Abstract
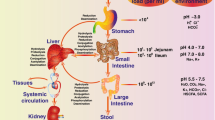
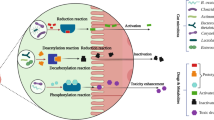
The intestinal mucosa and liver have long been considered as the main sites of drug metabolism, and the contribution of gut microbiota to drug metabolism has been under-estimated. However, it is now generally accepted that the gut microbiota plays an important role in drug metabolism prior to drug absorption or during enterohepatic circulation via various microbial enzymatic reactions in the intestine. Moreover, some drugs are metabolized by gut microbiota to specific metabolite(s) that cannot be formed in the liver. More importantly, the metabolism of drugs by gut microbiota prior to absorption can alter the systemic bioavailability of certain drugs. Therefore, understanding drug metabolism by gut microbiota is critical for explaining changes in the pharmacokinetics of drugs, which may cause significant alterations in drug-induced pharmacodynamics and toxicities. In this review, we describe recent progress with regard to the role of metabolism by gut microbiota in some drug-induced alterations of either pharmacological or toxicological effects to emphasize the clinical importance of gut microbiota for safe and effective use of drugs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo D, Bjarnason I (2006) Is non-steroidal anti-inflammaory drug (NSAID) enteropathy clinically more important than NSAID gastropathy? Postgrad Med J 82:186–191
Boer J, Young-Sciame R, Lee F, Bowman KJ, Yang X, Shi JG, Nedza FM, Frietze W, Galya L, Combs AP, Yeleswaram S, Diamond S (2016) Roles of UGT, P450, and gut microbiota in the metabolism of epacadostat in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 44:1668–1674
Brandi G, Dabard J, Raibaud P, Di Battista M, Bridonneau C, Pisi AM, Morselli Labate AM, Pantaleo MA, De Vivo A, Biasco G (2006) Intestinal microflora and digestive toxicity of irinotecan in mice. Clin Cancer Res 12:1299–1307
Chen LZ, Sabo JP, Philip E, Rowland L, Mao Y, Latli B, Ramsden D, Mandarino DA, Sane RS (2015) Mass balance, metabolite profile, and in vitro-in vivo comparison of clearance pathways of deleobuvir, a hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:25–37
Coburn SP, Mahuren JD, Wostmann BS, Snyder DL, Townsend DW (1989) Role of intestinal microflora in the metabolism of vitamin B-6 and 4′-deoxypyridoxine examined using germfree guinea pigs and rats. J Nutr 119:181–188
Davey KJ, Cotter PD, O’sullivan O, Crispie F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, O’mahony SM (2013) Antipsychotics and the gut microbiome: olanzapine-induced metabolic dysfunction is attenuated by antibiotic administration in the rat. Transl Psychiatry 3:e309
Gerritsen J, Smidt H, Rijkers GT, De Vos WM (2011) Intestinal microbiota in human health and disease: the impact of probiotics. Genes Nutr 6:209–240
Gorbach SL (1996) Microbiology of the gastrointestinal tract. In: Baron S (ed) Medical microbiology, 4th edn. University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston
Haiser HJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2013) Developing a metagenomic view of xenobiotic metabolism. Pharmacol Res 69:21–31
Hashim H, Azmin S, Razlan H, Yahya NW, Tan HJ, Manaf MR, Ibrahim NM (2014) Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection improves levodopa action, clinical symptoms and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 9:e112330
Ilett KF, Tee LB, Reeves PT, Minchin RF (1990) Metabolism of drugs and other xenobiotics in the gut lumen and wall. Pharmacol Ther 46:67–93
Ishizaki J, Tsuda T, Suga Y, Ito S, Arai K, Sai Y, Miyamoto K (2012) Change in pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid as a function of age in rats and effect of coadministered amoxicillin/clavulanate. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1009–1013
Jackson MA, Goodrich JK, Maxan ME, Freedberg DE, Abrams JA, Poole AC, Sutter JL, Welter D, Ley RE, Bell JT, Spector TD, Steves CJ (2016) Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 65:749–756
Jahromi MF, Liang JB, Ho YW, Mohamad R, Goh YM, Shokryazdan P (2012) Lovastatin production by Aspergillus terreus using agro-biomass as substrate in solid state fermentation. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:196264
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Nageshwar Reddy D (2015) Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 21:8787–8803
Jeong HG, Kang MJ, Kim HG, Oh DG, Kim JS, Lee SK, Jeong TC (2013) Role of intestinal microflora in xenobiotic-induced toxicity. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:84–99
Jourova L, Anzenbacher P, Anzenbacherova E (2016) Human gut microbiota plays a role in the metabolism of drugs. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 160:317–326
Kang MJ, Kim HG, Kim JS, Oh DG, Um YJ, Seo CS, Han JW, Cho HJ, Kim GH, Jeong TC, Jeong HG (2013) The effect of gut microbiota on drug metabolism. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 9:1295–1308
Kang MJ, Ko GS, Oh DG, Kim JS, Noh K, Kang W, Yoon WK, Kim HC, Jeong HG, Jeong TC (2014) Role of metabolism by intestinal microbiota in pharmacokinetics of oral baicalin. Arch Pharm Res 37:371–378
Kim DH, Kobashi K (1986) The role of intestinal flora in metabolism of phenolic sulfate esters. Biochem Pharmacol 35:3507–3510
Kim D, Yoo SA, Kim WU (2016a) Gut microbiota in autoimmunity: potential for clinical applications. Arch Pharm Res 39:1565–1576
Kim IS, Yoo DH, Jung IH, Lim S, Jeong JJ, Kim KA, Bae ON, Yoo HH, Kim DH (2016b) Reduced metabolic activity of gut microbiota by antibiotics can potentiate the antithrombotic effect of aspirin. Biochem Pharmacol 122:72–79
Kodawara T, Masuda S, Yano Y, Matsubara K, Nakamura T, Masada M (2014) Inhibitory effect of ciprofloxacin on beta-glucuronidase-mediated deconjugation of mycophenolic acid glucuronide. Biopharm Drug Dispos 35:275–283
Koppel N, Maini Rekdal V, Balskus EP (2017) Chemical transformation of xenobiotics by the human gut microbiota. Science 356:eaag2770
Latini R, Tognoni G, Kates RE (1984) Clinical pharmacokinetics of amiodarone. Clin Pharmacokinet 9:136–156
Lee SH, An JH, Lee HJ, Jung BH (2012a) Evaluation of pharmacokinetic differences of acetaminophen in pseudo germ-free rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 33:292–303
Lee SH, An JH, Park HM, Jung BH (2012b) Investigation of endogenous metabolic changes in the urine of pseudo germ-free rats using a metabolomic approach. J Chromatogr B 887–888:8–18
Lee JR, Muthukumar T, Dadhania D, Taur Y, Jenq RR, Toussaint NC, Ling L, Pamer E, Suthanthiran M (2015) Gut microbiota and tacrolimus dosing in kidney transplantation. PLoS ONE 10:e0122399
Li H, He J, Jia W (2016) The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 12:31–40
Liang X, Bittinger K, Li X, Abernethy DR, Bushman FD, Fitzgerald GA (2015) Bidirectional interactions between indomethacin and the murine intestinal microbiota. Elife 4:e08973
Loguidice A, Wallace BD, Bendel L, Redinbo MR, Boelsterli UA (2012) Pharmacologic targeting of bacterial beta-glucuronidase alleviates nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced enteropathy in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 341:447–454
Lozupone CA, Stombaugh JI, Gordon JI, Jansson JK, Knight R (2012) Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489:220–230
Matuskova Z, Anzenbacherova E, Vecera R, Tlaskalova-Hogenova H, Kolar M, Anzenbacher P (2014) Administration of a probiotic can change drug pharmacokinetics: effect of E. coli Nissle 1917 on amidarone absorption in rats. PLoS ONE 9:e87150
Mccabe M, Sane RS, Keith-Luzzi M, Xu J, King I, Whitcher-Johnstone A, Johnstone N, Tweedie DJ, Li Y (2015) Defining the role of gut bacteria in the metabolism of deleobuvir: in vitro and in vivo studies. Drug Metab Dispos 43:1612–1618
Mcgill MR, Jaeschke H (2013) Metabolism and disposition of acetaminophen: recent advances in relation to hepatotoxicity and diagnosis. Pharm Res 30:2174–2187
Meredith PA, Elliott HL (1992) Clinical pharmacokinetics of amlodipine. Clin Pharmacokinet 22:22–31
Mikov M (1994) The metabolism of drugs by the gut flora. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 19:201–207
Mikov M, Caldwell J, Dolphin CT, Smith RL (1988) The role of intestinal microflora in the formation of the methylthio adduct metabolites of paracetamol. Studies in neomycin-pretreated and germ-free mice. Biochem Pharmacol 37:1445–1449
Nakayama H, Kinouchi T, Kataoka K, Akimoto S, Matsuda Y, Ohnishi Y (1997) Intestinal anaerobic bacteria hydrolyse sorivudine, producing the high blood concentration of 5-(E)-(2-bromovinyl)uracil that increases the level and toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. Pharmacogenetics 7:35–43
Nattel S (1986) Pharmacodynamic studies of amiodarone and its active N-desethyl metabolite. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 8:771–777
Neuvonen PJ, Backman JT, Niemi M (2008) Pharmacokinetic comparison of the potential over-the-counter statins simvastatin, lovastatin, fluvastatin and pravastatin. Clin Pharmacokinet 47:463–474
Noh K, Kang Y, Nepal MR, Jeong KS, Oh Do G, Kang MJ, Lee S, Kang W, Jeong HG, Jeong TC (2016) Role of intestinal microbiota in baicalin-induced drug interaction and its pharmacokinetics. Molecules 21:337
O’hara AM, Shanahan F (2006) The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep 7:688–693
Ohno S, Nakajin S (2009) Determination of mRNA expression of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and application for localization in various human tissues by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Drug Metab Dispos 37:32–40
Okuda H, Nishiyama T, Ogura K, Nagayama S, Ikeda K, Yamaguchi S, Nakamura Y, Kawaguchi K, Watabe T, Ogura Y (1997) Lethal drug interactions of sorivudine, a new antiviral drug, with oral 5-fluorouracil prodrugs. Drug Metab Dispos 25:270–273
Roberts AB, Wallace BD, Venkatesh MK, Mani S, Redinbo MR (2013) Molecular insights into microbial beta-glucuronidase inhibition to abrogate CPT-11 toxicity. Mol Pharmacol 84:208–217
Rowland IR, Mallett AK, Bearne CA, Farthing MJ (1986) Enzyme activities of the hindgut microflora of laboratory animals and man. Xenobiotica 16:519–523
Saitta KS, Zhang C, Lee KK, Fujimoto K, Redinbo MR, Boelsterli UA (2014) Bacterial beta-glucuronidase inhibition protects mice against enteropathy induced by indomethacin, ketoprofen or diclofenac: mode of action and pharmacokinetics. Xenobiotica 44:28–35
Shaw LM, Holt DW, Oellerich M, Meiser B, Van Gelder T (2001) Current issues in therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid: report of a roundtable discussion. Ther Drug Monit 23:305–315
Shaw LM, Figurski M, Milone MC, Trofe J, Bloom RD (2007) Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:1062–1072
Sousa T, Paterson R, Moore V, Carlsson A, Abrahamsson B, Basit AW (2008) The gastrointestinal microbiota as a site for the biotransformation of drugs. Int J Pharm 363:1–25
Stearns JC, Lynch MD, Senadheera DB, Tenenbaum HC, Goldberg MB, Cvitkovitch DG, Croitoru K, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Neufeld JD (2011) Bacterial biogeography of the human digestive tract. Sci Rep 1:170
Syer SD, Blackler RW, Martin R, De Palma G, Rossi L, Verdu E, Bercik P, Surette MG, Aucouturier A, Langella P, Wallace JL (2015) NSAID enteropathy and bacteria: a complicated relationship. J Gastroenterol 50:387–393
Tang BK, Kalow W (1995) Variable activation of lovastatin by hydrolytic enzymes in human plasma and liver. 4. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 47:449–451
Tlaskalova-Hogenova H, Stepankova R, Kozakova H, Hudcovic T, Vannucci L, Tuckova L, Rossmann P, Hrncir T, Kverka M, Zakostelska Z, Klimesova K, Pribylova J, Bartova J, Sanchez D, Fundova P, Borovska D, Srutkova D, Zidek Z, Srutkova D, Schwarzer M, Drastich P, Funda DP (2011) The role of gut microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 8:110–120
Turpeinen M, Hofmann U, Klein K, Murdter T, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2009) A predominate role of CYP1A2 for the metabolism of nabumetone to the active metabolite, 6-methoxy-2-naphthylacetic acid, in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 37:1017–1024
Vyas KP, Kari PH, Pitzenberger SM, Halpin RA, Ramjit HG, Arison B, Murphy JS, Hoffman WF, Schwartz MS, Ulm EH, Duggan DE (1990) Biotransformation of lovastatin. I. Structure elucidation of in vitro and in vivo metabolites in the rat and mouse. Drug Metab Dispos 18:203–211
Wang M, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G (2005) Comparison of bacterial diversity along the human intestinal tract by direct cloning and sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:219–231
Wilson ID, Nicholson JK (2017) Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl Res 179:204–222
Wostmann BS (1981) The germfree animal in nutritional studies. Annu Rev Nutr 1:257–279
Yoo DH, Kim IS, Van Le TK, Jung IH, Yoo HH, Kim DH (2014) Gut microbiota-mediated drug interactions between lovastatin and antibiotics. Drug Metab Dispos 42:1508–1513
Yoo HH, Kim IS, Yoo DH, Kim DH (2016) Effects of orally administered antibiotics on the bioavailability of amlodipine: gut microbiota-mediated drug interaction. J Hypertens 34:156–162
Zamek-Gliszczynski MJ, Hoffmaster KA, Nezasa K, Tallman MN, Brouwer KL (2006) Integration of hepatic drug transporters and phase II metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms of hepatic excretion of sulfate, glucuronide, and glutathione metabolites. Eur J Pharm Sci 27:447–486
Zhang SH, Wang YZ, Meng FY, Li YL, Li CX, Duan FP, Wang Q, Zhang XT, Zhang CN (2015) Studies of the microbial metabolism of flavonoids extracted from the leaves of Diospyros kaki by intestinal bacteria. Arch Pharm Res 38:614–619
Zhong ZY, Sun BB, Shu N, Xie QS, Tang XG, Ling ZL, Wang F, Zhao KJ, Xu P, Zhang M, Li Y, Chen Y, Liu L, Xia LZ, Liu XD (2016) Ciprofloxacin blocked enterohepatic circulation of diclofenac and alleviated NSAID-induced enteropathy in rats partly by inhibiting intestinal beta-glucuronidase activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:1002–1012
Zhu Y, Wang F, Li Q, Zhu M, Du A, Tang W, Chen W (2014) Amlodipine metabolism in human liver microsomes and roles of CYP3A4/5 in the dihydropyridine dehydrogenation. Drug Metab Dispos 42:245–249
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2017R1D1A3B04033313) and from Yeungnam University (214-A-345-027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Keumhan Noh and You Ra Kang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noh, K., Kang, Y.R., Nepal, M.R. et al. Impact of gut microbiota on drug metabolism: an update for safe and effective use of drugs. Arch. Pharm. Res. 40, 1345–1355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0986-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0986-y