Abstract
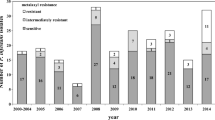
Late blight disease caused by Phytophthora infestans is an important yield reducing, prolific, and destructive pathogen of Solanaceae family members, mainly tomato and potato. P. infestans may cause entire crop loss unless controlled by chemical and cultural control measures. The Cukurova region of Turkey is one of the main potato-producing areas of Turkey and climatic conditions incite P. infestans to develop and cause severe yield losses in the region. A total of 186 isolates of P. infestans were obtained through survey studies conducted during the 2013–2014 potato-growing seasons in the Cukurova region comprised of Hatay, Adana and Mersin provinces in Turkey. All the isolates were analyzed for their metalaxyl resistance, mating type, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplotype and allozyme genotype diversity. P. infestans isolates were metalaxyl sensitive and both mating types were found in the potato-growing areas of the Cukurova region. The A1 mating type was more common (68.8%) than A2 (22.5%) and 8.6% of the P. infestans isolates were self-compatible. mtDNA haplotypes were diverse in the region and Ia was the most common type. Allozyme analyses revealed that the US-1 (Gpi 86/100) and US-6 (Gpi 100/100) patterns were prevalent in the potato-growing areas of the Cukurova region. This study contains the first data on molecular and biochemical characterization of potato late blight in Turkey.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, B., Sandstrom, M., & Stromberg, A. (1998). Indications of soil-borne inoculum of Phytophthora infestans. Potato Research, 41, 305–310.
Barton, N. H., & Charlesworth, B. (1998). Why sex and recombination? Science, 281, 1986–1989.
Brurberg, M. B., Hannukkala, A., & Hermansen, A. (1999). Genetic variability of Phytophthora infestans in Norway and Finland as revealed by mating type and fingerprint probe RG57. Mycological Research, 103, 1609–1615.
Carlisle, D. J., Cooke, L. R., & Brown, A. E. (2001). Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Northern Ireland isolates of Phytophthora infestans. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 107, 291–303.
Carter, D. A., Archer, S. A., Buck, K. W., Shaw, D. S., & Shattock, R. C. (1990). Restriction fragment length polymorphisms of mitochondrial DNA of Phytophthora infestans. Mycological Research, 94, 1123–1128.
Carter, D. A., Archer, S. A., Buck, K. W., Shaw, D. S., & Shattock, R. C. (1991). DNA polymorphisms in Phytophthora infestans the U.K. experience (pp. 272–294). Cambridge University Press.
Caten, C. E., & Jinks, J. L. (1968). Spontaneous variability of single isolates of Phytophthora infestans. I. Cultural variation. Canadian Journal of Botany, 46(4), 329–348.
Chen, C. H., Wang, T. C., Black, L., Sheu, Z. M., Perez, F., & Deahl, K. (2009). Phenotypic and genotypic changes in the Phytophthora infestans population in Taiwan 1991 to 2006. Journal of Phytopathology, 157, 248–255.
Chowdappa, P., Kumar, N. B. J., Madhura, S., Kumar, M. S. P., Myers, K. L., Fry, W. E., Squire, J. S., & Cooke, D. (2013). Emergence of 13_A2 blue lineage of Phytophthora infestans was responsible for severe outbreaks of late blight on tomato in south-west India. Journal of Phytopathology, 161, 49–58.
Cooke, D. E. L., Cano, L. M., Raffaele, S., Bain, R. A., Cooke, L. R., Etherington, G. J., Deahl, K. L., Farrer, R. A., Gilroy, E. M., Goss, E. M., Grünwald, N. J., Hein, I., MacLean, D., & Kamoun, S. (2012). Genome analyses of an aggressive and invasive lineage of the Irish potato famine pathogen. PLoS Pathogens. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002940.
Danies, G., Small, I. M., Myers, K., Childers, R., & Fry, W. E. (2013). Phenotypic characterization of recent clonal lineages of Phytophthora infestans in the United States. Plant Disease, 97(7), 873–881.
Day, J. P., & Shattock, R. C. (1997). Aggressiveness and other factors relating to displacement of populations of Phytophthora infestans in England and Wales. European Journal of Plant. Pathology, 103, 397–391.
Day, J. P., Wattier, R. A. M., Shaw, D. S., & Shattock, R. C. (2004). Phenotypic diversity in Phytophthora infestans on potato in Great Britain, 1995-1998. Plant Pathology, 53, 303–315.
Deahl, K. L., Inglis, D. A., & DeMuth, S. P. (1993). Testing for resistance to metalaxyl in Phytophthora infestans isolates from northwestern Washington. American Potato Journal., 10, 779–795.
Dey, T., Saville, A., Myers, K., Tewari, S., Cooke, D., Tripaty, S., Fry, W., Ristaino, J. B., & Roy, S. (2018). Large sub-clonal variation in Phytophthora infestans from recent severe late blight epidemics in India. Article in Scientific Reports. February, 2018, 4429. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22192-1.
Dowley, L. J., & O’Sullivan, E. (1981). Metalaxyl-resistant strains of Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary in Ireland. Potato Research., 24, 417–421.
Drenth, A., Tas, I. C. Q., & Govers, F. (1994). DNA fingerprinting uncovers a new sexually reproducing population of Phytophthora infestans in the Netherlands. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 100, 97–107.
Drenth, A., Goodwin, S. B., Fry, W. E., & Davidse, L. C. (1993). Genotypic diversity of Phytophthora infestans in The Netherlands revealed by DNA polymorphisms. Phytopathology, 83(10), 1087–1092.
Erselius, L.J., Hohl, H.R., Ordonez, M.E., Oyarzun, P.J., Jarrin, F., Velasco, A., Ramon, M.P, Forbes, G.A., (1998). Genetic diversity among isolates of from various host in Ecuador, CIP program report 1997–1998.
Evenhuis, A., Scheepers, H. T. A. M., Bus, C. B., & Stegeman, W. (1996). Synergy of cymoxanil and mancozeb when used to control potato late blight. Potato Research, 39, 551–559.
Flier, W. G., Kroon, L. P. N. M., Hermansen, A., van Raaij, H. M. G., Speiser, B., Tamm, L., Fuchs, J. G., Lambion, J., Razzaghian, J., Andrivon, D., Wilcockson, S., & Leifert, C. (2007). Genetic structure and pathogenicity of populations of Phytophthora infestans from organic potato crops in France, Norway, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. Plant Pathology, 56, 562–572.
Fontem, D. A., Olanya, O. M., Tsopmbeng, G. R., & Owona, M. A. P. (2005). Pathogenicity and metalaxyl sensitivity of Phytophthora infestans isolates obtained from garden huckleberry, potato and tomato in Cameroon. Crop Protection, 24, 449–456.
Forbes, G. A., Goodwin, S. B., Drenth, A., Oyarzun, P., Ordonez, M. E., & Fry, W. E. (1998). A global marker database for Phytophthora infestans. Plant Disease, 82, 811–818.
Fry, W. E. (2008). Phytophthora infestans: The plant (and R gene) destroyer. Molecular Plant Pathology, 9, 385–402.
Fry, W. E., Goodwin, S. B., Dyer, A. T., Matusazak, J. M., Drenth, A., Tooley, P. W., Sujkowski, L. S., Koh, Y. J., Cohen, B. A., Spielman, L. J., Deahl, K. L., & Inglis, D. A. (1993). Historical and recent migrations of Phytophthora infestans: Chronology, pathways, and implications. Plant Disease, 77, 653–661.
Fry, W. E., Birch, P. R. J., Judelson, H. S., Grünwald, N. J., Danies, G., Everts, K. L., Gevens, A. J., Gugino, B. K., Johnson, D. A., Johnson, S. B., McGrath, M. T., Myers, K. L., Ristaino, J. B., Roberts, P. D., Secor, G., & Smart, C. D. (2015). Five reasons to consider Phytophthora infestans a re-emerging pathogen. Phytopathology, 105, 966–981.
Galindo, J., & Gallegly, M. E. (1960). The nature of sexuality in Phytophthora infestans. Phytopathology, 50, 123–128.
Gavino, P. D., & Fry, W. E. (2002). Diversity in and evidence for selection on the mitochondrial genome of Phytophthora infestans. Mycologia, 94, 781–793.
Goodwin, S. B. (1997). The population genetics of Phytophthora. Phytopathology, 87, 462–473.
Goodwin, S. B., Cohen, B. A., Deahl, K. L., & Fry, W. E. (1994a). Migration from northern Mexico as the probable cause of recent genetic changes in populations of Phytophthora infestans in the United States and Canada. Phytopathology, 84, 553–558.
Goodwin, S. B., Cohen, B. A., & Fry, W. E. (1994b). Panglobal distribution of a single clonal lineage of the Irish potato famine fungus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 91, 11591–11595.
Goodwin, S. B., Schineider, R. E., & Fry, W. E. (1995a). Use of cellulose-acetate electrophoresis for rapid identification of allozyme genotypes of Phytophthora infestans. Plant Disease., 79, 1181–1185.
Goodwin, S. B., Sujkowski, L. S., Dyer, A. T., Fry, B. A., & Fry, W. E. (1995b). Direct detection of gene flow and probable sexual reproduction of Phytophthora infestans in northern North America. Phytopathology, 83, 473–479.
Goodwin, S. B., Smart, C. D., Sandrock, R. W., Deahl, K. L., Punja, Z. K., & Fry, W. E. (1998). Genetic change within populations of Phytophthora infestans in the United States and Canada during 1994 to 1996: Role of migration and recombination. Phytopathology, 88(9), 939–949.
Griffin, D., O’Sullivan, E., Harmey, M. A., & Dowley, L. J. (2002). DNA fingerprinting, metalaxyl resistance and mating type determination of the Phytophthora infestans population in the Republic of Ireland. Potato Research, 45, 25–36.
Griffith, G. W., & Shaw, D. S. (1998). Polymorphisms in Phytophthora infestans: Four mitochondrial haplotypes are detected after PCR amplification of DNA from pure cultures or from host lesions. Appl. Environ. Microbiology, 64(10), 4007.
Hanson, K., & Shattock, R. C. (1998). Formation of oospores of Phytophthora infestans in cultivars of potato with different levels of race-nonspecific resistance. Plant Pathology, 47, 123–129.
Haverkort, A. J., Struik, P. C., Visser, R. G. F., & Jacobsen, E. (2009). Applied biotechnology to combat late blight in potato caused by Phytophthora infestans. Potato Research., 52, 249–264.
Hermansen, A., Hannukkala, A., Hafskjold Nærstad, R., & Brurberg, M. B. (2000). Variation in populations of Phytophthora infestans in Finland and Norway: Mating type, metalaxyl resistance and virulence phenotype. Plant Pathology, 49, 11–22.
Hohl, H. R., & Iselin, K. (1984). Strains of Phytophthora infestans from Switzerland with A2 mating type behavior. Trans. Br. Mycoogyl. Soc., 83, 529–530.
Judelson, H. S. (1997). The genetics and biology of Phytophthora infestans: Modern approaches to a historical challenge. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 22, 65–76.
Lebreton, L., Laurent, C., & Andrivon, D. (1998). Evolution of Phytophthora infestans population in the two most important potato protection areas of France during 1992-96. Plant Pathology, 47, 427–439.
Li, B., Chen, Q., Lv, X., Lan, C., Zhao, J., Qiu, R., & Weng, Q. (2009). Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Phytophthora infestans isolates from China. Journal of Phytopathology, 157, 558–567.
Li, Y., van-der Lee, T., Zhu, J. H., Jind, G. H., Lane, C. Z., Zhu, S. X., Zhang, R. F., Liu, B. W., Zhao, Z. J., Kessel, G., Huanga, S. W., & Jacobsen, E. (2013). Population structure of Phytophthora infestans in China – geographic clusters and presence of the EU genotype Blue_13. Plant Pathology., 62, 932–942.
McLoad, A., Denman, S., Sadie, A., & Denner, F. D. N. (2001). Characterization of south African isolates of Phytophthora infestans. Plant Disease., 85, 287–291.
Njoroge, A. W., Andersson, B., & Lees, A. K. (2018). Genotyping of Phytophthora infestans in eastern-Africa reveals a dominating invasive European lineage. Phytopathology. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-07-18-0234-r.
Peters, R. D., Plant, H. W., & Hall, R. (1998a). Characterization of changes in populations of Phytophthora infestans in Canada during mating types and metalaxyl sensitivity markers. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 20, 259–273.
Peters, R. D., Plant, H. W., & Hall, R. (1998b). Use of allozyme markers to determine genotypes of Phytophthora infestans in Canada. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 21, 144–153.
Rekad, F. Z., Cooke, L., Puglısı, I., Randall, E., Guenaouı, Y., Bouznad, Z., Evolı, M., Pane, A., Schena, L., Di Sanlio, G. M., & Caccıola, S. A. (2017). Characterization of Phytophthora infestans populations in northwestern Algeria during 2008-2014. Fungal Biology, 467–477.
Ristaino, J. B. (2006). Tracking the evolutionary history of the potato late blight pathogen with historical collections. Outlooks on Pest Management, 17(5), 228–231.
Runno-Paurson, E., Kiiker, R., Joutsjoki, T., & Hannukkala, A. (2016). High genotypic diversity found among population of Phytophthora infestans collected in Estonia. Fungal Biology, 120, 385–392.
Shattock, R. C. (1988). Studies on the inheritance of resistance to metalaxyl in Phytophthora infestas. Plant Pathology, 37, 4–11.
Shattock, R. C. (2002). Phytophthora infestans: Populations, pathogenicity and phenylamides. Pest Management Science, 58, 944–950.
Shattock, R. C., Shaw, D. S., Fyfe, A. M., Dunn, J. R., Loney, K. H., & Shattock, J. A. (1990). Phenotypes of Phytophthora infestans collected in England and Wales from 1995 to 1988: Mating type, response to metalaxyl and isozyme analysis. Plant Pathology, 39, 242–248.
Shtienberg, D. S., Bergeron, N., Nicholson, A. G., Fry, W. E., & Ewing, E. E. (1990). Development and evaluation of general model for yield loss assessment in potatoes. Phytopathology., 80(5), 466–472.
Spielman, L. J., Drenth, A., Davidse, L. C., Sujkowski, L. J., Gu, W., Tooley, P. W., & Fry, W. E. (1991). A second world-wide migration and population displacement of Phytophthora infestans? Plant Pathology, 40, 422–430.
Statsyuk, N.V., Kuznetsova, I.N., Kozlovskaya, B.E., Kozlovsky, S.N., Elansky, E.V., Valeva, E.V., Flippov, A.V. (2010). Characteristics of the Phytophthora infestans population in Russia. Twelfth EuroBlight workshop in France. EPPO. Special Report no.14,247–254.
Sujkowski, L. S., Goodwin, S. B., Dyer, A. T., & Fry, W. E. (1994). Increased genotypic diversity via migration and possible occurrence of sexual reproduction of Phytophthora infestans in Poland. Phytopathology, 84, 201–207.
Sujkowski, L., Fry, B. A., Power, R. J., Goodwin, S. B., Peever, T. L., Hamlen, R. A., & Fry, W. E. (1995). Sensitivities of Mexican isolates of Phytophthora infestans to chlorothalonil, cymoxanil, and metalaxyl. Plant Disease, 79, 1117–1120.
Świeżyński, K. M., Domański, L., Zarzycka, H., & Zimnoch-Guzowska, E. (2000). The reaction of potato differentials to Phytophthora infestans isolates collected in nature. Plant Breeding, 119, 119–126.
Tosun, N., Yıldırım, A., Türküsay, H., & Tanyolaç, B. (2007). Genetic variation among Phytophthora infestans (tomato blight) isolates from Western Turkey revealed by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Pakistan Journal of. Botonical, 39(3), 897–902, 2007.
TUIK (2015). http://www.tuik.gov.tr. Accessed 23 Aug 2018.
TUIK (2016). http://www.tuik.gov.tr. Accessed 23 Aug 2018.
Turkensteen, L. J., Flier, W. G., Wanningen, R., & Mulder, A. (2000). Production, survival and infectivity of oospores of Phytophthora infestans. Plant Pathology, 49, 688–696.
Wang, J., Fernández-Pavía, S. P., Larsen, M. M., Garay-Serrano, E., Gregorio-Cipriano, R., Rodríguez-Alvarado, G., Grünwald, N. J., & Goss, E. M. (2017). High levels of diversity and population structure in the potato late blight pathogen at the Mexico Centre of origin. Molecular Ecology, 26, 1091–1107.
Widmark, A.-K., Andersson, B., Cassel-Lundhagen, A., Sandstr€om, M., & Yuen, J. E. (2007). Phytophthora infestans in a single field in Southwest Sweden early in spring: Symptoms, spatial distribution and genotypic variation. Plant Pathology, 56, 573–579.
Yoshida, K., Schuenemann, J. W., Cano, L. M., Pais, M., Mishra, B., Sharma, R., Lanz, C., Martin, F. N., Kamoun, S., Krause, J., Thines, N., Weige, D., & Burbano, H. A. (2013). The rise and fall of the Phytophthora infestans lineage that triggered the Irish potato famine. eLife, 2, e00731. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00731.
Funding
This study is a part of the project fully supported by the Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) with project number, TOVAG-112O112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunacti, H., Ay, T. & Can, C. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of Phytophthora infestans populations from potato in Turkey. Phytoparasitica 47, 429–439 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-019-00737-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-019-00737-y