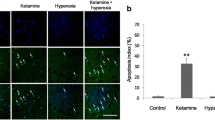
Abstract
Ketamine is widely used as an anesthetic in pediatric clinical practice. However, numerous studies have reported that exposure to ketamine during the developmental period induces neurotoxicity. Here we investigate the neuroprotective effects of baicalin, a natural flavonoid compound, against ketamine-induced apoptotic neurotoxicity in the cortex and hippocampus of the Sprague–Dawley postnatal day 7 (PND7) rat pups. Our results revealed that five continuous injections of ketamine (20 mg/kg) at 90-min intervals over 6 h induced obvious morphological damages of neuron by Nissl staining and apoptosis by TUNEL assays in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of PND7 rat pups. Baicalin (100 mg/kg) pretreatment alleviated ketamine-induced morphological change and apoptosis. Caspase-3 activity and caspase-3 mRNA expression increase induced by ketamine were also inhibited by baicalin treatment. LY294002, an inhibitor of PI3K, abrogated the effect of baicalin against ketamine-induced caspase-3 activity and caspase-3 mRNA expression increase. In addition, Western blot studies indicated that baicalin not only inhibited ketamine-induced p-Akt and p-GSK-3β decrease, but also relieved ketamine-induced p-CREB and BDNF expression decrease. Baicalin also attenuated ketamine-induced Bcl-2/Bax decrease and caspase-3 expression increase. Further in vitro experiments proved that baicalin mitigated ketamine-induced cell viability decrease in the MTT assay, morphological change by Rosenfeld’s staining, and caspase-3 expression increase by Western blot in the primary neuron–glia mixed cultures. LY294002 abrogated the protective effect of baicalin. These data demonstrate that baicalin exerts neuroprotective effect against ketamine-induced neuronal apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt and its downstream CREB/BDNF/Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Therefore, baicalin appears to be a promising agent in preventing or reversing ketamine’s apoptotic neurotoxicity at an early developmental stage.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00491-w
29 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-023-00641-8
References
Chen T, Willoughby KA, Ellis EF (2004) Group I metabotropic receptor antagonism blocks depletion of calcium stores and reduces potentiated capacitative calcium entry in strain-injured neurons and astrocytes. J Neurotrauma 21(3):271–281
Cheng F, Lu Y, Zhong X, Song W, Wang X, Sun X, Qin J, Guo S, Wang Q (2013) Baicalin’s Therapeutic Time Window of Neuroprotection during Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Its Antioxidative Effects In Vitro and In Vivo. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:120261
Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM (2003) The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22(53):8590–8607
Du K, Montminy M (1998) CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J Biol Chem 273(49):32377–32379
Finkbeiner S (2000) CREB couples neurotrophin signals to survival messages. Neuron 25(1):11–14
Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Wilder RT, Voigt RG, Olson MD, Sprung J, Weaver AL, Schroeder DR, Warner DO (2011) Cognitive and behavioral outcomes after early exposure to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics 128(5):e1053–e1061
Forde JE, Dale TC (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(15):1930–1944
Frebel K, Wiese S (2006) Signalling molecules essential for neuronal survival and differentiation. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 6):1287–1290
Green SM, Cote CJ (2009) Ketamine and neurotoxicity: clinical perspectives and implications for emergency medicine. Ann Emerg Med 54(2):181–190
Hetman M, Cavanaugh JE, Kimelman D, Xia Z (2000) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in neuronal apoptosis induced by trophic withdrawal. J Neurosci 20(7):2567–2574
Huang L, Liu Y, Jin W, Ji X, Dong Z (2012) Ketamine potentiates hippocampal neurodegeneration and persistent learning and memory impairment through the PKCgamma-ERK signaling pathway in the developing brain. Brain Res 1476:164–171
Hudson AE, Hemmings HC Jr (2011) Are anaesthetics toxic to the brain? Br J Anaesth 107(1):30–37
Ikonomidou C, Bosch F, Miksa M, Bittigau P, Vockler J, Dikranian K, Tenkova TI, Stefovska V, Turski L, Olney JW (1999) Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Science 283(5398):70–74
Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2013) Functional implications of an early exposure to general anesthesia: are we changing the behavior of our children? Mol Neurobiol 48(2):288–293
Jiang H, Lv P, Li J, Wang H, Zhou T, Liu Y, Lin W (2013) Baicalin inhibits colistin sulfate-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. Neural Regen Res 8(28):2597–2604
Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Woodgett JR (2011) GSK-3: functional Insights from Cell Biology and Animal Models. Front Mol Neurosci 4:40
Khalil SR, Abd-Elhakim YM, Selim ME, Al-Ayadhi LY (2015) Apitoxin protects rat pups brain from propionic acid-induced oxidative stress: the expression pattern of Bcl-2 and Caspase-3 apoptotic genes. Neurotoxicology 49:121–131
Lee B, Sur B, Shim I, Lee H, Hahm DH (2014a) Baicalin improves chronic corticosterone-induced learning and memory deficits via the enhancement of impaired hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cAMP response element-binding protein expression in the rat. J Nat Med 68(1):132–143
Lee W, Ku SK, Bae JS (2014b) Anti-inflammatory Effects of Baicalin, Baicalein, and Wogonin in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-0013-0
Lei G, Xia Y, Johnson KM (2008) The role of Akt-GSK-3beta signaling and synaptic strength in phencyclidine-induced neurodegeneration. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(6):1343–1353
Li YC, Gao WJ (2011) GSK-3beta activity and hyperdopamine-dependent behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):645–654
Li CT, Zhang WP, Fang SH, Lu YB, Zhang LH, Qi LL, Huang XQ, Huang XJ, Wei EQ (2010) Baicalin attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activation in PC12 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31(2):137–144
Li J, Wu H, Xue G, Wang P, Hou Y (2013) 17beta-Oestradiol protects primary-cultured rat cortical neurons from ketamine-induced apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt/Bcl-2 Signalling. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12124
Liu F, Paule MG, Ali S, Wang C (2011) Ketamine-induced neurotoxicity and changes in gene expression in the developing rat brain. Curr Neuropharmacol 9(1):256–261
Liu F, Patterson TA, Sadovova N, Zhang X, Liu S, Zou X, Hanig JP, Paule MG, Slikker W Jr, Wang C (2013a) Ketamine-induced neuronal damage and altered N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor function in rat primary forebrain culture. Toxicol Sci 131(2):548–557
Liu JR, Baek C, Han XH, Shoureshi P, Soriano SG (2013b) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in ketamine-induced developmental neuroapoptosis in rats. Br J Anaesth 110(Suppl 1):i3–i9
Li-Weber M (2009) New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents Wogonin Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev 35(1):57–68
Lixuan Z, Jingcheng D, Wenqin Y, Jianhua H, Baojun L, Xiaotao F (2010) Baicalin attenuates inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation in cigarette smoke induced inflammatory models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 23(5):411–419
Michel PP, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (2002) Parkinson’s disease: cell death mechanisms. Rev Neurol (Paris) 158(122):24–32
Parisi OI, Scrivano L, Sinicropi MS, Picci N, Puoci F (2015) Engineered polymer-based nanomaterials for diagnostic. Therapeutic Theranostic Appl, Mini Rev Med Chem
Pitanga BP, Silva VD, Souza CS, Junqueira HA, Fragomeni BO, Nascimento RP, Silva AR, Costa Mde F, El-Bacha RS, Costa SL (2011) Assessment of neurotoxicity of monocrotaline, an alkaloid extracted from Crotalaria retusa in astrocyte/neuron co-culture system. Neurotoxicology 32(6):776–784
Sakamoto K, Karelina K, Obrietan K (2011) CREB: a multifaceted regulator of neuronal plasticity and protection. J Neurochem 116(1):1–9
Scallet AC, Schmued LC, Slikker W Jr, Grunberg N, Faustino PJ, Davis H, Lester D, Pine PS, Sistare F, Hanig JP (2004) Developmental neurotoxicity of ketamine: morphometric confirmation, exposure parameters, and multiple fluorescent labeling of apoptotic neurons. Toxicol Sci 81(2):364–370
Shang Y, Wu Y, Yao S, Wang X, Feng D, Yang W (2007) Protective effect of erythropoietin against ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons: involvement of PI3K/Akt and GSK-3 beta pathway. Apoptosis 12(12):2187–2195
Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1999) CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu Rev Biochem 68:821–861
Song JX, Choi MY, Wong KC, Chung WW, Sze SC, Ng TB, Zhang KY (2012) Baicalein antagonizes rotenone-induced apoptosis in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells related to Parkinsonism. Chin Med 7(1):1
Soriano SG, Liu Q, Li J, Liu JR, Han XH, Kanter JL, Bajic D, Ibla JC (2010) Ketamine activates cell cycle signaling and apoptosis in the neonatal rat brain. Anesthesiology 112(5):1155–1163
Sprung J, Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Barbaresi WJ, Bojanic K, Welch TL, Olson MD, Hanson AC, Schroeder DR, Wilder RT, Warner DO (2012) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder after early exposure to procedures requiring general anesthesia. Mayo Clin Proc 87(2):120–129
Straiko MM, Young C, Cattano D, Creeley CE, Wang H, Smith DJ, Johnson SA, Li ES, Olney JW (2009) Lithium protects against anesthesia-induced developmental neuroapoptosis. Anesthesiology 110(4):862–868
Takadera T, Ishida A, Ohyashiki T (2006) Ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 210(1–2):100–107
Vutskits L, Gascon E, Kiss JZ (2007) Effects of ketamine on the developing central nervous system. Ideggyogy Sz 60(3–4):109–112
Wang C, Sadovova N, Patterson TA, Zou X, Fu X, Hanig JP, Paule MG, Ali SF, Zhang X, Slikker W Jr (2008) Protective effects of 7-nitroindazole on ketamine-induced neurotoxicity in rat forebrain culture. Neurotoxicology 29(4):613–620
Yon JH, Daniel-Johnson J, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2005) Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Neuroscience 135(3):815–827
Zheng WH, Quirion R (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) induces the activation/phosphorylation of Akt kinase and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) by activating different signaling pathways in PC12 cells. BMC Neurosci 7:51
Zheng WX, Wang F, Cao XL, Pan HY, Liu XY, Hu XM, Sun YY (2014) Baicalin protects PC-12 cells from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide via anti-apoptotic effects. Brain Inj 28(2):227–234
Zhou J, Ping FF, Lv WT, Feng JY, Shang J (2014) Interleukin-18 directly protects cortical neurons by activating PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB/CREB pathways. Cytokine 69(1):29–38
Zuo D, Wang C, Li Z, Lin L, Duan Z, Qi H, Li L, Sun F, Wu Y (2014) Existence of glia mitigated ketamine-induced neurotoxicity in neuron-glia mixed cultures of neonatal rat cortex and the glia-mediated protective effect of 2-PMPA. Neurotoxicology 44:218–230
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (81403023), the Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (LJQ2015111), and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, D., Lin, L., Liu, Y. et al. Baicalin Attenuates Ketamine-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Developing Rats: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and CREB/BDNF/Bcl-2 Pathways. Neurotox Res 30, 159–172 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9611-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9611-y