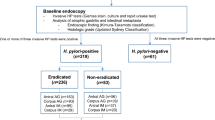
Abstract
Improvements of atrophy and intestinal metaplasia which is seen after H. pylori eradication may be regarded as an important factor of gastric cancer prevention. Although many studies reported the alteration of gastric mucosa after H. pylori eradication, most of the results do not agree. Recently, two meta-analyses showed significant improvement of atrophy (one study showed improvement in both corpus and antrum, and the other showed improvement in corpus but not in antrum), whereas improvement of intestinal metaplasia was not shown in either corpus or antrum. However, one reason why conclusions are different is considered to be that the observation period after eradication was short, and another reason is considered to be that almost studies examined only two points in gastric mucosa for histological analysis. Further examination with a greater number of subjects and with longer follow up period should be required to clarify the mechanism of gastric injury and improvement of gastric mucosa, especially atrophy and intestinal metaplasia after H. pylori eradication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ito M, Takata S, Tatsugami M, Wada Y, Imagawa S, Matsumoto Y, et al. Clinical prevention of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:365–71.
Murakami K, Kodama M, Sato R, Okimoto T, Watanabe K, Fujioka T. Helicobacter pylori eradication and associated changes in the gastric mucosa. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2005;3:757–64.
Rokkas T, Pistiolas D, Sechopoulos P, Robotis I, Margantinis G. The long-term impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication on gastric histology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter. 2007;12(Suppl 2):32–8.
Wang J, Xu L, Shi R, Huang X, Li SW, Huang Z, et al. Gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication: a meta-analysis. Digestion. 2011;83:253–60.
Kodama M, Murakami K, Okimoto T, Sato R, Uchida M, Abe T, Shiota S, Nakagawa Y, Mizukami K, Fujioka T. Ten-year prospective follow-up of histological changes at 5 points on the gastric mucosa as recommended by the updated Sydney system after Helicobacter pylori eradication. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:394–403.
Ito M, Haruma K, Kamada T, Mihara M, Kim S, Kitadai Y, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy improves atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia: a 5-year prospective study of patients with atrophic gastritis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:1449–56.
Watanabe H, Yamaguchi N, Kuwayama H, Sekine C, Uemura N, Kaise M, et al. Improvement in gastric histology following Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in Japanese peptic ulcer patients. J Int Med Res. 2003;31:362–9.
Zhou L, Sung JJ, Lin S, Jin Z, Ding S, Huang X, et al. A five-year follow-up study on the pathological changes of gastric mucosa after H. pylori eradication. Chin Med J. 2003;116:11–4.
Toyokawa T, Suwaki K, Miyake Y, Nakatsu M, Ando M. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection improved gastric mucosal atrophy and prevented progression of intestinal metaplasia, especially in the elderly population: a long-term prospective cohort study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:544–7.
Vannella L, Lahner E, Bordi C, Pilozzi E, Di Giulio E, Corleto VD, Osborn J, Delle Fave G, Annibale B. Reversal of atrophic body gastritis after H. pylori eradication at long-term follow-up. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43:295–9.
Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291:187–94.
Forbes GM, et al. Long-term follow-up of gastric histology after Helicobacter pylori eradication. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996;11:670–3.
Satoh K, et al. A follow-up study of atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia after eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter. 1998;3:236–40.
van der Hulst RW, van der Ende A, Dekker FW, Ten Kate FJ, Weel JF, Keller JJ, Kruizinga SP, Dankert J, Tytgat GN. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on gastritis in relation to cagA: a prospective 1-year follow-up study. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:25–30.
Lahner E, Bordi C, Cattaruzza MS, Iannoni C, Milione M, Delle Fave G, et al. Long-term follow-up in atrophic body gastritis patients: atrophy and intestinal metaplasia are persistent lesions irrespective of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:471–81.
Ohkusa T, Fujiki K, Takashimizu I, Kumagai J, Tanizawa T, Eishi Y, Yokoyama T, Watanabe M. Improvement in atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in patients in whom Helicobacter pylori was eradicated. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:380–6.
Sung JJ, Chung SC, Ling TK, Yung MY, Cheng AF, Hosking SW, Li AK. One-year follow-up of duodenal ulcers after 1-wk triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89(2):199–202.
Yamaoka Y, Kodama T, Kashima K, Graham DY, Sepulveda AR. Variants of the 3′ region of the cagA gene in Helicobacter pylori isolates from patients with different H. pylori-associated diseases. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36(8):2258–63.
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Fujita A, Yamazaki S, Asaka M, Azuma T, Hatakeyama M. Biological activity of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA is determined by variation in the tyrosine phosphorylation sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99(22):14428–33.
Azuma T, Yamazaki S, Yamakawa A, Ohtani M, Muramatsu A, Suto H, Ito Y, Dojo M, Yamazaki Y, Kuriyama M, Keida Y, Higashi H, Hatakeyama M. Association between diversity in the Src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase binding site of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein and gastric atrophy and cancer. J Infect Dis. 2004;189(5):820–7.
Satomi S, Yamakawa A, Matsunaga S, Masaki R, Inagaki T, Okuda T, Suto H, Ito Y, Yamazaki Y, Kuriyama M, Keida Y, Kutsumi H, Azuma T. Relationship between the diversity of the cagA gene of Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer in Okinawa, Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41(7):668–73.
Abe T, Kodama M, Murakami K, Matsunari O, Mizukami K, Inoue K, et al. Impact of Helicobacter pylori CagA diversity on gastric mucosal damage: an immunohistochemical study of East Asian type CagA. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:688–93.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, K., Kodama, M., Nakagawa, Y. et al. Long-term monitoring of gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Clin J Gastroenterol 5, 247–250 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-012-0317-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-012-0317-2