Abstract
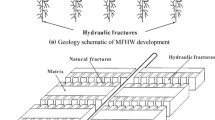
Optimum horizontal well spacing and fracture spacing are obtained through characterizing the changes in flow regime caused by pressure interference in multiple transverse fractured horizontal wells. To obtain this aim, appropriate hydraulic fracture spacing was calculated by using flow regime characteristic called pseudo pseudosteady state where the pressure interference between neighbored two fractures. In addition, the fracture spacing calculated for the shale gas reservoir with permeability of 0.0001 md was applied to calculate the horizontal well spacing when two wells were drilled. Through the calculated optimum fracture spacing and well spacing, we determined the optimal number of horizontal wells in a shale gas reservoir and presented the estimated ultimate recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulis, A., Nyaaba, C., Rai, R.R., and Jayakumar, R., 2013, Challenges evaluating shale gas well performance catalogue fingerprint: How do we account for what we don’t know? International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, Mar. 26–28, p. 1–19.
Cinco-Ley, H. and Samaniego-V, F., 1981, Transient pressure analysis for fractured wells. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 33, 1749–1766.
Ehlig-Economides, C.A., 1992, Computation of test area of investigation in nonradial geometries. European Petroleum Conference, Cannes, Nov. 16–18, p. 37–49.
Gringarten, A.C., Ramey, H.J. Jr., and Raghavan, R., 1975, Applied pressure analysis for fractured wells. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 27, 887–892.
Issaka, M.B. and Ambastha, A.K., 1992, Drawdown and buildup pressure derivative analyses for horizontal wells. European Petroleum Conference, Cannes, Nov. 16–18, p. 155–165.
Larsen, L. and Hegre, T.M., 1994., Pressure transient analysis of multifractured horizontal wells. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Sep. 25–28, p. 265–276.
Loucks, R.G. and Ruppel, S.C., 2007, Mississippian barnett shale: Lithofacies and depositional setting of a deep-water shale-gas succession in the fort worth basin, texas. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 91, 579–601.
Rubin, M.B., 1983, Experimental study of hydraulic fracturing in an impermeable material. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 105, 116–124.
Shang, Y., Park, H.-D., Shi, Y., Yuan, G., and Sun, Y., 2010, Some large values of in-situ stress and related engineering geological problems in china. Geosciences Journal, 14, 135–153.
Song, B. and Ehlig-Economides, C.A., 2011, Rate-normalized pressure analysis for determination of shale gas well performance. North American Unconventional Gas Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, June 14–16, p. 1–14.
Wei, Y. and Economides, M.J., 2005, Transverse hydraulic fractures from a horizontal well. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Oct. 9–12, p. 1–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Chun, M., Jung, W. et al. Optimum design of multi-stage hydraulically fractured multi-horizontal shale gas well using flow regime analysis. Geosci J 19, 481–487 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-014-0058-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-014-0058-y