Abstract
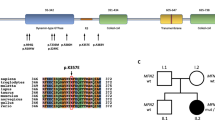
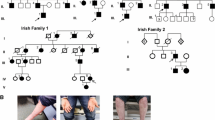
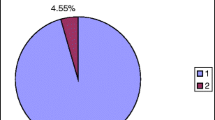
Mutations in TRPV4 are linked to a group of clinically distinct, but also overlapping axonal neuropathies, including Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2C (CMT2C), scapuloperoneal spinal muscular atrophy, and congenital distal spinal muscular atrophy. The incidence of TRPV4-linked cases ranges from 0 to 7% in overall axonal neuropathy cohorts from European countries and Australia. However, the data from other areas remain largely unknown. In this study, we screened for TRPV4 mutations in a well-characterized USA cohort of 62 unrelated CMT2 patients without mutations in MFN2, GARS, NEFL, and GDAP1. All 15 coding exons of TRPV4 were analyzed by Sanger-sequencing. Clinical features of TRPV4-linked patients were compared with those lacking TRPV4 mutations. We identified two TRPV4 mutations in two patients. A TRPV4-R316C was identified in a patient with family history, while a TRPV4-R269C in an apparently sporadic case. Marked clinical variations were observed in the patients with TRPV4 mutations. Our data suggest that TRPV4-linked CMT2C accounts for a sizable fraction in this USA cohort of CMT2; it has a wide phenotypic spectrum, and vocal cord paralysis, scapular weakness and wasting, skeletal dysplasia, and hearing loss are suggestive signs for TRPV4-linked CMT2C.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer-Grumbach, M., et al. (2010). Alterations in the ankyrin domain of TRPV4 cause congenital distal SMA, scapuloperoneal SMA and HMSN2C. Nature Genetics,42, 160–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.508.
Deng, H. X., et al. (2010). Scapuloperoneal spinal muscular atrophy and CMT2C are allelic disorders caused by alterations in TRPV4. Nature Genetics,42, 165–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.509.
Dohrn, M. F., et al. (2017). Frequent genes in rare diseases: Panel-based next generation sequencing to disclose causal mutations in hereditary neuropathies. Journal of Neurochemistry,143, 507–522. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14217.
Drew, A. P., et al. (2015). Improved inherited peripheral neuropathy genetic diagnosis by whole-exome sequencing. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine,3, 143–154. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.126.
Echaniz-Laguna, A., et al. (2014). Phenotypic spectrum and incidence of TRPV4 mutations in patients with inherited axonal neuropathy. Neurology,82, 1919–1926. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000450.
Fawcett, K. A., et al. (2012). Comprehensive analysis of the TRPV4 gene in a large series of inherited neuropathies and controls. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry,83, 1204–1209. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-303055.
Fecto, F., et al. (2011). Mutant TRPV4-mediated toxicity is linked to increased constitutive function in axonal neuropathies. Journal of Biological Chemistry,286, 17281–17291. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m111.237685.
Foley, C., et al. (2012). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in Northern England. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry,83, 572–573. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2011-300285.
Gess, B., Schirmacher, A., Boentert, M., & Young, P. (2013). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Frequency of genetic subtypes in a German neuromuscular center population. Neuromuscular Disorders,23, 647–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2013.05.005.
Klein, C. J., et al. (2011). TRPV4 mutations and cytotoxic hypercalcemia in axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies. Neurology,76, 887–894. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0b013e31820f2de3.
Landoure, G., et al. (2010). Mutations in TRPV4 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2C. Nature Genetics,42, 170–174. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.512.
Murphy, S. M., et al. (2012). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Frequency of genetic subtypes and guidelines for genetic testing. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry,83, 706–710. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-302451.
Rudnik-Schoneborn, S., et al. (2016). Diagnostic algorithms in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies: Experiences from a German genetic laboratory on the basis of 1206 index patients. Clinical Genetics,89, 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12594.
Saporta, A. S., et al. (2011). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease subtypes and genetic testing strategies. Annals of Neurology,69, 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22166.
Shy, M. E. (2018). Reply: The classification of Charcot-Marie-Tooth diseases, a never-ending story: CMT4? Brain: A Journal of Neurology,141, e71. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy208.
Sivera, R., et al. (2013). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Genetic and clinical spectrum in a Spanish clinical series. Neurology,81, 1617–1625. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a9f56a.
Skre, H. (1974). Genetic and clinical aspects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth’s disease. Clinical Genetics,6, 98–118.
Verhoeven, K., et al. (2006). MFN2 mutation distribution and genotype/phenotype correlation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2. Brain: A Journal of Neurology,129, 2093–2102. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl126.
Zimon, M., et al. (2010). Dominant mutations in the cation channel gene transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 cause an unusual spectrum of neuropathies. Brain,133, 1798–1809. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq109.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by NIH (NS078287, NS099623 to H.-X.D., and U54NS065712 to M.E.S). M.E.S is also supported by the MDA and CMTA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H-XD, TS, and MES designed this study. SD, YS, LZ, TS, and H-XD performed sequencing analysis. SMEF collected clinical information. MES performed clinical studies. SD, H-XD, TS, and MES analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Michael E. Shy is a consultant for Alnylam, Inflectis, and Acceleron. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the University of Iowa (Iowa City, IA) and University of Wisconsin (UW; Madison, WI), and written informed assent/consent was provided by participants under a protocol approved by the ethics board of the NIH Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (Protocol INC6611).
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, S., Feely, S.M.E., Shi, Y. et al. Incidence and Clinical Features of TRPV4-Linked Axonal Neuropathies in a USA Cohort of Charcot–Marie–Tooth Disease Type 2. Neuromol Med 22, 68–72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08564-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08564-4