Abstract
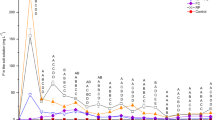
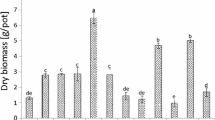
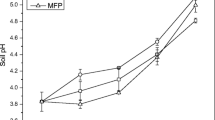
The mining of heavy minerals from sand dunes along the east coast of South Africa is a controversial issue. We report a field experiment that was conducted on backfilled land at the Hillendale mine in northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, to test the effect of filtercake (FC), a locally available source of organic matter, to soil and its ability to support sugarcane growth. Five treatments were evaluated including FC applied at 10, 30 and 100 Mg ha−1. In two other treatments, inorganic fertilizer (IF) was applied alone (without FC) to the reconstituted soil at the recommended rate and at three times the recommended rate, as based on the fertility status of the reconstituted soil. Sugarcane was also grown in an adjacent unmined area in disturbed soil used for cropping. In agreement with fractional light interception, yield of the plant crop on the unmined area (77 Mg ha−1 year−1) was better than on the reconstituted soil treated with IF (59–67 Mg ha−1 year−1) and FC (22–39 Mg ha−1 year−1). Stalk length, rather than tiller number and stalk diameter, was the most important contributor to these yield differences. Based on foliar nutrient content, poor yields in all treatments could be attributed to Fe toxicity caused by oxygen deprivation in the reconstituted soil. In the FC treatments, yields were worsened by N deficiency resulted from immobilization of N. These unexpected outcomes clearly have implications for the efficient rehabilitation of formerly productive agriculture land in the wake of mining locally and worldwide.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asensio, V., F.A. Vega, M.L. Andrade, and E.F. Covelo. 2013. Tree vegetation and waste amendments to improve the physical condition of copper mine soils. Chemosphere 90: 603–610.
Beater, B.A. 1962. The sampling and analysis of field sites. Mt Edgecombe: South African Sugar Association Experiment Station.
Becker, M., and F. Asch. 2005. Iron toxicity in rice—conditions and management concepts. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 168: 558–573. doi:10.1002/jpln.200520504.
Bell, L.C. 2001. Establishment of native ecosystems after mining—Australian experience across diverse biogeographic zones. Ecological Engineering 17: 179–186.
Bokhtiar, S.M., and K. Sakurai. 2005. Effect of application of inorganic and organic fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of sugarcane. Sugar Tech 7: 33–37.
Bronick, C.J., and R. Lal. 2005. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 124: 3–22. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.005.
Buckney, R.T., and D.A. Morrison. 1992. Temporal trends in plant species composition on mined sand dunes in Myall Lakes National Park, Australia. Australian Journal of Ecology 17: 241–254.
Chaudhuri, S., L.M. McDonald, J. Skousen, and M.E. Pena-Yewtukhiw. 2013. Soil organic carbon molecular properties: Effects of time since reclamation in a minesoil chronosequence. Land Degradation and Development. doi:10.1002/Idr.2202.
Daniels, W.L., Orndorff, Z.W., Alley, M.M., Zelazny, L.W., and C. Teutsch. 2007. Sustainable indicators for mineral sands mining in Virginia, USA. ‘3rd International conference on Sustainable Development Indicators in the Mineral Industry’, June 2007, Milos Island, Greece.
Dee, B.M., R.J. Haynes, and J.H. Meyer. 2002. Sugar mill wastes can be important soil amendments. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 76: 51–59.
Erasmus, J. 2013. Amakhosi and conservationists in KZN face off over dune mining. Mail and Guardian http://mg.co.za/article/2013-02-07-amakhosi-and-conservationists-in-kzn-face-off-over-dune-mining. Accessed 7 Nov 2013.
Fenton, G., and M. Conyers. 2002. Interpreting soil tests for calcium, magnesium and Ca:Mg ratios. Leaflet no 7. (NSW Agriculture: Orange) http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au. Accessed on 28 Feb 2008.
Ghasemi-Fasaei, R., and A. Ronaghi. 2008. Interaction of iron with copper, zinc, and manganese in wheat as affected by iron and manganese in a calcareous soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition 31: 839–848. doi:10.1080/01904160802043148.
Gilbert, R.A., D.R. Morris, C.R. Rainbolt, J.M. McCray, R.E. Perdomo, B. Eiland, G. Powell, and G. Montes. 2008. Sugarcane response to mill mud, fertilizer, and soybean nutrient sources and a sandy soil. Agronomy Journal 100: 845–854. doi:10.2134/agronj2007.0247.
Golder Associates. 2004. Hillendale soil baseline assessment for rehabilitation purposes, 1–49 Tronox KZN Sands Report: Empangeni.
Haigh, M., Reed, H., D’Aucourt, M., Plamping, K., Cullis, M., Woodruffe, P., Sawyer, S., Panhuis, W., Wilding, G., Farrugia, F., and S. Powell. 2013. Effect of planting method on the growth of Alnus glutinosa and Quercus peracea in compacted open-cast coal-mine spoils, South Wales. Land Degradation and Development. doi:10.1002/Idr.2201.
Henry, P.C., and W. Rhebergen. 1994. A review of the effectiveness of gypsum, filtercake and deep ploughing for ameliorating irrigated duplex soils in Swaziland. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 68: 59–64.
Hillel, D. 1982. Introduction to soil physics, 224–226. San-Diego: Academic Press.
Hue, N.V., S. Vega, and J.A. Silva. 2001. Manganese toxicity in a Hawaiian oxisol affected by soil pH and organic amendments. Soil Science Society of America Journal 65: 153–160.
Kutilek, M., and D.R. Nielsen. 1994. Soil hydrology, 130–218. Cremlingen-Destedt: Catena Verlag.
Lewis, J.W. 1980. Environmental aspects of mineral sand mining in Australia. Minerals and Environment 2: 145–158.
López-Piňeiro, A., S. Murillo, C. Barreto, A. Muňoz, J.M. Rato, A. Albarrán, and A. García. 2007. Changes in organic matter and residual effect of amendment with two-phase olive-mill waste on degraded agricultural soils. Science of the Total Environment 378: 84–98.
Lubke, R.A., and A.M. Avis. 1999. A review of the concepts and application of rehabilitation following heavy mineral dune mining. Pollution Bulletin 37: 546–557.
Lucas, S.T., E.M. D’Angelo, and M.A. Williams. 2014. Improving soil structure by promoting fungal abundance with organic soil amendments. Applied Soil Ecology 75: 13–23.
Mbagwu, J.S.C. 1992. Improving the productivity of a degraded ultisol in Nigeria using organic and inorganic amendments. Part 2: Changes in physical properties. Bioresource Technology 42: 167–175.
Mengel, K., and E.A. Kirkby. 1987. Principles of plant nutrition, 687. Worblaufen-Bern: International Potash Institute.
Meyer, J.H., A.B. Tucker, and R.A. Wood. 1997. The SASEX Fertilizer advisory service: Over 40 years’ service to the South African sugar industry. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 71: 42–49.
Meyer, J.H., R. Van Antwerpen, P.C. Henry, and N. Leibbrandt. 1992. Improved cane yields from vertical mulching under rainfed and irrigated cane conditions. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 66: 89–94.
Meyer, J.H., R.A. Wood, D.J. Nixon, A.L. Rampersad, B.L. Schroeder, and A.W. Schumann. 2004. The SASEX fertilizer advisory service: A review of 50 years of service to the South African Sugar Industry. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 78: 359–371.
Miller, D.E., and W.H. Gardner. 1962. Water infiltration into stratified soil. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings 26: 115–118.
Moberly, P.K., and J.H. Meyer. 1978. Filter cake—A field and glasshouse evaluation. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 52: 131–136.
Moore, P. 2011. Heavy minerals. International mining. pp. 60–68. http://www.infomine.com/library/publications/docs/InternationalMining/Moore2011b.pdf. Accessed 7 Nov 2013.
Mukherjee, A., R. Lal, and A.R. Zimmerman. 2014. Effects of biochar and other amendments on the physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of an artificially degraded soil. Science of the Total Environment 487: 26–36.
Neilsen, D., G.H. Neilsen, A.H. Sinclair, and D.J. Linehan. 1992. Soil phosphorus status, pH and manganese nutrition in wheat. Plant and Soil 145: 45–50.
Obi, M.E., and P.O. Ebo. 1995. The effects of organic and inorganic amendments on soil physical properties and maize production in a severely degraded sandy soil in southern Nigeria. Bioresource Technology 51: 117–123.
Odendaal, N. 2011. Exxaro takes in rehabilitation lessons from Hillendale as mines closure nears. http://www.miningweekly.com/article/exxaro-takes-in-rehabilitation-lessons-from-hillendale-as-mines-closure-nears-2011-11-25. Accessed 3 Nov 2013.
Orndorff, Z.W., Daniels, W.L., and J.M. Galbraith. 2005. Properties and classification of minerals sands mine soils in southeastern Virginia. ‘National Meeting of American Society of Mining Reclamation.’ June 19–23, Breckenridge, USA.
Pallavicini, Y., J.G. Alday, and C. Martínez-Ruiz. 2013. Factors affecting herbaceous richness and biomass accumulation patterns or reclaimed coal mines. Land Degradation and Development. doi:10.1002/Idr.2198.
Ponnamperuma, F.N. 1972. The chemistry of submerged soils. Advances in Agronomy 24: 29–96.
Ponnamperuma, F.N., E.M. Tianco, and T. Loy. 1967. Redox equilibria in flooded soils: The iron hydroxide systems. Soil Science 103: 374–382.
Prado, R.D.M., G. Caione, and C.N.S. Campos. 2013. Filter cake and vinasse as fertilizers contributing to conservation agriculture. Applied and Environmental Soil Science 2013: 1–8. doi:10.1155/2013/581984.
Radulescu, R., T. Lydia, S.A. Kiss, P. Ecaterina, and S. Éva. 2007. Effect of industrial chemical waste on the uptake of cations by green oat. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society 6: 629–633. doi:10.2298/JSC0706629R.
Rasul, G., K.S. Khan, T. Müller, and R.G. Joergensen. 2008. Soil microbial response to sugarcane filter cake and biogenic waste compost. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 171: 355–360. doi:10.1002/jpln.200700094.
Rasul, G., A.A. Khan, and K.S. Khan. 2009. Immobilization and mineralization of nitrogen in a saline and alkaline soil during microbial use of sugarcane filtercake amended with glucose. Biological Fertility of Soils 42: 289–296. doi:10.1007/500374-008-0333-2.
Rate, A.W., K.M. Lee, and P.A. French. 2004. Application of biosolids in mineral sands mine rehabilitation: Use of stockpiled topsoil decreases trace element uptake by plants. Resources Technology 91: 223–231. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00206-2.
Ridge, R. 2013. Fertilizing for high yield and quality sugarcane. International Potash Institute: Horgen http://www.ipipotash.org/udocs/414-ipi-bulletin-no21-sugarcane-2013.pdf. Accesses 15 Nov 2013.
Roth, G. 1971. The effects of filter cake on fertility and yield of sugarcane. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 45: 142–148.
Rowell, D.L. 1988. Flooded and poorly drained soils. In Russell’s soil conditions and plant growth, 11th ed, ed. A. Wild, 899–927. Harlow: Longman Scientific and Technical.
SASRI (South African Sugarcane Research Institute Association). 2010. Information sheet. Variety N41. SASRI, Mt Edgecombe. pp. 1–2. http://www.sasa.org.za/Libraries/Variety_Information/N41.sflb.ashx. Accessed 7 Nov 2013.
SAWS (South African Weather Service). 2013. Climate data base. Pretoria: SAWS.
Schroeder, B.L., R.A. Wood, and J.H. Meyer. 1993. Foliar analysis in the South African Sugar Industry for diagnostic and nutrient trend purposes. Plant Nutrition—From Genetic Engineering to Field 54: 299–302.
Shainberg, I., M.E. Sumner, W.P. Miller, M.P.W. Farina, M.A. Pavan, and M.V. Fey. 1989. Use of gypsum on soils: A review. Advances in Soil Science 9: 2–101.
Shrestha, R.K., and R. Lal. 2006. Ecosystem carbon budgeting and soil carbon sequestration in reclaimed mine soil. Environment International 32: 781–796. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.001.
Tyler, R.M., and R.C.A. Minnit. 2004. A review of sub-Saharan heavy mineral sand deposits: Implications for new projects in southern Africa. The Journal of the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 104: 89–99.
Van Aarde, R.J., A.M. Smit, and A.S. Claassens. 1998. Soil characteristics of rehabilitating mine and unmined coastal Dunes at Richards Bay, KwaZulu-Natal, South-Africa. Restoration Ecology 6: 102–110.
Van Antwerpen, R., R.J. Haynes, J.H. Meyer, and D. Hlanze. 2003. Assessing organic amendments used by sugarcane growers for improving soil chemical and biological properties. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 77: 293–304.
VSN International. 2009. GenStat for Windows, 12th ed. Hemel Hempstead: VSN International.
Wang, J.J., C.W. Kennedy, H.P. Victor, A.E. Arceneax, and A.T. Guidry. 2005. Zinc fertilization of sugarcane in acid and calcareous soils. Journal of American Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 25: 49–61.
Acknowledgments
We thank Tronox KZN Sands for providing the funds and technical support to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Jaarsveld, C.M., Zharare, G.E., Smit, M.A. et al. Issues with the Amendment of Post-mined Reconstituted Soil with Organic Matter for Production of Sugarcane. Sugar Tech 18, 505–514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0426-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0426-1