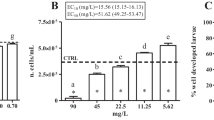
Abstract
The growth of fouling communities on ships’ hulls causes economic losses due to increased fuel consumption and to the deterioration of the metallic substrate by corrosion. Antifouling paints are formulated to avoid the settlement of these organisms and may contain biocides as active compounds. The objective of this research was to evaluate the antifouling performance of paints formulated with a “quebracho” tannin derivative (zinc “tannate”) and “boosters” (secondary biocides). The “boosters” used in this study were bismuth lactate, a zeolite exchanged with silver cations, and the same zeolite modified with silver chloride. Bioassays with “boosters” solutions were carried out employing Artemia persimilis. Soluble matrix antifouling paints were formulated and their action was assessed in a natural sea water environment. Results showed that the bismuth lactate resulted in a coating with almost triple service life of the antifouling paints with zinc “tannate.” Paints formulated with the silver composites behaved slightly better than the control paint.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukherjee, A, Mohan, KV, Ramesh, US, “Predicted Concentrations of Biocides from Antifouling Paints in Visakhapatnam Harbour.” J. Environ. Manag., 90 S51–S59 (2009)
Le, Y, Hou, P, Wang, J, Chen, JF, “Controlled Release Active Antimicrobial Corrosion Coatings with Ag/SiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticles.” Mater. Chem. Phys., 120 351–355 (2010)
Chambers, LD, Stokes, KR, Walsh, FC, Wood, RJK, “Modern Approaches to Marine Antifouling Coatings.” Surf. Coat. Technol., 201 3642–3652 (2006)
Pérez, M, García, M, Blustein, G, Stupak, M, “Tannin and Tannate from the Quebracho Tree: An Eco-Friendly Alternative for Controlling Marine Biofouling.” Biofouling, 23 (3/4) 151–159 (2007)
Laks, P, “Flavonoid Biocides: Phytoalexin Analogues from Condensed Tannins.” Phytochemistry, 26 (6) 1617–1621 (1987)
Xie, D, Dixon, R, “Proanthocyanidin Biosynthesis—Still More Questions than Answers?” Phytochemistry, 66 2127–2144 (2005)
Scalbert, A, “Antimicrobial Properties of Tannins.” Phytochemistry, 30 3875–3883 (1991)
Pérez, M, Blustein, G, García, M, del Amo, B, Stupak, M, “Cupric Tannate: A Low Copper Content Antifouling Pigment.” Prog. Org. Coat., 55 311–315 (2006)
Bellotti, N, Deyá, C, del Amo, B, Romagnoli, R, “Antifouling Paint with Zinc “Tannate”.” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 49 3386–3390 (2010)
Karlsson, J, Eklund, B, “New Biocide-Free Anti-Fouling Paints are Toxic.” Mar. Pollut. Bull., 49 456–464 (2004)
Konstantinou, IK, Albanis, TA, “Worldwide Occurrence and Effects of Antifouling Paint Booster Biocides in the Aquatic Environment: A Review.” Environ. Int., 30 235–248 (2004)
Konstantinou, I, Antifouling Paint Biocides. Springer, Berlin, 2006
Meyer, B, “Approaches to Prevention, Removal and Killing of Biofilms.” Int. Biodet. Biodeg., 51 249–253 (2003)
Stobie, N, Duffy, B, Colreavy, J, McHale, P, Hinder, S, McCormack, D, “Dual-Action Hygienic Coatings: Benefits of Hydrophobicity and Silver Ion Release for Protection of Environmental and Clinical Surfaces.” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 345 286–292 (2010)
Arai, T, Harino, H, Ohji, M, Langston, WJ, Ecotoxicology of Antifouling Biocides. Springer, Tokyo, 2009
Redfield, A, Weiss, C, “The Resistance of Metallic Silver to Marine Fouling.” Biol. Bull., 94 (1) 25–28 (1948)
Top, A, Ülkü, S, “Silver, Zinc, and Copper Exchange in a Na-Clinoptilolite and Resulting Effect on Antibacterial Activity.” Appl. Clay Sci., 27 13–19 (2004)
Yang, HL, Lin, J, Huang, C, “Application of Nanosilver Surface Modification to RO Membrane and Spacer for Mitigating Biofouling in Seawater Desalination.” Water Res., 43 3777–3786 (2009)
Fujino, J, Motontani, S, Inohara, K, Katsumura, R, Application Number: JP19870086523 19870407
GB 1000775, Applicant M&T CHEMICALS INC, Application Number: GB19630046719 19631126
GB 1041058, Applicant M&T CHEMICALS INC, Application Number: GB19630023641 19630613
Ferreira, E, Nogueira, A, Souza, G, Batista, L, “Effect of Drying Method and Length of Storage on Tannin and Total Phenol Concentrations in Pigeon Pea Seeds.” Food Chem., 86 17–23 (2004)
Dominy, N, Davoust, E, Minekus, M, “Adaptive Function of Soil Consumption: An In Vitro Study Modeling the Human Stomach and Small Intestine.” J. Exp. Biol., 207 319–324 (2004)
Erdemoğlu, SB, Gűcer, Ş, “Selective Determination of Aluminum Bound with Tannin in Tea Infusion.” Anal. Sci., 21 1005–1008 (2005)
Snell, FD, Snell, CT, Colorimetric Methods of Analysis. D. Van Nostrand Company, New York, 1941
Leyva, RR, Medellín, CN, Guerrero, CR, Berber, MM, Aragón, PA, Jacobo, AA, “Intercambio iónico de plata (I) en solución acuosa sobre clinoptilolita.” Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient., 21 (4) 193–200 (2005)
Harris, DC, Análisis Químico Cuantitativo. Iberoam, México, 1992
Wilson, CL, Wilson, DW, Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. Elsevier, London, 1960
Dahms, HU, Hellio, C, “Laboratory Bioassays for Screening Marine Antifouling Compounds.” In: Hellio, C, Yebra, D (eds.) Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologies, pp. 275–307. Woodhead Publishing Limited/CRC Press, Cambridge, 2009
Persoone, G, Jaspers, E, Clasus, C, “Ecotoxicological Testing for the Marine Environment.” Proc. of the International Symposium on Ecotoxicological Testing for the Marine Environment Ghent, Belgium, 1983
Persoone, G, Wells, PG, “Artemia in Aquatic Toxicology: A Review.” In: Sorgeloos, P, Bengtoson, DA, Decleir, W, Jaspers, F (eds.) Artemia Research and Its Applications. Morphology, Genetics, Strain Characterization, Toxicology, Vol. 1, pp. 259–275. University Press, Belgium, 1987
Vetere, V, Pérez, M, García, M, Deyá, M, Stupak, M, del Amo, B, “A Non-Toxic Antifouling Compound for Marine Paints.” Surf. Coat. Int., 12 386–389 (1999)
Ortega-Morales, B, Chan-Bacab, M, Miranda-Tello, E, Fardeau, M, Carrero, J, Stein, T, “Antifouling Activity of Sessile Bacilli Derived from Marine Surfaces.” Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 35 9–15 (2008)
Díaz Baez, M, Bulus Rossini, G, Pica Granados, Y, “Métodos Estadísticos para el Análisis de Resultados de Toxicidad Ensayos toxicológicos y métodos de evaluación de calidad de aguas.” In: Castillo, G (ed.) Estandarización, intercalibración, resultados y aplicaciones, Chap. 5. IDRC Books, Canada, 2004
Bastida, R, Martin, JP, La vida entre mareas: vegetales y animales de las costas de Mar del Plata. INIDEP, Mar del Plata, 2004
Del Amo, B, Giúdice, CA, Rascio, V, “Influence of Binder Dissolution Rate on the Bioactivity of Antifouling Paints.” J. Coat. Technol., 56 63–69 (1984)
Del Amo, B, Giúdice, CA, Sindoni, O, “High Build Soluble Matrix Antifouling Paints Based on Vinyl Resin.” Prog. Org. Coat., 17 2287–2300 (1989)
Del Amo, B, Giúdice, CA, Villoria, G, “Antifouling Paints of High Sea Water Dissolution Rate.” Eur. Coat. J., 1 8–14 (1990)
Ytreberg, E, Karlsson, J, Eklund, B, “Comparison of Toxicity and Release Rates of Cu and Zn from Anti-Fouling Paints Leached in Natural and Artificial Brackish Seawater.” Sci. Total Environ., 408 2459–2466 (2010)
Sillén, L, Martell, A, Stability Constants of Metal-Ion Complexes. The Chemical Society, Burlington House, London, 1964
Kumar, R, Munstedt, H, “Silver Ion Release from Antimicrobial Polyamide/Silver Composites.” Biomaterials, 26 2081–2088 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas de la Provincia de Buenos Aires (CICBA), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT) and Universidad Nacional de La Plata (UNLP) for their support in carrying out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellotti, N., Deyá, C., del Amo, B. et al. “Quebracho” tannin derivative and boosters biocides for new antifouling formulations. J Coat Technol Res 9, 551–559 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-012-9403-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-012-9403-0