Abstract
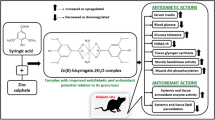
The increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) worldwide has underscored the urgency of developing an efficient therapeutic agent. Recently, Zn complexes have been attracting attention due to their antidiabetic activity. In this study, we designed and synthesized a new Zn complex, Zn-3,4-heptanedione-bis(N 4-methylthiosemicarbazonato) (Zn-HTSM), characterized its physicochemical properties, and examined its antidiabetic activity in KK-Ay type 2 DM model mice. It was demonstrated that Zn-HTSM has adequate lipophilicity for the cellular permeability, shows potent hypoglycemic activity, and improves glucose intolerance in KK-Ay mice. We also analyzed the levels of serum adipokines after continuous oral administration of Zn-HTSM. The level of serum leptin of KK-Ay mice is significantly reduced by the treatment of Zn-HTSM. Nevertheless, the levels of serum insulin and adiponectin were not improved. These data suggested that the Zn-HTSM acts on the leptin metabolism. Our present studies indicate that Zn-HTSM is a candidate oral antidiabetic agent for the treatment of type 2 DM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ (2010) Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87:4–14
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:367–377
Bays H, Mandarino L, DeFronzo RA (2004) Role of the adipocyte, free fatty acids, and ectopic fat in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor agonists provide a rational therapeutic approach. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:463–478
Falcão-Pires I, Castro-Chaves P, Miranda-Silva D, Lourenço AP, Leite-Moreira AF (2012) Physiological, pathological and potential therapeutic roles of adipokines. Drug Discovery Today 17:880–889
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2006) Adipocytes as regulator of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 444:847–853
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H (2008) Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 70:537–556
Maret W, Sandstead HH (2006) Zinc requirements and the risks and benefits of zinc supplementation. J Trace Elem Med Biol 20:3–18
Chausmer AB (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17:109–115
Salgueiro MJ, Krebs N, Zubillaga MB, Weill R, Postaire E, Lysionek AE, Caro RA, De Paoli T, Hager A, Boccio J (2001) Zinc and diabetes mellitus—is there a need of zinc supplementation in diabetes mellitus patients? Biol Trace Elem Res 81:215–228
Chen MD, Liou SJ, Lin PY, Yang VC, Alexander PS, Lin WH (1998) Effects of zinc supplementation on the plasma glucose level and insulin activity in genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 61:303–311
Anderson RA, Roussel AM, Zouari N, Mahjoub S, Matheau JM, Kerkeni A (2001) Potential antioxidant effects of zinc and chromium supplementation in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Nutr 20:212–218
Kinlaw WB, Levine AS, Morley JE, Silvis SE, McClain CJ (1983) Abnormal zinc metabolism in type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 75:273–277
Sakurai H, Katoh A, Kiss T, Jakusch T, Hattori M (2010) Metallo-allixinate complexes with anti-diabetic and anti-metabolic syndrome activities. Metallomics 2:670–682
Adachi Y, Yoshida J, Kodera Y, Kato A, Yoshikawa Y, Kojima Y, Sakurai H (2004) A new insulin-mimetic bis(allixinato)zinc(II) complex: structure–activity relationship of zinc(II) complexes. J Biol Inorg Chem 9:885–893
Yoshikawa Y, Murayama A, Adachi Y, Sakurai H, Yasui H (2011) Challenge of studies on the development of new Zn complexes (Zn(opt)(2)) to treat diabetes mellitus. Metallomics 3:686–692
Yoshikawa Y, Adachi Y, Sakurai H (2007) A new type of orally active anti-diabetic Zn(II)-dithiocarbamate complex. Life Sci 80:759–766
Karmaker S, Saha TK, Yoshikawa Y, Sakurai H (2009) A zinc(II)/poly(g-glutamic acid) complex as an oral therapeutic for the treatment of type-2 diabetic KKAy mice. Macromol Biosci 9:279–286
Basuki W, Hiromura M, Sakurai H (2007) Insulinomimetic Zn complex (Zn(opt)2) enhances insulin signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Inorg Biochem 101:692–699
Nakayama A, Hiromura M, Adachi Y, Sakurai H (2008) Molecular mechanism of antidiabetic zinc–allixin complexes: regulations of glucose utilization and lipid metabolism. J Biol Inorg Chem 13:675–684
Naito Y, Yoshikawa Y, Yasui H (2011) Cellular mechanism of zinc-hinokitiol complexes in diabetes mellitus. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 84:298–305
Ishiki M, Klip A (2005) Minireview: recent developments in the regulation of glucose transporter-4 traffic: new signals, locations, and partners. Endocrinology 146:5071–5078
Kasuga NC, Sekino K, Ishikawa M, Honda A, Yokoyama M, Nakano S, Shimada N, Koumo C, Nomiya K (2003) Synthesis, structural characterization and antimicrobial activities of 12 zinc(II) complexes with four thiosemicarbazone and two semicarbazone ligands. J Inorg Biochem 96:298–310
David PH (1972) Physico-chemical properties of the antitumor agent, 3-ethoxy-2-oxobutyraldehyde bis (thiosemicarbazonato) copper(II). Bioinorg Chem 1:255–271
Kubota M, Iida Y, Magata Y, Kitamura Y, Kawashima H, Saji H (2000) Mechanisms of [2,3-butanedione bis(N-4-dimethylthiosemicarbazone)]zinc (Zn-ATSM(2))-induced protection of cultured hippocampal neurons against N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated glutamate cytotoxicity. Jpn J Pharmacol 84:334–338
Green MA, Klippenstein DL, Tennison JR (1988) Copper(II) bis(thiosemicarbazone) complexes as potential tracers for evaluation of cerebral and myocardial blood flow with PET. J Nucl Med 29:1549–1557
Christlieb M, Holland JP, Dilworth JR (2010) Investigation of the UV–vis absorption of bis(N-methylthiosemicarbazonato) zinc Zn[ATSM]. Inorg Chim Acta 363:1133–1139
Cowley AR, Davis J, Dilworth JR, Donnelly PS, Dobson R, Nightingale A, Peach J.M, Shore B, Kerr D, Seymour L (2005) Fluorescence studies of the intra-cellular distribution of zinc bis(thiosemicarbazone) complexes in human cancer cells. Chem Commun 845–847
Donnelly PS, Caragounis A, Du T, Laughton KM, Volitakis I, Cherny RA, Sharples RA, Hill AF, Li QX, Masters CL, Barnham KJ, White AR (2008) Selective intracellular release of copper and zinc ions from bis(thiosemicarbazonato) complexes reduces levels of Alzheimer disease amyloid-beta peptide. J Biol Chem 283:4568–4577
Betts HM, Barnard PJ, Bayly SR, Dilworth JR, Gee AD, Holland JP (2008) Controlled axial coordination: solid-phase synthesis and purification of metallo-radiopharmaceuticals. Angew Chem-Int Edit 47:8416–8419
Hayase M, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, Shintaku H, Hosoda K, Nakao K (1996) Regulation of obese gene expression in KK mice and congenic lethal yellow obese KKAy mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 271:E333–E339
Yoshikawa Y, Kawabe K, Tadokoro M, Suzuki Y, Yanagihara N, Nakayama A, Sakurai H, Kojima Y (2002) New zinc(II) complexes with tetradentate amino acid derivatives: structure characterization, solution chemistry, and in vitro insulinomimetic activity. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 75:2423–2432
Haase H, Maret W (2003) Intracellular zinc fluctuations modulate protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling. Exp Cell Res 291:289–298
Varela L, Horvath TL (2012) Leptin and insulin pathways in POMC and AgRP neurons that modulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. EMBO Rep 13:1079–1086
Bevan P (2001) Insulin signalling. J Cell Sci 114:1429–1430
Kellerer M, Koch M, Metzinger E, Mushack J, Capp E, Haring HU (1997) Leptin activates PI-3 kinase in C2C12 myotubes via janus kinase-2 (JAK-2) and insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) dependent pathways. Diabetologia 40:1358–1362
Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Ikemoto S, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1999) Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy. Nature 401:73–76
Kieffer TJ, Habener JF (2000) The adipoinsular axis: effects of leptin on pancreatic β-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E1–E14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadowaki, S., Munekane, M., Kitamura, Y. et al. Development of New Zinc Dithiosemicarbazone Complex for Use as Oral Antidiabetic Agent. Biol Trace Elem Res 154, 111–119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9704-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9704-x