Abstract
Background
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) may be useful in the management of chemotherapy-induced liver injury.
Aims
The present study evaluates the possible therapeutic effects of NAC on chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity.
Methods
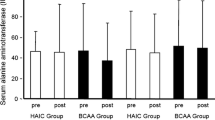
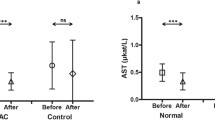
A total of 102 patients’ files who were diagnosed with cancer between 2015 and 2019 were evaluated retrospectively. Two patient groups with and without NAC were selected. NAC was administered in a 3-μg/kg IV dose in a 24-h infusion to 70 patients when any alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) values reached three times the normal levels. The other group consisted of 32 patients who were not treated with NAC. Alanine aminotransferase and GGT values were recorded at pretreatment, and on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, and 7th days in both the NAC and non-NAC groups from files.
Results
In the NAC group, ALT and GGT values on day 1, 3, 5, and 7 differed from each other, decreasing from day 1 to day 7. A statistically significant difference was noted between the values in the NAC group (p < 0.001). In the non-NAC group, the ALT values on day 7 were lower than the ALT values on day 1. A comparison of the ALT and GGT values in the NAC and non-NAC groups found that the values in the NAC group decreased earlier than in the non-NAC group.
Conclusions
This study shows that NAC has a therapeutic effect on hepatotoxicity in children being treated with chemotherapeutic agents due to underlying malign diseases. The early reduction in the results of liver function tests is important for the continuation of chemotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ranjeeta B, Rajender Reddy K (2014) Drug-induced liver injury due to cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Semin Liver Dis 34:162–171. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1375957
Sabuncuoğlu S, Ozgunes H (2011) Chemotherapy, free radicals and oxidative stress. Hacet Univ Fac Pharm J 31:137–150
Weijl NI, Cleton FJ, Osanto S (1997) Free radicals and antioxidants in chemotherapy-induced toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 23:209–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0305-7372(97)90012-8
Crohns M, Liippo K, Erhola M et al (2009) Concurrent decline of several antioxidants and markers of oxidative stress during combination chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer. Clin Biochem 42:1236–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.05.003
Simone CB, Simone NL, Simone V (2007) Antioxidants and other nutrients do not interfere with chemotherapy or radiation therapy and can increase kill and increase survival. Altern Ther Health Med 13:22–28
Facorro G, SarrasagueMM TH, Hager A et al (2004) Oxidative study of patients with total body irradiation: effects of amifostine treatment. Bone Marrow Transplant 33:793–798. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704427
Chen Y, JungsuwadeP VM, Butterfield DA, St Clair DK (2007) Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy: oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Mol Interv 7:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1124/mi.7.3.6
SariI CA, Kaynar L, Saraymen R et al (2008) Disturbance of pro-oxidative/antioxidative balance in allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Ann Clin Lab Sci 38:120–125
Brea-Calvo G, Rodríguez-Hernández A, Fernández-Ayala et al (2006) Chemotherapy induces an increase in coenzyme Q10 levels in cancer cell lines. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1293–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.11.014
Sangeetha P, Das UN, Koratkar R, Suryaprabha P (1990) Increase in free radical generation and lipid peroxidation following chemotherapy in patients with cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 8:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(90)90139-a
White AC, Sousa AM, Blumberg J et al (2006) Plasma antioxidants in subjects before hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 38:513–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705475
Clemens MR, Waladkhani AR, Bublitz K et al (1997) Supplementation with antioxidants prior to bone marrow transplantation. Wien Klin Wochenschr 109:771–776
Fridovich I (1983) Superoxide radical: an endogenous toxicant. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 23:239–257. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001323
Sugiyama S, Hayakawa M, Kato T et al (1989) Adverse effects of anti-tumor drug, cisplatin, on rat kidney mitochondria: disturbances in glutathione peroxidase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 159:1121–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(89)92225-0
Zhang JG, Zhong LF, Zhang M, Xia YX (1992) Protection effects of procaine on oxidative stress and toxicities of renal cortical slices from rats caused by cisplatin in vitro. Arch Toxicol 66:354–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01973631
Gill RA, Onstad GR, Cardamone JM et al (1982) Hepatic veno-occlusive disease caused by 6-thioguanine. Ann Intern Med 96:58–60. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-58
Stoneham S, Lennard L, Coen P et al (2003) Veno-occlusive disease in patients receiving thiopurines during maintenance therapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Br J Haematol 123:100–102. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04578.x
Lee WM (1995) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med 333:1118–1127. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199510263331706
DeLeve LD, Shulman HM, McDonald GB (2002) Toxic injury to hepatic sinusoids: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease). Semin Liver Dis 22:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-23204
Chughlay MF, Kramer N, Spearman CV et al (2016) N-acetylcysteine for non-paracetamol drug induced liver injury: a systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol 81:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12880
Koren G, Beatty K, Seto A et al (1992) The effects of impaired liver function on the elimination of antineoplastic agents. Ann Pharmacother 26:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1177/106002809202600311
Desai ZR, Van den Berg HW, Bridges JM, Shanks RG (1982) Can severe vincristine neurotoxicity be prevented? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 8:211–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00255486
Hohneker JA (1994) A summary of vinorelbine (Navelbine) safety datafrom north American clinical trials. Semin Oncol 21:42–46
Van den Berg HW, Desai ZR, Wilson R et al (1982) The pharmacokinetics of vincristine in man: reduced drug clearance associated with raised serum alkaline phosphatase and dose-limited elimination. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 8:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00255487
Stewart CF, Arbuck SG, Fleming RA, Evans WE (1990) Changes in the clearance of total and unbound etoposide in patients with liver dysfunction. J Clin Oncol 8:1874–1879. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1990.8.11.1874
Raymond E, Boige V, Faivre S et al (2002) Dosage adjustment and pharmacokinetic profile of irinotecan in cancer patients with hepatic dysfunction. J Clin Oncol 20:4303–4312. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.03.123
Neuman MG, Cameron RG, Haber JA et al (1999) Inducers of cytochrome P450 2E1 enhance methotrexate-induced hepatocytoxicity. Clin Biochem 32:519–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9120(99)00052-1
Jahovic N, Cevik H, Sehirli AO et al (2003) Melatonin prevents methotrexate-induced hepatorenal oxidative injury in rats. J Pineal Res 34:282–287
Cetiner M, Sener G, Sehirli AO et al (2005) Taurine protects against methotrexate-induced toxicity and inhibits leukocyte death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2005.03.009
Ali N, Rashid S, Nafees S et al (2017) Protective effect of chlorogenic acid against methotrexate induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat liver: an experimental approach. Chem Biol Interact 272:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2017.05.002
Szabo S (1984) Role of sulfhydryls and early vascular lesions in gastric mucosal injury. Acta Physiol Hung 64:203–214
Ross D (1988) Glutathione, free radicals and chemotherapeutic agents. Mechanisms of free-radical induced toxicity and glutathione-dependent protection. Pharmacol Ther 37:231–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/0163-7258(88)90027-7
Babiak RM, Campello AP, Carnieri EG (1998) Methotrexate: pentose cycle and oxidative stress. Cell Biochem Funct 16:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0844(1998120)16:4<283::AID-CBF801>3.0.CO;2-E
Manov I, Hırsh M, Iancu TC (2002) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and mechanisms of its protection by N-acetylcysteine: a study of Hep3B cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol 53:489–500. https://doi.org/10.1078/0940-2993-00215
Kumar O, Sugendran K, Vijayaraghavan R (2003) Oxidative stress associated hepatic and renal toxicity induced by ricin in mice. Toxicon 1:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-0101(02)00313-6
Akhgari M, Abdollahi M, Kebryaeezadeh A et al (2003) Biochemical evidence for free radical-induced lipid peroxidation as a mechanism for subchronic toxicity of malathion in blood and liver of rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 22:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327103ht346oa
Tafazoli S, Spehar DD, O’Brien PJ (2005) Oxidative stress mediated idiosyncratic drug toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 37:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1081/dmr-55227
Cetiner M, Sener G, Sehirli AO et al (2005) Taurine protects against methotrexate-induced toxicity and inhibits leukocyte death. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2005.03.009
Dervieux T, Brenner TL, Hon YY et al (2002) De novo purine synthesis inhibition and antileukemic effects of mercaptopurine alone or in combination with methotrexate in vivo. Blood 15:1240–1247. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-02-0495
Funding
This study was funded by the Karadeniz Technical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eroglu, N., Erduran, E., Reis, G.P. et al. Therapeutic effect of N-acetylcysteine on chemotherapy-induced liver injury. Ir J Med Sci 189, 1189–1194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02219-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-020-02219-1