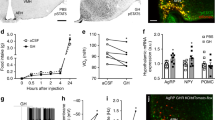
Abstract
Elevated levels of glucocorticoid, a steroid hormone released in response to stress, have been implicated in the pathophysiology of diabetes, which is now known to extend its effect on brain functions. Hence, we aimed to investigate the status of brain insulin signaling in response to dexamethasone (a synthetic glucocorticoid) treatment in female Charles Foster rat. This model exhibited pronounced hyperinsulinemia and glucose intolerance with loss in appetite and body weight. Immunoblotting of insulin receptor (INSR)-PI3kinase-AKT demonstrated reduced insulin signaling in hypothalamus but no change in hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum in dexamethasone-treated rats as compared to vehicle-treated rats, signifying the diversity of distribution and function of insulin in different brain regions. These results also correlated with appetite change, a key function governed by hypothalamus. Hence, we further explored the hypothalamic feeding circuit and found altered levels of neuropeptide genes (Agrp, Npy, Pomc) and candidate nutrient sensors (GLUT1, SirT1, and PPARγ). There was also a considerable reduction in glycogen content and appetite-regulating neurotransmitters (GABA, glutamate, dopamine) in dexamethasone-treated rats. Thus, concluding that dexamethasone not only induces peripheral insulin resistance but also impairs hypothalamic function of appetite regulation via the interwoven cascade of insulin signaling, neurotransmitters, and neuropeptides.

Reduced insulin signaling as well as elevated glucocorticoid levels in hypothalamus modulates the key appetite regulating neuropeptides, neurotransmitters, and nutrient sensors resulting into reduced appetite and bodyweight







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghasemi R, Haeri A, Dargahi L, Mohamed Z, Ahmadiani A (2013) Insulin in the brain: sources, localization and functions. Mol Neurobiol 47:145–171
Kleinridders A, Ferris HA, Cai W, Kahn CR (2014) Insulin action in brain regulates systemic metabolism and brain function. Diabetes 63:2232–2243
Grillo CA, Piroli GG, Lawrence RC, Wrighten SA, Green AJ, Wilson SP, Sakai RR, Kelly SJ, et al. (2015) Hippocampal insulin resistance impairs spatial learning and synaptic plasticity. Diabetes.
Kleinridders A, Cai W, Cappellucci L, Ghazarian A, Collins WR, Vienberg SG, Pothos EN, Kahn CR (2015) Insulin resistance in brain alters dopamine turnover and causes behavioral disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:3463–3468
Kullmann S, Heni M, Veit R, Scheffler K, Machann J, Haring HU, Fritsche A, Preissl H (2015) Selective insulin resistance in homeostatic and cognitive control brain areas in overweight and obese adults. Diabetes Care 38:1044–1050
Rafacho A, Ortsater H, Nadal A, Quesada I (2014) Glucocorticoid treatment and endocrine pancreas function: implications for glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and diabetes. J Endocrinol 223:R49–R62
Park S, Jang JS, Jun DW, Hong SM (2005) Exercise enhances insulin and leptin signaling in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus during dexamethasone-induced stress in diabetic rats. Neuroendocrinology 82:282–293
Juruena MF, Cleare AJ, Pariante CM (2004) The hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis, glucocorticoid receptor function and relevance to depression. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 26:189–201
Garcia-Caceres C, Quarta C, Varela L, Gao Y, Gruber T, Legutko B, Jastroch M, Johansson P et al (2016) Astrocytic insulin signaling couples brain glucose uptake with nutrient availability. Cell 166:867–880
Schwartz MW, Sipols AJ, Marks JL, Sanacora G, White JD, Scheurink A, Kahn SE, Baskin DG et al (1992) Inhibition of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression by insulin. Endocrinology 130:3608–3616
Sato I, Arima H, Ozaki N, Watanabe M, Goto M, Hayashi M, Banno R, Nagasaki H et al (2005) Insulin inhibits neuropeptide Y gene expression in the arcuate nucleus through GABAergic systems. J Neurosci 25:8657–8664
Zhang J (2007) The direct involvement of SirT1 in insulin-induced insulin receptor substrate-2 tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 282:34356–34364
Niswender KD, Morrison CD, Clegg DJ, Olson R, Baskin DG, Myers MG Jr, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2003) Insulin activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: a key mediator of insulin-induced anorexia. Diabetes 52:227–231
Mayer CM, Belsham DD (2009) Insulin directly regulates NPY and AgRP gene expression via the MAPK MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway in mHypoE-46 hypothalamic neurons. Mol Cell Endocrinol 307:99–108
Morley JE (1987) Neuropeptide regulation of appetite and weight. Endocr Rev 8:256–287
He J, Xu C, Kuang J, Liu Q, Jiang H, Mo L, Geng B, Xu G (2015) Thiazolidinediones attenuate lipolysis and ameliorate dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance. Metabolism 64:826–836
Kuo LE, Czarnecka M, Kitlinska JB, Tilan JU, Kvetnansky R, Zukowska Z (2008) Chronic stress, combined with a high-fat/high-sugar diet, shifts sympathetic signaling toward neuropeptide Y and leads to obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:232–237
Calogero AE, Liapi C, Chrousos GP (1991) Hypothalamic and suprahypothalamic effects of prolonged treatment with dexamethasone in the rat. J Endocrinol Investig 14:277–286
Shimizu H, Arima H, Ozawa Y, Watanabe M, Banno R, Sugimura Y, Ozaki N, Nagasaki H et al (2010) Glucocorticoids increase NPY gene expression in the arcuate nucleus by inhibiting mTOR signaling in rat hypothalamic organotypic cultures. Peptides 31:145–149
Popoli M, Yan Z, McEwen BS, Sanacora G (2013) The stressed synapse: the impact of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:22–37
Rhoads DE, DiRocco RJ, Osburn LD, Peterson NA, Raghupathy E (1984) Stimulation of synaptosomal uptake of neurotransmitter amino acids by insulin: possible role of insulin as a neuromodulator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119:1198–1204
Delgado TC (2013) Glutamate and GABA in appetite regulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:103
Meguid MM, Fetissov SO, Varma M, Sato T, Zhang L, Laviano A, Rossi-Fanelli F (2000) Hypothalamic dopamine and serotonin in the regulation of food intake. Nutrition 16:843–857
Kinote A, Faria JA, Roman EA, Solon C, Razolli DS, Ignacio-Souza LM, Sollon CS, Nascimento LF et al (2012) Fructose-induced hypothalamic AMPK activation stimulates hepatic PEPCK and gluconeogenesis due to increased corticosterone levels. Endocrinology 153:3633–3645
De Souza CT, Araujo EP, Bordin S, Ashimine R, Zollner RL, Boschero AC, Saad MJ, Velloso LA (2005) Consumption of a fat-rich diet activates a proinflammatory response and induces insulin resistance in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 146:4192–4199
El-Haschimi K, Pierroz DD, Hileman SM, Bjorbaek C, Flier JS (2000) Two defects contribute to hypothalamic leptin resistance in mice with diet-induced obesity. J Clin Invest 105:1827–1832
Melnyk RB (1987) Decreased binding to hypothalamic insulin receptors in young genetically obese rats. Physiol Behav 40:237–241
Belani M, Purohit N, Pillai P, Gupta S, Gupta S (2014) Modulation of steroidogenic pathway in rat granulosa cells with subclinical Cd exposure and insulin resistance: an impact on female fertility. Biomed Res Int 2014:460251
Duncan M, Singh B, Wise P, Carter G, Zadeh J (1995) A simple measure of insulin resistance. Lancet 346:120–121
Katyare SS, Pandya JD (2005) A simplified fluorimetric method for corticosterone estimation in rat serum, tissues and mitochondria. Indian J Biochem Biophys 42:48–53
Silber RH, Busch RD, Oslapas R (1958) Practical procedure for estimation of corticosterone or hydrocortisone. Clin Chem 4:278–285
Wingerd BD, and Stein G (1988) Rat dissection manual (Johns Hopkins University Press).
Chiu K, Lau W, Lau H, So K-F, Chang R-C (2007) Micro-dissection of rat brain for RNA or protein extraction from specific brain region journal of visualized experiments: JoVE 7.
Bhattacharyya S, Khanna S, Chakrabarty K, Mahadevan A, Christopher R, Shankar SK (2009) Anti-brain autoantibodies and altered excitatory neurotransmitters in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2489–2496
Reinhoud NJ, Brouwer HJ, van Heerwaarden LM, Korte-Bouws GA (2013) Analysis of glutamate, GABA, noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin, and metabolites using microbore UHPLC with electrochemical detection. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:888–894
Kilcoyne M, Gerlach JQ, Farrell MP, Bhavanandan VP, Joshi L (2011) Periodic acid-Schiff’s reagent assay for carbohydrates in a microtiter plate format. Anal Biochem 416:18–26
Ward CW, Menting JG, Lawrence MC (2013) The insulin receptor changes conformation in unforeseen ways on ligand binding: sharpening the picture of insulin receptor activation. BioEssays 35:945–954. doi:10.1002/bies 201370111
Derakhshan F, Toth C (2013) Insulin and the brain. Curr Diabetes Rev 9:102–116
Sakoda H, Ogihara T, Anai M, Funaki M, Inukai K, Katagiri H, Fukushima Y, Onishi Y, et al (2000) Dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance in 3 T3-L1 adipocytes is due to inhibition of glucose transport rather than insulin signal transduction. Diabetes 49:1700–1708
Schinkel AH, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CA, Borst P (1995) Absence of the mdr1a P-glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone, digoxin, and cyclosporin a. J Clin Invest 96:1698–1705
Miller AH, Spencer RL, Pulera M, Kang S, McEwen BS, Stein M (1992) Adrenal steroid receptor activation in rat brain and pituitary following dexamethasone: implications for the dexamethasone suppression test. Biol Psychiatry 32:850–869
Yin W, Gore AC (2010) The hypothalamic median eminence and its role in reproductive aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1204:113–122
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR et al (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease—is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis 7:63–80
Mastaitis JW, Wurmbach E, Cheng H, Sealfon SC, Mobbs CV (2005) Acute induction of gene expression in brain and liver by insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes 54:952–958
Cotero VE, Routh VH (2009) Insulin blunts the response of glucose-excited neurons in the ventrolateral-ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus to decreased glucose. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E1101–E1109
Shimizu H, Arima H, Watanabe M, Goto M, Banno R, Sato I, Ozaki N, Nagasaki H et al (2008) Glucocorticoids increase neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide gene expression via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling in the arcuate nucleus of rats. Endocrinology 149:4544–4553
Klockener T, Hess S, Belgardt BF, Paeger L, Verhagen LA, Husch A, Sohn JW, Hampel B et al (2011) High-fat feeding promotes obesity via insulin receptor/PI3K-dependent inhibition of SF-1 VMH neurons. Nat Neurosci 14:911–918
Barthel A, Okino ST, Liao J, Nakatani K, Li J, Whitlock JP Jr, Roth RA (1999) Regulation of GLUT1 gene transcription by the serine/threonine kinase Akt1. J Biol Chem 274:20281–20286
Chari M, Yang CS, Lam CK, Lee K, Mighiu P, Kokorovic A, Cheung GW, Lai TY et al (2011) Glucose transporter-1 in the hypothalamic glial cells mediates glucose sensing to regulate glucose production in vivo. Diabetes 60:1901–1906
Qi W-w, Zhong L-y, Li X-r, Li G, Liu Z-x, Hu J-f, Chen N-h (2012) Hyperglycemia induces the variations of 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor—G expression in hippocampus and hypothalamus of diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:107130
Sarruf DA, Yu F, Nguyen HT, Williams DL, Printz RL, Niswender KD, Schwartz MW (2009) Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in key neuronal subsets regulating glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis. Endocrinology 150:707–712
Lu M, Sarruf DA, Talukdar S, Sharma S, Li P, Bandyopadhyay G, Nalbandian S, Fan W et al (2011) Brain PPAR-gamma promotes obesity and is required for the insulin-sensitizing effect of thiazolidinediones. Nat Med 17:618–622
Obel LF, Muller MS, Walls AB, Sickmann HM, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A (2012) Brain glycogen-new perspectives on its metabolic function and regulation at the subcellular level. Front Neuroenergetics 4:1–15
Halse R, Bonavaud SM, Armstrong JL, McCormack JG, Yeaman SJ (2001) Control of glycogen synthesis by glucose, glycogen, and insulin in cultured human muscle cells. Diabetes 50:720–726
Krssak M, Brehm A, Bernroider E, Anderwald C, Nowotny P, Dalla Man C, Cobelli C, Cline GW et al (2004) Alterations in postprandial hepatic glycogen metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53:3048–3056
Tavoni TM, Obici S, de Castro RMA, Minguetti-Camara VC, Curi R, Bazotte RB (2013) Evaluation of liver glycogen catabolism during hypercortisolism induced by the administration of dexamethasone in rats. Pharmacol Rep 65:144–151
Allaman I, Pellerin L, Magistretti PJ (2004) Glucocorticoids modulate neurotransmitter-induced glycogen metabolism in cultured cortical astrocytes. J Neurochem 88:900–908
Tong Q, Ye CP, Jones JE, Elmquist JK, Lowell BB (2008) Synaptic release of GABA by AgRP neurons is required for normal regulation of energy balance. Nat Neurosci 11:998–1000
Wu Q, Boyle MP, Palmiter RD (2009) Loss of GABAergic signaling by AgRP neurons to the parabrachial nucleus leads to starvation. Cell 137:1225–1234
van den Pol AN (2003) Weighing the role of hypothalamic feeding neurotransmitters. Neuron 40:1059–1061
Stricker-Krongrad A, Beck B, Nicolas JP, Burlet C (1992) Central effects of monosodium glutamate on feeding behavior in adult long-Evans rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:881–886
Stanley BG, Ha LH, Spears LC, Dee MG 2nd (1993) Lateral hypothalamic injections of glutamate, kainic acid, D,L-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazole propionic acid or N-methyl-D-aspartic acid rapidly elicit intense transient eating in rats. Brain Res 613:88–95
Fukumoto K, Chaki S (2015) Involvement of serotonergic system in the effect of a metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor antagonist in the novelty-suppressed feeding test. J Pharmacol Sci 127:57–61
Schousboe A, Bak LK, Sickmann HM, Sonnewald U, Waagepetersen HS (2007) Energy substrates to support glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic function: role of glycogen, glucose and lactate. Neurotox Res 12:263–268
Sickmann HM, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, Benie AJ, Bouman SD (2012) Brain glycogen and its role in supporting glutamate and GABA homeostasis in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Neurochem Int 60:267–275
Acknowledgments
We extend our special thanks to Dr. Anil Pillai, Department of Psychiatry and Health Behaviour, Georgia Regents University, Augusta, GA, USA, for his critical comments and help in the preparation of the manuscript. We acknowledge Department of Biotechnology (DBT)-MSUB-ILSPARE for providing Central Instrumentation Facility, Animal House Facility of Biochemistry Department, and Department of Science and Technology for the fellowship and contingency received under DST INSPIRE FELLOWSHIP (No. 120479) to Ragitha Chruvattil.
Author’s Contribution
SG, RC, and GK conceived and designed the study; SB and SN assisted RC in the animal experiments; JM perfomed the neurotransmitter estimation under the supervision of MRY; and RC and SG analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
Financial assistance was provided by DST-INSPIRE FELLOWSHIP SCHEME and Department of Biotechnology (DBT) under the project (BT/PR5033/MED/30/792/2012).
Additional information
Highlights
• Hypothalamus is the prime region for onset of dexamethasone-induced brain insulin resistance.
• Dexamethasone modulates the hypothalamic appetite-regulating circuitry.
• Decision of appetite depends on cross talk of insulin signaling, glucocorticoid levels, nutrient sensors, neurotransmitters, and neuropeptides in hypothalamus.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 7304 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chruvattil, R., Banerjee, S., Nath, S. et al. Dexamethasone Alters the Appetite Regulation via Induction of Hypothalamic Insulin Resistance in Rat Brain. Mol Neurobiol 54, 7483–7496 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0251-2