Abstract
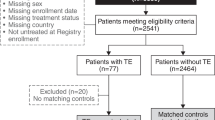
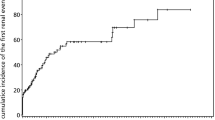
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is characterized by chronic, complement-mediated hemolysis, frequently leading to debilitating clinical symptoms and life-threatening complications such as thromboembolism (TE). A retrospective analysis was performed on 301 patients from the South Korean National PNH Registry to describe disease burden and identify TE-associated risk factors. TE was identified in 18 % of patients and was associated with increased risk for mortality [odds ratio (OR), 6.85; P < 0.001]. A multivariate analysis showed that PNH patients with elevated hemolysis [lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels ≥1.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN)] at diagnosis were at significantly higher risk for TE than patients with LDH <1.5 × ULN (OR 7.0; P = 0.013). The combination of LDH ≥1.5 × ULN with the clinical symptoms of abdominal pain, chest pain, dyspnea, or hemoglobinuria was associated with a greater increased risk for TE than elevated hemolysis or clinical symptoms alone. Continuous monitoring of these risk factors is critical for identifying PNH patients at risk for morbidities and mortality and allowing early intervention. (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01224483).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hillmen P, Lewis SM, Bessler M, Luzzatto L, Dacie JV. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1995;33319:1253–8.
Parker C, Omine M, Richards S, Nishimura J, Bessler M, Ware R, et al. Diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2005;10612:3699–709.
Takeda J, Miyata T, Kawagoe K, Iida Y, Endo Y, Fujita T, et al. Deficiency of the GPI anchor caused by a somatic mutation of the PIG-A gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell. 1993;734:703–11.
Tabbara IA. Hemolytic anemias. Diagnosis and management. Med Clin North Am. 1992;763:649–68.
Rother RP, Bell L, Hillmen P, Gladwin MT. The clinical sequelae of intravascular hemolysis and extracellular plasma hemoglobin: a novel mechanism of human disease. JAMA. 2005;29313:1653–62.
Nishimura J, Kanakura Y, Ware RE, Shichishima T, Nakakuma H, Ninomiya H, et al. Clinical course and flow cytometric analysis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in the United States and Japan. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;833:193–207.
Hillmen P, Muus P, Dührsen U, Risitano AM, Schubert J, Luzzatto L, et al. Effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on thromboembolism in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2007;11012:4123–8.
Hill A, Rother RP, Wang X, Morris SM Jr, Quinn-Senger K, Kelly R, et al. Effect of eculizumab on haemolysis-associated nitric oxide depletion, dyspnoea, and measures of pulmonary hypertension in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 2010;1493:414–25.
de Latour RP, Mary JY, Salanoubat C, Terriou L, Etienne G, Mohty M, et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: natural history of disease subcategories. Blood. 2008;1128:3099–106.
Kelly RJ, Hill A, Arnold LM, Brooksbank GL, Richards SJ, Cullen M, et al. Long-term treatment with eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sustained efficacy and improved survival. Blood. 2011;11725:6786–92.
Kim Y, Lim J, Kim M, Kim Y, Lee JW, Han K. Quantitation of CD55 and CD59 expression on reticulocytes and mature erythrocytes in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, aplastic anemia, and healthy control subjects. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2010;403:226–32.
Hillmen P, Hall C, Marsh JC, Elebute M, Bombara MP, Petro BE, et al. Effect of eculizumab on hemolysis and transfusion requirements in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 2004;3506:552–9.
Hillmen P, Young NS, Schubert J, Brodsky RA, Socié G, Muus P, et al. The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 2006;35512:1233–43.
Brodsky RA, Young NS, Antonioli E, Risitano AM, Schrezenmeier H, Schubert J, et al. Multicenter phase 3 study of the complement inhibitor eculizumab for the treatment of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2008;1114:1840–7.
Socié G, Mary JY, de Gramont A, Rio B, Leporrier M, Rose C, et al. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: long-term follow-up and prognostic factors. French Society of Haematology. Lancet. 1996;3489027:573–7.
Ziakas PD, Poulou LS, Rokas GI, Bartzoudis D, Voulgarelis M. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: sites, risks, outcome: an overview. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;53:642–5.
Kanakura Y, Ohyashiki K, Shichishima T, Okamoto S, Ando K, Ninomiya H, et al. Safety and efficacy of the terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in Japanese patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: the AEGIS clinical trial. Int J Hematol. 2011;931:36–46.
Hillmen P, Elebute M, Kelly R, Urbano-Ispizua A, Hill A, Rother RP, et al. Long-term effect of the complement inhibitor eculizumab on kidney function in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol. 2010;858:553–9.
Blum SF, Gardner FH. Intestinal infarction in paroxysmal nodturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1966;274:1137.
Doukas MA, DiLorenzo PE, Mohler DN. Intestinal infarction caused by paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol. 1984;161:75–81.
Adams T, Fleischer D, Marino G, Rusnock E, Li L. Gastrointestinal involvement in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: first report of electron microscopic findings. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;471:58–64.
Hill A, Sapsford RJ, Scally A, Kelly R, Richards SJ, Khurisgara G, et al. Under-recognized complications in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: raised pulmonary pressure and reduced right ventricular function. Br J Haematol. 2012;1583:409–14.
Hill A, Hillmen P, Richards SJ, Elebute D, Marsh JC, Chan J, et al. Sustained response and long-term safety of eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2005;1067:2559–65.
Hill A, Rother RP, Hillmen P. Improvement in the symptoms of smooth muscle dystonia during eculizumab therapy in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Haematologica. 2005;9012(Suppl):40.
Meyers G, Weitz I, Lamy T, Cahn JY, Kroon HA, Severino B, et al. Disease-related symptoms reported across a broad population of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 2007;11011:3683.
Hall C, Richards S, Hillmen P. Primary prophylaxis with warfarin prevents thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). Blood. 2003;102:3587–91.
Moyo VM, Mukhina GL, Garrett ES, Brodsky RA. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria using modern diagnostic assays. Br J Haematol. 2004;1261:133–8.
Pu JJ, Mukhina G, Wang H, Savage WJ, Brodsky RA. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in patients presenting as aplastic anemia. Eur J Haematol. 2011;871:37–45.
Risitano AM, Rotoli B. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: pathophysiology, natural history and treatment options in the era of biological agents. Biologics. 2008;22:205–12.
Umans JG, Levi R. Nitric oxide in the regulation of blood flow and arterial pressure. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:771–90.
Wiedmer T, Hall SE, Ortel TL, Kane WH, Rosse WF, Sims PJ. Complement-induced vesiculation and exposure of membrane prothrombinase sites in platelets of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1993;82:1192–6.
Weitz IC. Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria—insights into the role of complement in thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2010;125(Suppl 2):S106–7.
Weitz IC. Thrombosis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2011;373:315–21.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank G. Khursigara, PhD, of Alexion Pharmaceuticals; H. H. Cho of Handok Pharmaceuticals; K. Bonin, PhD, M. Hughes, PhD, and J. Safran of Infusion Communications for assistance in writing and editing; and P. McCloud, PhD, of McCloud Consulting for statistical analysis and interpretation. This work was supported by the Korean Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest
JWL has received honoraria for lectures and advisory boards and has received consulting fees from Alexion Pharmaceuticals. JHJ, JSK, S-SY, J-HL, and D-YJ have received consulting fees from Alexion Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jong Wook Lee and Jun Ho Jang contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.W., Jang, J.H., Kim, J.S. et al. Clinical signs and symptoms associated with increased risk for thrombosis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria from a Korean Registry. Int J Hematol 97, 749–757 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-013-1346-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-013-1346-4