Abstract
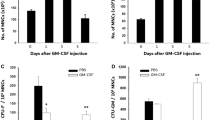
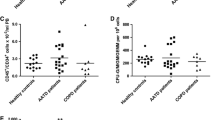
The effects of nanotechnology (electron-beam) –PEGylated (or immobilized; Im) hyaluronidase (HD) on the state of the pool of bone marrow progenitor cells and their mobilization induced by granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) were studied. A high specific activity of the drug Im-HD on progenitor cells of different classes was demonstrated using parenteral and enteral administration. An increase in the content of erythroid (E), granulomonocytic (GM), fibroblast (F) colony-forming units (CFU) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in bone marrow was shown, as well as G-CSF-induced stimulation of mobilization of precursors into the peripheral blood under the influence of Im-HD. The detected activity of this novel drug on progenitor cells indicates the potential for a safe and highly effective treatment for hematology practice and regenerative medicine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., & Zhdanov, V. V. (1999). The role of the microenvironment, inducing hematopoiesis during cytostatic myelosuppression (p. 114). Tomsk: STT.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., & Zyuzkov, G. N. (2006). Hypoxia and the blood system (p. 142). Tomsk: Tomsk Univ.
Avigdor, A., Goichberg, P., Shivtiel, S., Dar, A., Peled, A., Samira, S., Kollet, O., Hershkoviz, R., Alon, R., Hardan, I., Ben-Hur, H., Naor, D., Nagler, A., & Lapidot, T. (2004). CD44 and hyaluronic acid cooperate with SDF-1 in the trafficking of human CD34+ stem/progenitor cells to bone marrow. Blood, 103(8), 2981–2989.
Dygai, A. M., & Zyuzkov, G. N. (2009). Cellular therapy: new points of view. Science in Russia, Moscow. Science, 169(1), 4–8.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zhdanov, V. V., Vetoshkina, T. V., Guryantseva, L. A., Dubskaya, T. Y., Ermolaeva, L. A., Zyuzkov, G. N., Simanina, E. V., Sotnikova, N. V., Stavrova, L. A., Udut, E. V., Fomina, T. I., & Khrichkova, T. Y. (2007). Creation of experimental models and study of the regeneratory potential of stem cells on these models. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 143(1 suppl), 1–8.
Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Madonov, P. G., Udut, E. V., Miroshnichenko, L. A., Khrichkova, T. Y., Simanina, E. V., Stavrova, L. A., Artamonov, A. V., et al. (2011). Pharmacological properties of granulocytic colony-stimulating factor Pegylated using electron beam synthesis nanotechnologies. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 152(1), 133–137.
Draper, J. S., Smith, K., Gokhale, P., Moore, H. D., Maltby, E., Johnson, J., Meisner, L., Zwaka, T. P., Thomson, J. A., & Andrews, P. W. (2004). Recurrent gain of chromosomes 17q and 12 in cultured human embryonic stem cells. Nature Biotechnology, 22, 53–54.
Zyuz’kov, G. N., Suslov, N. I., Dygai, A. M., Zhdanov, V. V., & Goldberg, E. D. (2005). Role of stem cells in adaptation to hypoxia and mechanisms of neuroprotective effect of granulocytic colony-stimulating factor. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 140(5), 606–611.
Epshtein, O. I., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Sotnikova, N. V., Stavrova, L. A., Fomina, T. I., Vetoshkina, T. V., Sergeeva, S. A., Dubskaya, T. Y., Dygai, A. M., & Goldberg, E. D. (2005). Mechanisms of hepatoprotective effect of preparation containing superlow doses of antibodies to granulocytic colony-stimulating factor. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 140(5), 598–602.
Stavrova, L. A., Fomina, T. I., Plotnikov, M. B., Aliev, O. I., Sotnikova, N. V., Epshtein, O. I., Sergeeva, S. A., Guryantseva, L. A., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Dygai, A. M., & Goldberg, E. D. (2005). Pharmacological regulation of functional activity of stem cells in restoration of the myocardium during the postinfarction period. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 140(5), 593–597.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., & Zyuz’kov, G. N. (2006). Mechanisms of regulation of blood system during oxygen deficiency and the participation of neural stem cells in adaptation to hypoxia. Bull Siberian Med, 2, 43–51.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zhdanov, V. V., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Ermakova, N. N., Vetoshkina, T. V., Fomina, T. I., Ermolaeva, L. A., & Dubskaya, T. Y. (2007). Mechanisms of therapeutic effects of granulocytic colony-stimulating factor in experimental diabetes mellitus. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 146(4), 543–546.
Ermakova, N. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Stavrova, L. A., Guryantseva, L. A., Khrichkova, T. Y., Udut, E. V., Vetoshkina, T. V., Fomina, T. I., Ermolaeva, L. A., & Goldberg, E. D. (2009). Mechanisms underlying the effects of ultralow doses of antibodies to granulocytic colony-stimulating factor on recovery of damaged Pan-creatic tissue in experimental diabetes mellitus. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 148(3), 549–552.
Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Guryantseva, L. A., Stavrova, L. A., Khrichkova, T. Y., Dygai, A. M., & Goldberg, E. D. (2009). Role of mesenchymal precursor cells in the stimulation of wound healing under the effect of ultralow doses of antibodies to granulocytic colony-stimulating factor. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 148(3), 553–555.
Stavrova, L.A., Zyuźkov, G.N., Simanina, E.V., Miroshnichenko, L.A., Udut, E.V., Khrichkova, T.Y., Skurikhin, E.G., Pershina, O.V., Ermakova, N.N., Firsova, T.V., Zhdanov, V.V., Dygai, A.M., & Goldberg, E.D. (2009). Hemostimualting properties of preparation containing ultralow doses of antibodies to stem cell factor in cytostatic myelosuppression. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 148(3), 556–559.
Zhu, H., Mitsuhashi, N., Klein, A., Barsky, L. W., Weinberg, K., Barr, M. L., Demetriou, A., & Wu, G. D. (2006). The role of the hyaluronan receptor CD44 in mesenchymal stem cell migration in the extracellular matrix. Stem Cells, 24(4), 928–935.
Nedvetzki, S., Gonen, E., Assayag, N., Reich, R., Williams, R. O., Thurmond, R. L., Huang, J. F., Neudecker, B. A., Wang, F. S., Turley, E. A., & Naor, D. (2004). RHAMM, a receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility, compensates for CD44 in inflamed CD44-knockout mice: a different interpretation of redundancy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 101(52), 18081–18086.
Stern, R. (2003). Devising a pathway for hyaluronan catabolism: are we there yet? Glycobiology, 13(12), 105–115.
Noble, P. W. (2002). Hyaluronan and its catabolic products in tissue injury and repair. Matrix Biology, 21, 25–29.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Simanina, E. V., & Guryantseva, L. A. (2007). Role of hyaluronidase in the regulation of functions of mesenchymal precursor cells. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 143(4), 548–551.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., & Zhdanov, V. V. (2007). Mechanisms of mobilization of mesenchymal precursor cell under the effect of granulocytic colony-stimulating factor and hyaluronidase. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 144(6), 802–805.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Simanina, E. V., & Guryantseva, L. A. (2007). Role of hyaluronidase in the regulation of hemopoiesis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 144(6), 840–845.
Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Dygai, A. M., & Goldberg, E. D. (2007). Role of hyaluronidase in the regulation of hematopoiesis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 12, 690–695.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., Zyuz’kov, G. N., & Zhdanov, V. V. (2008). Effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and hyaluronidase on the formation of blood system reactions. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 145(6), 682–687.
Vereschagin, E. I., Han, D. H., Troitsky, A. W., Grishin, O. V., Petrov, S. E., Gulyaeva, E. P., Bogdanova, L. A., Korobeinikov, M. V., & Auslender, V. L. (2001). Radiation technology in the preparation of polyethylene oxide hydrophilic gels and immobilization of proteases for use in medical practice. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 24(3), 229–233.
Dygai, A. M., Vereschagin, E. I., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Madonov, P. G., Simanina, E. V., Stavrova, L. A., Udut, E. V., Khrichkova, T. Y., Miroshnichenko, L. A., Minakova, M. Y., Ermakova, N. N., Firsova, T. V., Dygai, A. M., Vereshchagin, E. I., Zyuz’kov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., & Madonov, P. G. (2009). Mobilization of progenitor cells into the blood by immobilized granulocytic colony-stimulating factor. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 147(4), 499–502.
Andreeva, T. V., & Zyuzkov, G. N. (2009). Hemostimulating activity of the immobilized granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Siberian Journal Cancer, 1(suppl), 15–16.
Sharaev, P. N., Strelkov, N. S., Shklayeva, E. V., et al. (1996). The determination of hyluronidase activity. Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics, 3, 21–22.
Goldberg, E. D., Dygai, A. M., & Schachov, V. P. (1992). Methods of tissue culture in hematology (p. 272). Tomsk: Tomsk Univ.
in’t Anker, P. S., Noort, W. A., Scherjon, S. A., Kleijburg-van der Keur, C., Kruisselbrink, A. B., van Bezooijen, R. L., Beekhuizen, W., Willemze, R., Kanhai, H. H., & Fibbe, W. E. (2003). Mesenchymal stem cells in human second-trimester bone marrow, liver, lung, and spleen exhibit a similar immunophenotype but a heterogenous multilineage differentiation potential. Haematologica, 88, 845–852.
Glanz, S. (1998). Medico-biological statistics. Moscow “Practice”, pp. 459
Bonnefoix, T., Bonnefoix, P., Callanan, M., Verdiel, P., & Sotto, J. J. (2001). Graphical representation of a generalized linear model-based statistical test estimating the fit of the single-hit poisson model to limiting dilution assays. Journal of Immunology, 167, 5725–5730.
Seyfulla, R. D., Timofeev, A. B., Ordzhonikidze, Z. G., Rozhkova, E. A., Kulikova, E. V., Druzhinin, A. E., Kuznetsov, Y. M., & Kim, E. K. (2008). Problems of using nanotechnology in pharmacology. Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology, 71(1), 61–69.
Piedmonte, D. M., & Treuheit, M. J. (2008). Formulation of Neulasta (pegfilgrastim). Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 60, 50–58.
Dygai, A. M., Zyuzkov, G. N., Zhdanov, V. V., Simanina, E. V., Stavrova, L. A., Udut, E. V., Khrichkova, T. Y., Minakova, M. Y., Ermakova, N. N., & Firsova, T. V. (2009). Effect of transplantation of peripheral blood mononuclears obtained using granulocytic colony-stimulating factor and Hyaluronidase on regeneration of hemopoietic tissue during myelosuppression. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 148(1), 120–125.
Bruns, I., Steidl, U., Fischer, J. C., Czibere, A., Kobbe, G., Raschke, S., Singh, R., Fenk, R., Rosskopf, M., Pechtel, S., von Haeseler, A., Wernet, P., Tenen, D. G., Haas, R., & Kronenwett, R. (2008). Pegylated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes CD34+ cells with different stem and progenitor subsets and distinct functional properties in comparison with unconjugated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Haematologica, 93, 347–355.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dygai, A.M., Zyuz’kov, G.N., Zhdanov, V.V. et al. Specific Activity of Electron-Beam Synthesis Immobilized Hyaluronidase on G-CSF Induced Mobilization of Bone Marrow Progenitor Cells. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 9, 140–147 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-012-9423-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-012-9423-2