitters and neuroinflammation modulation. Eur J Pharmacol 771:229–235
Davies DL, Shepherd M (1955) Reserpine in the treatment of anxious and depressed patients. Lancet 269(6881):117–120
de Freitas CM, Busanello A, Schaffer LF, Peroza LR, Krum BN, Leal CQ, Ceretta AP, da Rocha JB, Fachinetto R (2016) Behavioral and neurochemical effects induced by reserpine in mice. Psychopharmacology 233(3):457–467
Durlach J (1956) Treatment of emaciation with reserpine. Concours Med 78(7):725–728
Dutra RC, Andreazza AP, Andreatini R, Tufik S, Vital MA (2002) Behavioral effects of MK-801 on reserpine-treated mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26(3):487–495
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Faria RR, Abílio VC, Grassl C, Chinen CC, Negrão LT, de Castro JP, Fukushiro DF, Rodrigues MS, Gomes PH, Registro S, de Carvalho Rde C, D’Almeida V, Silva RH, Ribeiro Rde A, Frussa-Filho R (2005) Beneficial effects of vitamin C and vitamin E on reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia in rats: critical role of striatal catalase activity. Neuropharmacology 48(7):993–1001
Fernandes VS, Santos JR, Leão AH, Medeiros AM, Melo TG, Izídio GS, Cabral A, Ribeiro RA, Abílio VC, Ribeiro AM, Silva RH (2012) Repeated treatment with a low dose of reserpine as a progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 231(1):154–163
Fuentes P, Paris I, Nassif M, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2007) Inhibition of VMAT- 2 and DT-diaphorase induced cell death in a substantia nigra-derived cell line—an experimental cell model for dopamine toxicity studies. Chem Res Toxicol 20(5):776–783
Hanff TC, Furst SJ, Minor TR (2010) Biochemical and anatomical substrates of depression and sickness behavior. J Psychiatry Relat Sci 47(1):64–71
Hashimoto M, Tanabe Y, Fujii Y, Kikuta T, Shibata H, Shido O (2005) Chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid ameliorates the impairment of spatial cognition learning ability in amyloid beta-infused rats. J Nutr 135(3):549–555
Huang NY, Kostrzewa RM, Li C, Perry KW, Fuller RW (1997) Persistent spontaneous oral dyskinesias in haloperidol-withdrawn rats neonatally lesioned with 6-hydroxydopamine: absence of an association with the Bmax for [3H]raclopride binding to neostriatal homogenates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280(1):268–276
Ishibashi T, Ohno Y (2004) Antiparkinsonian actions of a selective 5-HT1A agonist, tandospirone, in rats. Biogen Amines 18:329–338
Jamwal S, Kumar P (2017) L-theanine, a component of green tea prevents 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP)-induced striatal toxicity by modulating nitric oxide pathway. Mol Neurobiol 54(3):2327–2337
Kakuda T (2011) Neuroprotective effects of theanine and its preventive effects on cognitive dysfunction. Pharmacol Res 64(2):162–168
Kelley JJ, Roberts RC (2004) Effects of haloperidol on cholinergic striatal interneurons: relationship to oral dyskinesias. J Neural Transm 111(8):1075–1091
Kostrzewa RM, Huang NY, Kostrzewa JP, Nowak P, Brus R (2007) Modeling tardive dyskinesia: predictive 5-HT2C receptor antagonist treatment. Neurotox Res 11(1):41–50
Kronbauer M, Segat HJ, De David Antoniazzi CT, Roversi K, Roversi K, Pase CS, Barcelos RC, Burger ME (2015) Magnesium supplementation prevents and reverses experimentally induced movement disturbances in rats: biochemical and behavioral parameters. Biol Trace Elem Res 166(2):163–172
Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A (2011) Role of LOX/COX pathways in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington’s disease-like symptoms in rats: protective effect of licofelone. Br J Pharmacol 164(2b):644–654
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Niculescu AB (2003) Oxidative mechanisms and tardive dyskinesia. CNS Drugs 17(1):47–62
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247(10):3170–3175
Nade VS, Shendye NV, Kawale LA, Patil NR, Khatri ML (2013) Protective effect of nebivolol on reserpine-induced neurobehavioral and biochemical alterations in rats. Neurochem Int 63(4):316–321
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2004) Reversal of reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and cognitive dysfunction by quercetin. Pharmacology 70(2):59–67
Neisewander JL, Castañeda E, Davis DA (1994) Dose-dependent differences in the development of reserpine-induced oral dyskinesia in rats: support for a model of tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 116(1):79–84
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Paris I, Martinez-Alvarado P, Cárdenas S, Perez-Pastene C, Graumann R, Fuentes P, Olea-Azar C, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2005) Dopamine-dependent iron toxicity in cells derived from rat hypothalamus. Chem Res Toxicol 18(3):415–419
Patel BA, Arundell M, Parker KH, Yeoman MS, O’Hare D (2005) Simple and rapid determination of serotonin and catecholamines in biological tissue using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 818(2):269–276
Patil R, Dhawale K, Gound H, Gadakh R (2012a) Protective effect of leaves of Murraya koenigii on reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Iran J Pharm Res 11(2):635–641
Patil RA, Hiray YA, Kasture SB (2012b) Reversal of reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and catalepsy by Nardostachys jatamansi. Indian J Pharmacol 44(3):340–344
Pérez-Vargas JE, Zarco N, Vergara P, Shibayama M, Segovia J, Tsutsumi V, Muriel P (2016) l-Theanine prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis via inhibition of nuclear factor κB and down-regulation of transforming growth factor β and connective tissue growth factor. Hum Exp Toxicol 35(2):135–146
Santos JR, Cunha JA, Dierschnabel AL, Campêlo CL, Leão AH, Silva AF, Engelberth RC, Izídio GS, Cavalcante JS, Abílio VC, Ribeiro AM, Silva RH (2013) Cognitive, motor and tyrosine hydroxylase temporal impairment in a model of parkinsonism induced by reserpine. Behav Brain Res 253:68–77
Selvakumar G, Vijayraja D, Krishnamoorthy D, Manivasagam T (2012) Morin attenuates haloperidol induced tardive dyskinesia and oxidative stress in mice. J Nat Sci Res 8(2):153–165
Sumathi T, Shobana C, Thangarajeswari M, Usha R (2015) Protective effect of L-theanine against aluminium induced neurotoxicity in cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of rat brain—histopathological, and biochemical approach. Drug Chem Toxicol 38(1):22–231
Teixeira AM, Reckziegel P, Müller L, Pereira RP, Roos DH, Rocha JB, Bürger ME (2009) Intense exercise potentiates oxidative stress in striatum of reserpine-treated animals. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92(2):231–235
Terashima T, Takido J, Yokogoshi H (1999) Time-dependent changes of amino acids in the serum, liver, brain and urine of rats administered with theanine. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63(4):615–618
Thangarajan S, Deivasigamani A, Natarajan SS, Krishnan P, Mohanan SK (2014) Neuroprotective activity of L-theanine on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rat striatum. Int J Neurosci 124(9):673–684
Túnez I, Collado JA, Medina FJ, Peña J, Del C, Muñoz M, Jimena I, Franco F, Rueda I, Feijóo M, Muntané J, Montilla P (2006) 17 eta-Estradiol may affect vulnerability of striatum in a 3-nitropropionic acid-induced experimental model of Huntington’s disease in ovariectomized rats. Neurochem Int 48(5):367–373
Wang MH, Lin RF, Tseng HC, Soung HS, Chang KC, Tsai CC (2015) (−)Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and oxidative stress in rat striatum. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 131:71–76
Yin C, Gou L, Liu Y, Yin X, Zhang L, Jia G, Zhuang X (2011) Antidepressant-like effects of L-theanine in the forced swim and tail suspension tests in mice. Phytother Res 25(11):1636–1639
Yokogoshi H, Kato Y, Sagesaka YM, Takihara-Matsuura T, Kakuda T, Takeuchi N (1995) Reduction effect of theanine on blood pressure and brain 5-hydroxyindoles in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59(4):615–618
Zhang G, Miura Y, Yagasaki K (2002) Effects of dietary powdered green tea and theanine on tumor growth and endogenous hyperlipidemia in hepatoma-bearing rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(4):711–716
Zheng G, Sayama K, Okubo T, Juneja LR, Oguni I (2004) Anti-obesity effects of three major components of green tea, catechins, caffeine and theanine, in mice. In Vivo 18(1):55–62
Zukhurova M, Prosvirnina M, Daineko A, Simanenkova A, Petrishchev N, Sonin D, Galagudza M, Shamtsyan M, Juneja LR, Vlasov T (2013) L-theanine administration results in neuroprotection and prevents glutamate receptor agonist-mediated injury in the rat model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Phytother Res 27(9):1282–1287
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Persistent BioMed Editing services located in Philadelphia, USA, for their valuable editing and proofreading of the current manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Yuan-Shan Br. of Taipei Veteran General Hospital (YSVH-10505), Mackay Memorial Hospital (MMH-105-69), and Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital (SKH-8302-104-DR-24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soung, HS., Wang, MH., Chang, KC. et al. L-Theanine Decreases Orofacial Dyskinesia Induced by Reserpine in Rats. Neurotox Res 34, 375–387 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9897-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9897-z