Abstract
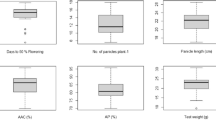
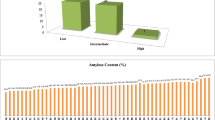
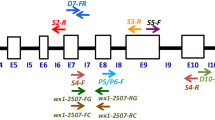
The sticky rice of Assam is traditionally classified as bora (glutinous) and chokuwa (semi-glutinous) based on their stickiness after cooking. The Waxy (Wx) gene encodes for granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS) that controls the synthesis of amylose, which is a key determinant of rice end-use quality attributes. In this report, we analysed the level of variation in grain quality traits in a collection of bora and chokuwa cultivars, and examined the nucleotide diversity at the Wx locus of selected rice accessions to identify the possible cause of low-amylose in these rice cultivar groups. The Wx gene sequencing from 24 bora and chokuwa cultivars revealed several nucleotide variations that can explain the variation in the amylose phenotypes. The nucleotide polymorphisms in the downstream intron regions were similar to those reported in Bangladeshi Beruin cultivars. Among the Wx polymorphisms, the CTn microsatellite in exon 1 and G/T SNP in intron 1 (G/T-Int1) should be considered for marker assisted breeding involving bora cultivars. The Wx gene tree, classified the bora accessions possessing the G/T-Int1 SNP as japonicas. However, cluster analysis using microsatellite markers classified the bora and chokuwa cultivars as indica, and intermediate of indica-aus. The findings of this study supplemented our understanding on the evolution of the Wx gene under human selection. The results will assist plant breeders to effectively improve the bora and chokuwa landraces.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayres NM, McClung AM, Larkin PD, Bligh HF, Jones CA and Park WD 1997 Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 94 773–781
Bao JS, Corke H and Sun M 2002 Microsatellites in starch-synthesizing genes in relation to starch physicochemical properties in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 105 898–905
Biselli C, Cavalluzzo D, Perrini R, Gianinetti A, Bagnaresi P, Urso S, Orasen G, Desiderio F, et al. 2014 Improvement of marker-based predictability of Apparent Amylose Content in japonica rice through GBSSI allele mining. Rice 7 1
Bligh HF, Larkin PD, Roach PS, Jones CA, Fu H and Park WD 1998 Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties. Plant Mol. Biol. 38 407–415
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y and Buckler ES 2007 TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23 2633–2635
Cagampang GB, Perez CM and Juliano BO 1973 A gel consistency test for eating quality of rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 24 1589–1594
Cai XL, Wang ZY, Xing YY, Zhang JL and Hong MM 1998 Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5′ UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content. Plant J. 14 459–465
Chen MH, Bergman C, Pinson S ane Fjellstrom R 2008 Waxy gene haplotypes: Associations with apparent amylose content and the effect by the environment in an international rice germplasm collection. J. Cereal Sci. 47 536–545
Choudhury BI, Khan ML and Dayanandan S 2014 Genetic relatedness among indigenous rice varieties in the Eastern Himalayan region based on nucleotide sequences of the Waxy gene. BMC Res. Notes 7 953
Chung HJ, Liu Q, Lee L and Wei D 2011 Relationship between the structure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of rice starches with different amylose contents. Food Hydrocoll. 25 968–975
Das B, Sengupta S, Parida SK, Roy B, Ghosh M, Prasad M and Ghose TK 2013 Genetic diversity and population structure of rice landraces from Eastern and North Eastern States of India. BMC Genet. 14 71
Dobo M, Ayres N, Walker G and Park WD 2010 Polymorphism in the GBSS gene affects amylose content in US and European rice germplasm. J. Cereal Sci. 52 450–456
Dutta L and Barua JN 1978 Nutrient composition of glutinous and non-glutinous rice varieties grown in Assam [India]. Ind. J. Agric. Sci. 48 610–613
Fan CC, Yu XQ, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Luo LJ and Zhang Q 2005 The main effects, epistatic effects and environmental interactions of QTLs on the cooking and eating quality of rice in a doubled-haploid line population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 110 1445–1452
Fortune PM, Schierenbeck KA, Ainouche AK, Jacquemin J, Wendel JF and Aïnouche ML 2007 Evolutionary dynamics of Waxy and the origin of hexaploid Spartina species (Poaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 43 1040–1055
Golomb L 1976 The origin, spread and persistence of glutinous rice as a staple crop in mainland Southeast Asia. J. Southeast Asian Stud. 71–5
Hammer O, Harper DA and Ryan PD 2001 Paleontological statistics software: package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 4 9
Hirano HY, Eiguchi M and Sano Y 1998 A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during the domestication of rice. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15 978–987
Hirano HY and Sano Y 1991 Molecular characterization of the waxy locus of rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Cell Physiol. 32 989–997
Hore DK 2005 Rice diversity collection, conservation and management in northeastern India. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 52 1129–1140
Hori Y, Fujimoto R, Sato Y and Nishio T 2007 A novel wx mutation caused by insertion of a retrotransposon-like sequence in a glutinous cultivar of rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 115 217–224
IBM Corp. Released 2016 IBM SPSS statistics for Macintosh, version 24.0. Armonk, New York: IBM Corp
Ingram AL and Doyle JJ 2003 The origin and evolution of Eragrostis tef (Poaceae) and related polyploids: evidence from nuclear waxy and plastid rps16. Am. J. Bot. 90 116–122
International Rice Research Institute 2013 Standard Evaluation System (SES) for Rice, 5th ed. IRRI, Manila
Isshiki M, Morino K, Nakajima M, Okagaki RJ, Wessler SR, Izawa T and Shimamoto K 1998 A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5′ splice site of the first intron. Plant J. 15 133–138
Jayamani P, Negrao S, Brites C and Oliveira MM 2007 Potential of Waxy gene microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphisms to develop japonica varieties with desired amylose levels in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Cereal Sci. 46 178–186
Juliano B 1985 Criteria and test for rice grain quality; in Rice chemistry and technology. (Saint Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists) pp. 443–513
Juliano BO, Perez CM, Blakeney AB, Castillo T, Kongseree N, Laignelet B, Lapis ET, Murty VV et al. 1981 International cooperative testing on the amylose content of milled rice. Starch-Stärke 33 157–162
Juliano BO and Villareal CP 1993 Grain quality evaluation of world rices. IRRI: Manila, Philippines
Juliano BO 1992 Structure and function of the rice grain and its fractions. Cereal Foods World 37 772–774
Larkin PD and Park WD 2003 Association of waxy gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with starch characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Breed. 12 335–339
Librado P and Rozas J 2009 DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25 1451–1452
Liu K and Muse SV 2005 PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21 2128–2129
Liu L, Ma X, Liu S, Zhu C, Jiang L, Wang Y, Shen Y, Ren Y et al. 2009 Identification and characterization of a novel Waxy allele from a Yunnan rice landrace. Plant Mol. Biol. 71 609–626
Mason-Gamer RJ, Weil CF and Kellogg EA 1998 Granule-bound starch synthase: structure, function, and phylogenetic utility. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15 1658–1673
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R et al. 2002 Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res. 9 199–207
Mikami I, Aikawa M, Hirano HY and Sano Y 1999 Altered tissue-specific expression at the Wx gene of the opaque mutants in rice. Euphytica 105 91–97
Mikami I, Uwatoko N, Ikeda Y, Yamaguchi J, Hirano HY, Suzuki Y and Sano Y 2008 Allelic diversification at the wx locus in landraces of Asian rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 116 979–989
Morishima HI, Sano YO and Oka H-I 1992 Evolutionary studies in cultivated rice and its wild relatives; in Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology vol 8 (eds) D Futuyma, J Antonovics (New York: Oxford University Press) pp 135–184
Olsen K, Caicedo A, Polato N, McClung A, McCouch S and Purugganan M 2006 Selection under domestication: Evidence for a sweep in the rice Waxy genomic region. Genetics 173 975–983
Olsen KM and Purugganan MD 2002 Molecular evidence on the origin and evolution of glutinous rice. Genetics 162 941–950
Peakall R and Smouse PE 2012 GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research – an update. Bioinformatics 28 2537–2539
Prathepa P and Baimai V 2004 Variation of Wx microsatellite allele, waxy allele distribution and differentiation of chloroplast DNA in a collection of Thai rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 140 231–237
Rathi S and Sarma RN 2012 Microsatellite diversity in indigenous glutinous rice landraces of Assam. Ind. J. Biotechnol. 11 23–29
Roy S, Banerjee A, Mawkhlieng B, Misra AK, Pattanayak A, Harish GD, Singh SK, Ngachan SV et al. 2015 Genetic diversity and population structure in aromatic and quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces from Northeastern India. PloS one 10 e0129607
Roy S, Marndi BC, Mawkhlieng B, Banerjee A, Yadav RM, Misra AK and Bansal KC 2016 Genetic diversity and structure in hill rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces from the Northeastern Himalayas of India. BMC Genet. 17 107
Sano Y, Katsumata M and Amano E 1985 Correlations between the amounts of amylose and Wx protein in rice endosperm. SABRAO J. 17 121–127
Shahid S, Begum R, Razzaque S and Seraj ZI 2016 Variability in amylose content of Bangladeshi rice cultivars due to unique SNPs in Waxy allele. J. Cereal Sci. 71: 1–9
Shaptadvipa B and Sarma RN 2009 Study on apparent amylose content in context of polymorphism information content along with indices of genetic relationship derived through SSR markers in Birain, Bora and Chokuwa groups of traditional glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.) of Assam. Asian J. Biochem. 4 45–54.
Shu QY, Wu DX, Xia YW, Gao MW, Ayres NM, Larkin PD and Park WD 1999 Microsatellites polymorphism on the waxy gene locus and their relationship to amylose content in indica and japonica rice, Oryza sativa L. Acta Genet. Sin. 26 350–358
Sridharan V and Singh RA 2007 conditional role of U2AF in splicing of introns with unconventional polypyrimidine tracts. Mol. Cell Biol. 27 7334–7344
Swofford DL 1998 PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods) (Sunderland: Sinauer Associates)
Tian Z, Qian Q, Liu Q, Yan M, Liu X, Yan C, Liu G, Gao Z et al. 2009 Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106 21760–21765
Wanchana S, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S and Vanavichit A 2003 Duplicated coding sequence in the waxy allele of tropical glutinous rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 165 1193–1199
Wang ZY, Zheng FQ, Shen GZ, Gao JP, Snustad DP, Li MG, Zhang JL and Hong MM 1995 The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J. 7 613–622
Watabe T 1967 Glutinous rice in northern Thailand (Kyoto: CSEAS, Kyoto University)
Wei-Hua Q, You-Tao C, Rong-Sheng W, Xin W, Li-Rong C, Wan-Xia Z and Qing-Wen Y 2012 Nucleotide diversity in Waxy gene and validation of single nucleotide polymorphism in relation to amylose content in Chinese microcore rice germplasm. Crop Sci. 52 1689–1697
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. N. Umakanta, ICAR-RC for NEHR, Umiam, Meghalaya, for helping with the association analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Ashis Kumar Nandi.
Corresponding editor: Ashis Kumar Nandi
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Banerjee, A., Basak, N. et al. Genetic diversity analysis of specialty glutinous and low-amylose rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces of Assam based on Wx locus and microsatellite diversity. J Biosci 45, 86 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00059-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00059-w