Abstract
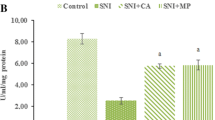
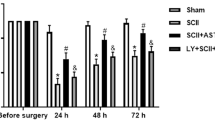
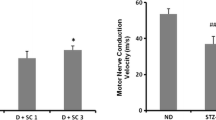
This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of quercetin against ischemia–reperfusion (IR) injury induced in the sciatic nerve of the rat. Quercetin (20 mg/kg) was given during ischemia just before reperfusion. Four groups of rats (Q+IR3, Q+IR7, Q+IR14, and Q+IR28) received 3, 7, 14, and 28 days of reperfusion, respectively, after the intraperitoneal injection of quercetin. After reperfusion, a behavioral test was performed and the sciatic functional index was calculated. Each sciatic nerve was stained to check for edema and ischemic fiber degeneration. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to detect TNF-alpha and NF-kappa B, and TUNEL staining was carried out to detect apoptosis. The Q+IR3, Q+IR7, and Q+IR14 groups showed significantly increased behavioral scores and ameliorated sciatic functional index values compared to IR-injured rats that received vehicle alone during ischemia and then the same period of reperfusion. The Q+IR3, Q+IR7, Q+IR14, and Q+IR28 groups presented significant ischemic fiber degeneration (IFD), TNF-alpha expression, and apoptosis as compared with the IR-injured and perfused rats that did not receive quercetin. The Q+IR3, Q+IR7, and Q+IR28 groups also exhibited significantly decreased NF-kappa B expression (p < 0.001, p = 0.001, p = 0.026) as compared with the IR-injured rats that were perfused but did not receive quercetin. These results imply that quercetin may be beneficial in the treatment of sciatic IR injury because of its antiapoptotic and antiinflammatory effects and its ability to decrease the expression of NF-kappa B.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alipour M, Gholami MR, Jafari Anarkooli I, Sohrabi D, Tajki J, Pourheidar M (2011) Intraperitoneal aminoguanidine improves sciatic nerve ischemia–reperfusion injury in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31(5):765–773
Atik B, Erkutlu I, Tercan M, Buyukhatipoglu H, Bekerecioglu M, Pence S (2011) The effects of exogenous melatonin on peripheral nerve regeneration and collagen formation in rats. J Surg Res 166(2):330–336
Bagdatoglu C, Saray A, Surucu HS, Ozturk H, Tamer L (2002) Effect of trapidil in ischemia/reperfusion injury of peripheral nerves. Neurosurgery 51(1):212–219 (discussion 219–220)
Cevik O, Cadirci S, Sener TE, Tinay I, Akbal C, Tavukcu HH, Cetinel S, Kiran D, Sener G (2013) Quercetin treatment against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat corpus cavernosum tissue: a role on apoptosis and oxidative stress. Free Radic Res 47(9):683–691
Chattopadhyay P, Shukla G, Wahi AK (2009) Protective effect of l-arginine against necrosis and apoptosis induced by experimental ischemic and reperfusion in rat liver. Saudi J Gastroenterol 15(3):156
Gholami MR, Abolhassani F, Pasbakhsh P, Akbari M, Sobhani A, Sohrabi D, Mehrania K (2007) The effects of simvastatin on functional recovery of rat reperfused sciatic nerve. Pak J Biol Sci 10(23):4256–4260
Gholami MR, Abolhassani F, Pasbakhsh P, Akbari M, Sobhani A, Eshraghian MR, Kamalian N, Amoli FA, Dehpour AR, Sohrabi D (2008) The effects of simvastatin on ischemia–reperfusion injury of sciatic nerve in adult rats. Eur J Pharmacol 590(1–3):111–114
Gholami M, Zendedel A, Khanipour Khayat Z, Ghanad K, Nazari A, Pirhadi A (2015) Selenium effect on ischemia–reperfusion injury of gastrocnemius muscle in adult rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 164(2):205–211
Ghosh A, Sarkar S, Mandal AK, Das N (2013) Neuroprotective role of nanoencapsulated quercetin in combating ischemia–reperfusion induced neuronal damage in young and aged rats. PLoS One 8(4):e57735
Gomez-Florit M, Monjo M, Ramis JM (2014) Identification of quercitrin as a potential therapeutic agent for periodontal applications. J Periodontol 85(7):966–974
Gonzalez-Segovia R, Quintanar JL, Salinas E, Ceballos-Salazar R, Aviles-Jimenez F, Torres-Lopez J (2008) Effect of the flavonoid quercetin on inflammation and lipid peroxidation induced by Helicobacter pylori in gastric mucosa of guinea pig. J Gastroenterol 43(6):441–447
Iida H, Schmelzer JD, Schmeichel AM, Wang Y, Low PA (2003) Peripheral nerve ischemia: reperfusion injury and fiber regeneration. Exp Neurol 184(2):997–1002
Inal M, Altinisik M, Bilgin MD (2002) The effect of quercetin on renal ischemia and reperfusion injury in the rat. Cell Biochem Funct 20(4):291–296
Ishikawa Y, Kitamura M (2000) Anti-apoptotic effect of quercetin: intervention in the JNK-and ERK-mediated apoptotic pathways. Kidney Int 58(3):1078–1087
Martini ND, Katerere DR, Eloff JN (2004) Biological activity of five antibacterial flavonoids from Combretum erythrophyllum (Combretaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 93(2–3):207–212
Mojzis J, Hviscova K, Germanova D, Bukovicova D, Mirossay L (2001) Protective effect of quercetin on ischemia/reperfusion-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Physiol Res 50(5):501–506
Patra JK, Kim ES, Oh K, Kim HJ, Kim Y, Baek KH (2014) Antibacterial effect of crude extract and metabolites of Phytolacca americana on pathogens responsible for periodontal inflammatory diseases and dental caries. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:343
Rizzo A, Carratelli CR, Losacco A, Iovene MR (2014) Antimicrobial effect of natural polyphenols with or without antibiotics on Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in vitro. Microb Drug Resist 20(1):1–10
Sandhir R, Mehrotra A (2013) Quercetin supplementation is effective in improving mitochondrial dysfunctions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid: implications in Huntington’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(3):421–430
Saray A, Can B, Akbiyik F, Askar I (1999) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury of the peripheral nerve: an experimental study. Microsurgery 19(8):374–380
Saray A, Apan A, Kisa U (2003) Free radical-induced damage in experimental peripheral nerve injection injury. J Reconstr Microsurg 19(6):401–406
Sayan H, Ozacmak VH, Ozen OA, Coskun O, Arslan SO, Sezen SC, Aktas RG (2004) Beneficial effects of melatonin on reperfusion injury in rat sciatic nerve. J Pineal Res 37(3):143–148
Su Y, Ma L, Wen Y, Wang H, Zhang S (2014) Studies of the in vitro antibacterial activities of several polyphenols against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 19(8):12630–12639
Acknowledgments
This study was approved by the Lorestan University of Medical Sciences. The authors would like to give special thanks to the Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran, for their financial support. The authors also thank the head and staff of the Razi Herbal Medicines Research Center of Lorestan Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholami, M., Khayat, Z.K., Anbari, K. et al. Quercetin ameliorates peripheral nerve ischemia–reperfusion injury through the NF-kappa B pathway. Anat Sci Int 92, 330–337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-016-0336-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-016-0336-z