Abstract
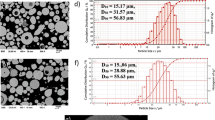
The unlubricated tribological characteristics of coating layers containing an Fe-based amorphous matrix have been investigated in air using an alumina ball with a diameter of 3.1 mm. From the ball-on-disk test system, the friction coefficient could be measured for up to 3,000 seconds. The temperature changes on the worn surfaces were also simultaneously measured using an infrared thermometer. Three different types of coating layers having an Fe-based amorphous matrix, an Fe-based amorphous matrix with embedded Ni-based self-fluxing alloy particles, and an Fe-based amorphous matrix with embedded WC particles were prepared through a high velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) process. Although the coating layers have certain levels of porosity, unique frictional characteristics attributed to the amorphous matrix were observed during the friction tests. Compared with conventional bearing steels such as AISI 521000 (Hv=840), excellent tribological and wear characteristics were obtained, demonstrating that an Fe-based bulk metallic glass powder is a viable engineering material for practical anti-wear coating applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Miyoshi and D. H. Buckley, Friction and wear of some ferrous base metallic glasses, ASLE Trans., 27(4) (1983) 295–304.
W. Clement, R. H. Willens and P. Duwez, Non-crystalline structure in solidified gold-silicon alloys, Nature, 187 (1960) 869.
H. S. Chen, Thermodynamic considerations on the formation and stability of metallic glasses, Acta. Materials, 22 (1974) 1505.
Z. P. Lu, C. T. Liu, J. R. Thomposn and W. D. Porter, Structural amorphous steels, Phys. Rev. Lett., 92, (2004) 245503.
V. Ponnambalam, S. J. Poon and G. J. Shiflet, Fe-based bulk metallic glasses with diameter thickness larger than one centimeter, J. Mater. Res., 19 (2004) 1320.
H. Ma, L. L. Shi, J. Xu, Y. Li and E. Ma, Appl. Phys. Lett., 87 (2005) 181915.
M. F. Ashby and A. L. Greer, Metallic glasses as structural materials, Scripta Materialia, 54 (2006) 321–326.
S. Wang and B. C. Giessen, Rapidly quenched metals, Proc. 4th int. Conf., Japan (1981) 1403–1406.
B. Prakash and K. Hiratsuka, Sliding wear behavior of some Fe-, Co- and Ni-based metallic glasses during rubbing against bearing steel, Tribology Letters, 8 (2000) 153–160.
J. C. Perron, Constantes physico-chimiques, Techniques de l’Ingenieur, vol. K4, Imprimerie Strasbourgeoise, Schiltigheim, France, 1994.
M. Cherigui, H. I. Feraoun, N. E. Feninehe, H. Aourag and C. Coddet, Structure of amorphous iron-based coatings processed by HVOF and APS thermally spraying, Materials Chemistry and Physics, 85 (2004) 113–119.
A. Scrivani, S. Ianelli, A. Rossi, R. Groppetti, F. Casadei and G. Rizzi, A contribution to the surface analysis and characterization of HVOF coatings for petrochemical application, Wear, 250 (2001) 107–113.
Bharat B, Handbook of Nanotechnology, 2004.
U. Harms, T. D. Shen and R. B. Schwarz, Thermal conductivity of Pd40Ni40-xCuxP20 metallic glasses, Scripta Materialia, 47 (2002) 411–414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Seock-Sam Kim received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Kyungpook National University, Korea, in 1973 and 1976, respectively. He received his Ph. D. in Mechanical Engineering from Tohoku University in 1987. He is currently a Professor at the school of Mechanical Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Korea. His research interests are in the area of fracture mechanics and tribology.
Seong-Hoon Yi received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Materials Science and Engineering from Korea University, Korea, in 1984 and 1986, respectively. He received his ph. D. in Materials Science and Engineering from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in 1997. He is currently a Professor at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University. His research interests are in the area of development and application for Bulk Metallic Glasses.
Beom-Taek Jang received his M.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Kyungpook National University in 2006. He is currently working on a doctoral course at the same department of Kyungpook National University in Daegu, Korea. His research interests include tribology, and FEM analysis of surface contact problem.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, BT., Yi, SH. & Kim, SS. Tribological behavior of Fe-based bulk metallic glass. J Mech Sci Technol 24, 89–92 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1123-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1123-8