Abstract
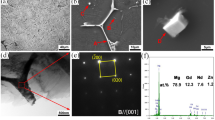
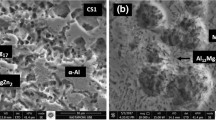
In this paper, the microstructure evolution of the rapidly solidified (RS) Mg61.7Zn34Gd4.3 (at%, atomic ratio) alloy at high temperatures was investigated. The hardness and elastic modulus of the main precipitated phases were also analyzed and compared with those of the α-Mg matrix on the basis of nanoindentation tests. The results show that the RS alloy consists of either a petal-like icosahedral quasicrystal (IQC) phase (~20 μm) and block-shaped H1 phase (~15 μm) or IQC particles with an average grain size of ~107 nm as well as a small proportion of amorphous phase, which mainly depends on the holding time at the liquid temperature and the thickness of the ribbons. The IQC phase gradually transforms at 400°C to a short-rod-shaped μ-phase (Mg28.6Zn63.8Gd7.7) with a hexagonal structure. The hardness of the IQC phase is higher than that of H1 phase, and both phases exhibit a higher hardness than the α-Mg matrix and the μ-phase. The elasticity of the H1 phase is superior to that of the α-Mg matrix. The IQC phase possesses a higher elastic modulus than H1 phase. The easily formed H1 phase exhibits the poorest plastic deformation capacity among these phases but a higher elastic modulus than the α-Mg matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.C.T, Alloys of magnesium, Nature, 141(1938), p. 45.
J.D. Robson, Critical assessment 9: Wrought magnesium alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 31(2015), No. 3, p. 257.
B.L. Mordike and T. Ebert, Magnesium: properties-applications-potential, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 302(2001), No. 1, p. 37.
S. Amani and G. Faraji, Recrystallization and mechanical properties of WE43 magnesium alloy processed via cyclic expansion extrusion, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 6, p. 672.
N. Tahreen and D.L. Chen, A critical review of Mg-Zn-Y Series alloys containing I, W, and LPSO phases, Adv. Eng. Mater., 18(2016), No. 12, p. 1983.
L. Zhang, Z. Liu, and P.L. Mao, Effect of annealing on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-2.5Zn-0.5Y alloy, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 21(2014), No. 8, p. 779.
D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin and A. Inoue, Formation and properties of quasicrystals, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 38(2008), p. 403.
A.P. Tsai, A. Niikura, A. Inoue, T. Masumoto, Y. Nishida, K. Tsuda, and M. Tanaka, Highly ordered structure of icosahe-dral quasicrystals in Zn-Mg-RE (RE ≡ rare earth metals) systems, Philos. Mag. Lett. 70(1994), No. 3, p. 169.
S. Ranganathan and K. Chattopadhyay, Quasicrystals, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 21(1991), No. 1, p. 437.
W.A. Cassada, Y. Shen, S.J. Poon, and G.J. Shiflet, Mg32(Zn Al)49-type icosahedral quasicrystals formed by solid state reaction and rapid solidification, Phys. Rev. B, 34(1986), No. 10-15, p. 7413.
D.H. Bae, S.H. Kim, D.H. Kim, and W.T. Kim, Deformation behavior of Mg-Zn-Y alloys reinforced by icosahedral qua-sicrystalline particles, Acta Mater., 50(2002), No. 9, p. 2343.
D.K. Xu, T.T. Zu, M. Yin, Y.B. Xu, and E.H. Han, Mechanical properties of the icosahedral phase reinforced duplex Mg-Li alloy both at room and elevated temperatures, J. Alloys Compd., 582(2014), p. 161.
A. Singh, M. Nakamura, M. Watanabe, A. Kato, and A.P. Tsai, Quasicrystal strengthened Mg-Zn-Y alloys by extrusion, Scripta Mater., 49(2003), No. 5, p. 417.
X.D. Wang, W.B. Du, Z.H. Wang, K. Liu, and S.B. Li, Microstructures and mechanical properties of quasicrystal reinforced AZ31 matrix composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 530(2011), p. 446.
A.P. Tsai, Discovery of stable icosahedral quasicrystals: progress in understanding structure and properties, Chem. Soc. Rev., 42(2013), No. 12, p. 5352.
J. Gröbner, A. Kozlov, X.Y. Fang, S.M. Zhu, J.F. Nie, M.A. Gibson, and R. Schmid-Fetzer, Phase equilibria and transformations in ternary Mg-Gd-Zn alloys, Acta Mater., 90(2015), p. 400.
J.F. Liu, Z.Q. Yang, and H.Q. Ye, In situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of quasicrystal-crystal transformations in Mg-Zn-Y alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 621(2015), p. 179.
S.V. Ketov, Y.H. Sun, S. Nachum, Z. Lu, A. Checchi, A.R. Beraldin, H.Y. Bai, W.H. Wang, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, M.A. Carpenter, and A.L. Greer, Rejuvenation of metallic glasses by non-affine thermal strain, Nature, 524(2015), No. 7564, p. 200.
Y.N. Wang, J. Yang, and Y.P. Bao, Effects of non-metallic inclusions on machinability of free-cutting steels investigated by nano-indentation measurement, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 46(2015), No. 1, p. 281.
A. Rahnama, H. Kotadia, S. Clark, V. Janik, and S. Sridhar, Nano-mechanical properties of Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight steels, Sci. Rep., 8(2018), art. No. 9065.
A.C. Fisher-Cripps, Nanoidentation, Springer, New York, 2012, p. 60.
R. Yang, Q. Zhang, P. Xiao, J. Wang, and Y.L. Bai, Two opposite size effects of hardness at real nano-scale and their distinct origins, Sci. Rep., 7(2017), art. No. 10653.
J.Y. Zhang, P. Jia, D.G. Zhao, G.R. Zhou, and X.Y. Teng, Melt holding time as an important factor on the formation of quasicrystal phase in Mg67Zn30Gd3 alloy, Physica B, 533(2018), p. 28.
D.B. Miracle, A structural model for metallic glasses, Nat. Mater., 3(2004), No. 10, p. 697.
K. Sugiyama, K. Yasuda, T. Ohsuna, and K. Hiraga, The structures of hexagonal phases in Mg-Zn-RE (RE = Sm and Gd) alloys, Z. Kristallogr., 213(1998), No. 10, p. 537.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 51401070). We also gratefully acknowledge Dr. Li You from University of Science and Technology Beijing for the discussion of TEM results’ analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Wb., Xue, Zy. & Mao, Wm. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and micromechanical properties of the rapidly solidified Mg61.7Zn34Gd4.3 alloy containing icosahedral phase. Int J Miner Metall Mater 26, 869–877 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1799-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1799-4