Abstract
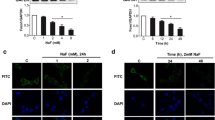
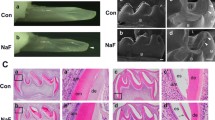
The objectives of this study are to establish the in vitro culture system for rat primary ameloblast and to investigate the effects of fluoride on cell viability, apoptosis, and ameloblastin (AMBN) secretion of primary rat ameloblast in vitro. Ameloblast was isolated from the tooth germ of the maxillomandibular molar and cultured in vitro. Cells were treated with NaF at 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2, and 6.4 mM for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay and apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry. The activation of Fas ligand (FasL)/Fas pathway was detected using immunoblotting for FasL, Fas, cleaved caspase-8, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved PARP. Secretion of AMBN in culture medium was measured using ELISA. Primary rat ameloblast was successfully isolated and cultured. The effects of low-dose fluoride on cell viability were bi-phasic, while high-dose fluoride resulted in decreased cell viability uniformly. Fluoride induced ameloblast apoptosis via activation of FasL/Fas signaling pathway and diminished secretion of AMBN by ameloblast. Fluoride could decrease ameloblast viability, induce ameloblast apoptosis via activating FasL/Fas signaling pathway, and reduce AMBN secretion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark MB, Slayton RL, Section on Oral Health (2014) Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting. Pediatrics 134(3):626–633
DenBesten P, Li W (2011) Chronic fluoride toxicity: dental fluorosis. Monogr Oral Sci 22:81–96
Lee JH, Jung JY, Jeong YJ, et al. (2008) Involvement of both mitochondrial- and death receptor-dependent apoptotic pathways regulated by Bcl-2 family in sodium fluoride-induced apoptosis of the human gingival fibroblasts. Toxicology 243(3):340–347
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516
Strasser A, Jost PJ, Nagata S (2009) The many roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity 30(2):180–192
He P, Zhang Y, Kim SO, Radlanski RJ, Butcher K, Schneider RA, DenBesten PK (2010) Ameloblast differentiation in the human developing tooth: effects of extracellular matrices. Matrix Biol 29(5):411–419
Zhang X, Diekwisch TGH, Luan X (2011) Structure and function of ameloblastin as an extracellular matrix protein: adhesion, calcium binding, and CD63 interaction in human and mouse. Eur J Oral Sci 119(Suppl 1):270–279
João SMA, Arana-Chavez VE (2003) Expression of connexin 43 and ZO-1 in differentiating ameloblasts and odontoblasts from rat molar tooth germs. Histochem Cell Biol 119(1):21–26
Nanci A, Zalzal S, Kan FW (1993) High-resolution scanning electron microscopy of rat incisor ameloblasts. Scanning Microsc 7(1):165–174 discussion 174–175
Starr TK, Scott PM, Marsh BM, Zhao L, Than BLN, O’Sullivan MG, Sarver AL, Dupuy AJ, Largaespada DA, Cormier RT (2011) A sleeping beauty transposon-mediated screen identifies murine susceptibility genes for adenomatous polyposis coli (Apc)-dependent intestinal tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(14):5765–5770
Ravindranath RMH, Tam W-Y, Bringas P, Santos V, Fincham AG (2001) Amelogenin-cytokeratin 14 interaction in ameloblasts during enamel formation. J Biol Chem 276(39):36586–36597
Fukumoto S, Yamada A, Nonaka K, Yamada Y (2005) Essential roles of ameloblastin in maintaining ameloblast differentiation and enamel formation. Cells Tissues Organs 181(3–4):189–195
Green DR, Llambi F (2015) Cell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(12). doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a006080
Barbier O, Arreola-Mendoza L, Del Razo LM (2010) Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 188(2):319–333
Ma L, Zhang Y, Zhong M, Zhu L, Zhang K, Gu H, Liu L, Zhang S, Cheng R (2014) Effect of fluoride on the viability and apoptosis of ameloblasts in vitro. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue Shanghai J Stomatol 23(5):519–523
Suzuki M, Bandoski C, Bartlett JD (2015) Fluoride induces oxidative damage and SIRT1/autophagy through ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 89:369–378
Kubota K, Lee DH, Tsuchiya M, Young CS, Everett ET, Martinez-Mier EA, Snead ML, Nguyen L, Urano F, Bartlett JD (2005) Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in ameloblasts responsible for dental enamel formation. J Biol Chem 280(24):23194–23202
Zhang Y, Yan Q, Li W, DenBesten PK (2006) Fluoride down-regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-20 in human fetal tooth ameloblast-lineage cells in vitro. Eur J Oral Sci 114(Suppl 1):105–110 discussion 127–129, 380
Yan Q, Zhang Y, Li W, Denbesten PK (2007) Micromolar fluoride alters ameloblast lineage cells in vitro. J Dent Res 86(4):336–340
Burgener D, Bonjour JP, Caverzasio J (1995) Fluoride increases tyrosine kinase activity in osteoblast-like cells: regulatory role for the stimulation of cell proliferation and Pi transport across the plasma membrane. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 10(1):164–171
Thrane EV, Refsnes M, Thoresen GH, Låg M, Schwarze PE (2001) Fluoride-induced apoptosis in epithelial lung cells involves activation of MAP kinases p38 and possibly JNK. Toxicol Sci 61(1):83–91
Jacinto-Alemán LF, Hernández-Guerrero JC, Trejo-Solís C, Jiménez-Farfán MD, Fernández-Presas AM (2010) In vitro effect of sodium fluoride on antioxidative enzymes and apoptosis during murine odontogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med 39(9):709–714
Sierant ML, Bartlett JD (2012) Stress response pathways in ameloblasts: implications for amelogenesis and dental fluorosis. Cells 1(3):631–645
Robinson C, Connell S, Kirkham J, Brookes SJ, Shore RC, Smith AM (2004) The effect of fluoride on the developing tooth. Caries Res 38(3):268–276
Riksen EA, Kalvik A, Brookes S, Hynne A, Snead ML, Lyngstadaas SP, Reseland JE (2011) Fluoride reduces the expression of enamel proteins and cytokines in an ameloblast-derived cell line. Arch Oral Biol 56(4):324–330
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the special research project of Education Department of Shaanxi Provincial Government (research project number: 2013JK0784).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Xi’an Medical College. All animal procedures described herein were approved by the Experimental Animal Center of Xi’an Medical College.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhu, Y. & Wang, D. High-Dose Fluoride Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Ameloblastin Secretion in Primary Rat Ameloblast. Biol Trace Elem Res 174, 402–409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0738-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0738-8